Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Axial involvement, affecting the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) and/or spine, is a clinically relevant manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) that can influence management strategies. Previous studies have reported a wide range (25% to 70%) of axial involvement prevalence due to differing definitions and detection methods. The Axial Involvement in Psoriatic Arthritis (AXIS) cohort, a collaborative project of ASAS and GRAPPA, aimed to systematically evaluate the clinical and imaging characteristics of axial involvement in individuals with PsA.
Methods: AXIS was a prospective, multicenter, multinational, cross-sectional study conducted across 19 countries globally. Eligible participants (pts) were individuals with PsA meeting the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) with musculoskeletal symptom duration of ≤10 years, who had not received biological or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs). Pts underwent standardized clinical assessments and radiography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the SIJ and spine. Imaging studies were evaluated both locally and centrally for the presence of imaging signs indicative of axial involvement. The primary outcome, determined by investigators’ judgment, was the presence of axial involvement, assessed both before and after the central imaging review.
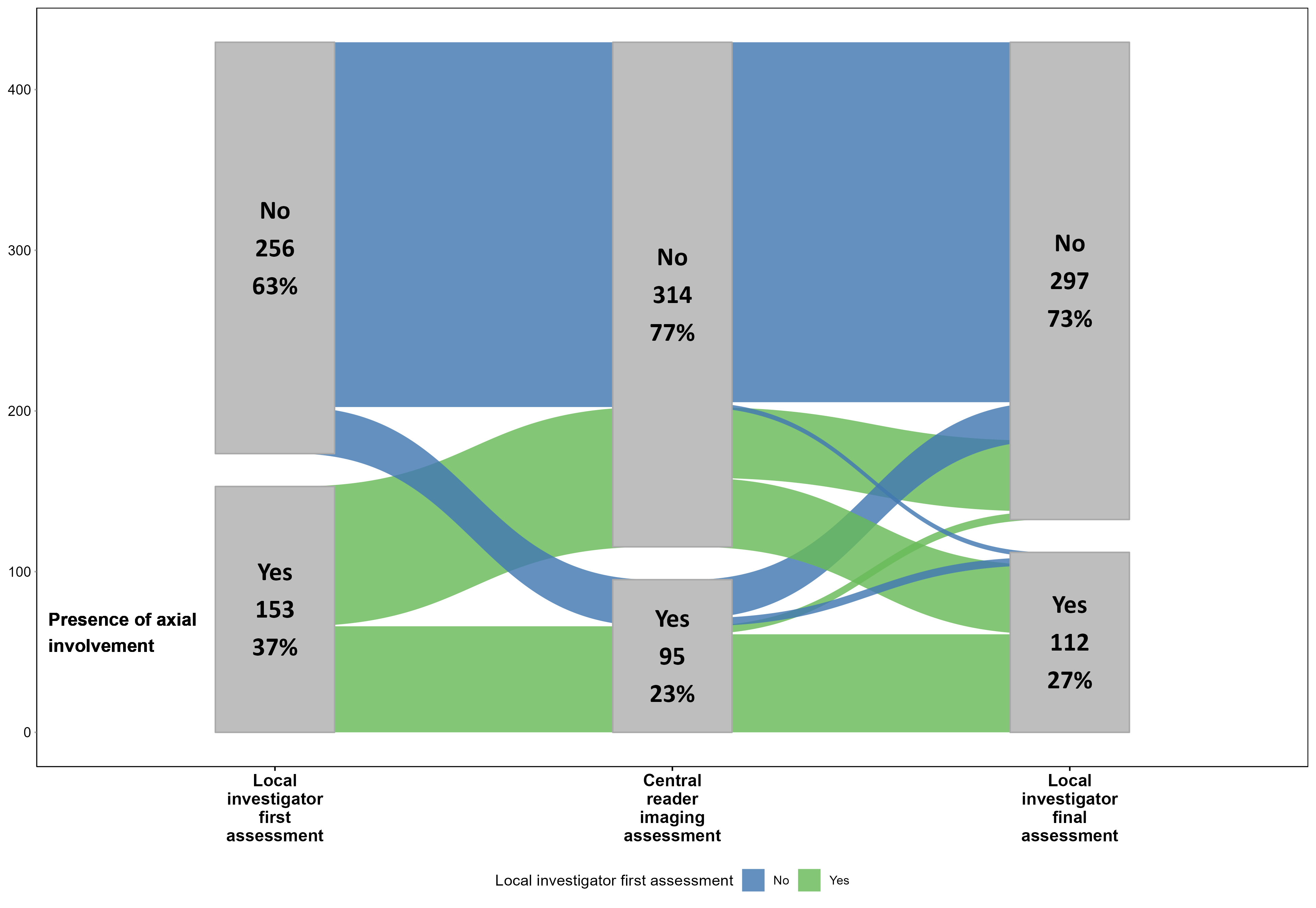
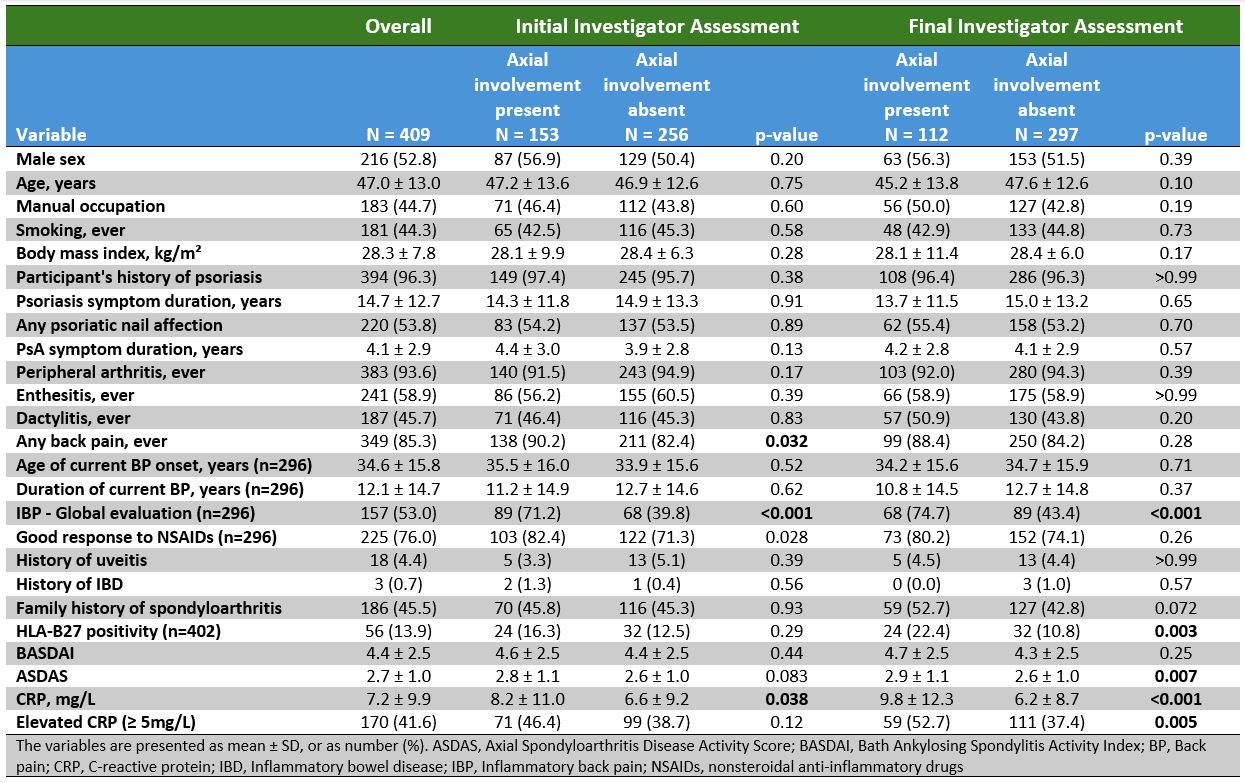
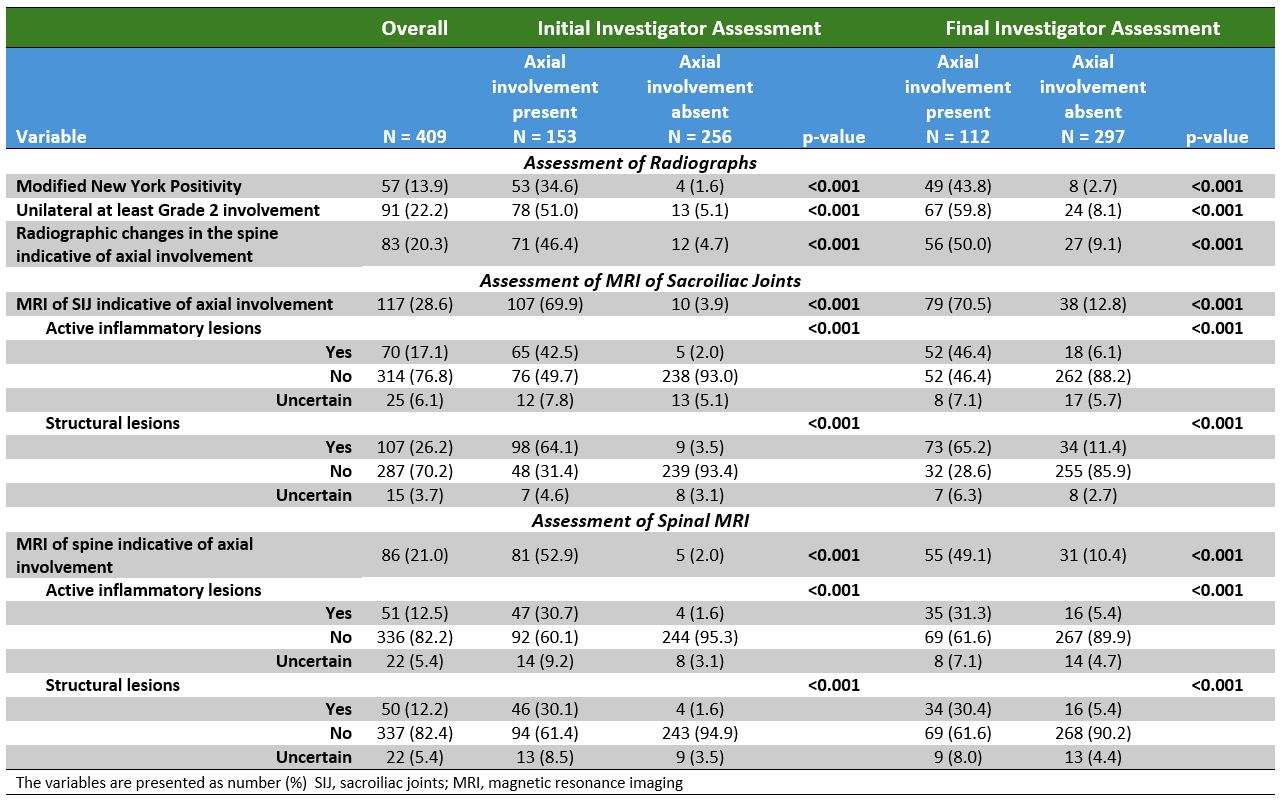
Results: Of the 409 enrolled individuals with PsA, initial evaluation by local investigators identified likely axial involvement in 153 pts (37.4%). This decreased to 112 pts(27.4%) after final evaluation incorporating expert assessment of imaging (Figure 1). Of the 112, pts with axial involvement were slightly younger (average 45.2 vs. 47.6 years), were more frequently males (56.3% vs. 51.5%), and had a higher frequency of HLA-B27 (22.4% vs. 10.8%), inflammatory back pain (IBP) (74.7% vs. 43.4%), and elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (52.7% vs. 37.4%)(Table 1). Active inflammatory and structural changes on imaging clearly discriminated between pts with and without axial involvement (Table 2). Central imaging review identified imaging findings indicative of axial involvement in 95 of 409 pts (23.2%). Among the 112 pts classified as having axial involvement, 66 (58.9%) showed findings indicative of axial involvement on at least one imaging modality by central review. In contrast, only 29 pts (9.8%) without axial involvement had any positive imaging findings by central review
