Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders II: GCA Clinical & Epidemiology (0514–0518)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:50PM
Background/Purpose: To investigate the characteristics of disease flare after successful treatment with tocilizumab (TCZ) in patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA).