Conclusion: After local investigators’ final assessment, axial involvement was detected in 27.4% of pts with PsA. The presence of IBP, HLA-B27 positivity, higher CRP levels, and the presence of active inflammatory and structural changes in the SIJs and spine were associated with axial involvement in PsA pts. Further work is underway to develop classification criteria for axial involvement in PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Torgutalp M, Azevedo V, Baraliakos X, Van den Bosch F, Braun J, Cauli A, Coates L, Chandran V, Diekhoff T, van Gaalen F, Garcia Salinas R, Gensler L, Goel N, Gottlieb A, van der Heijde D, Helliwell P, Hermann K, Kalyoncu U, Kiltz U, Lambert R, Leung Y, Llop M, Lopez A, van Lunteren M, Maharaj A, Maksymowych W, Marzo-Ortega H, Mathew A, Mease P, Nash P, Ostergaard M, Proft F, Protopopov M, Rohekar S, SCHIOTIS R, Sieper J, Soriano E, Tam L, Wei J, Ziade N, Gladman D, Poddubnyy D. Characteristics of Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Presenting with Axial Involvement: Results of a Prospective International Multicenter Study (AXIS) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-presenting-with-axial-involvement-results-of-a-prospective-international-multicenter-study-axis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-presenting-with-axial-involvement-results-of-a-prospective-international-multicenter-study-axis/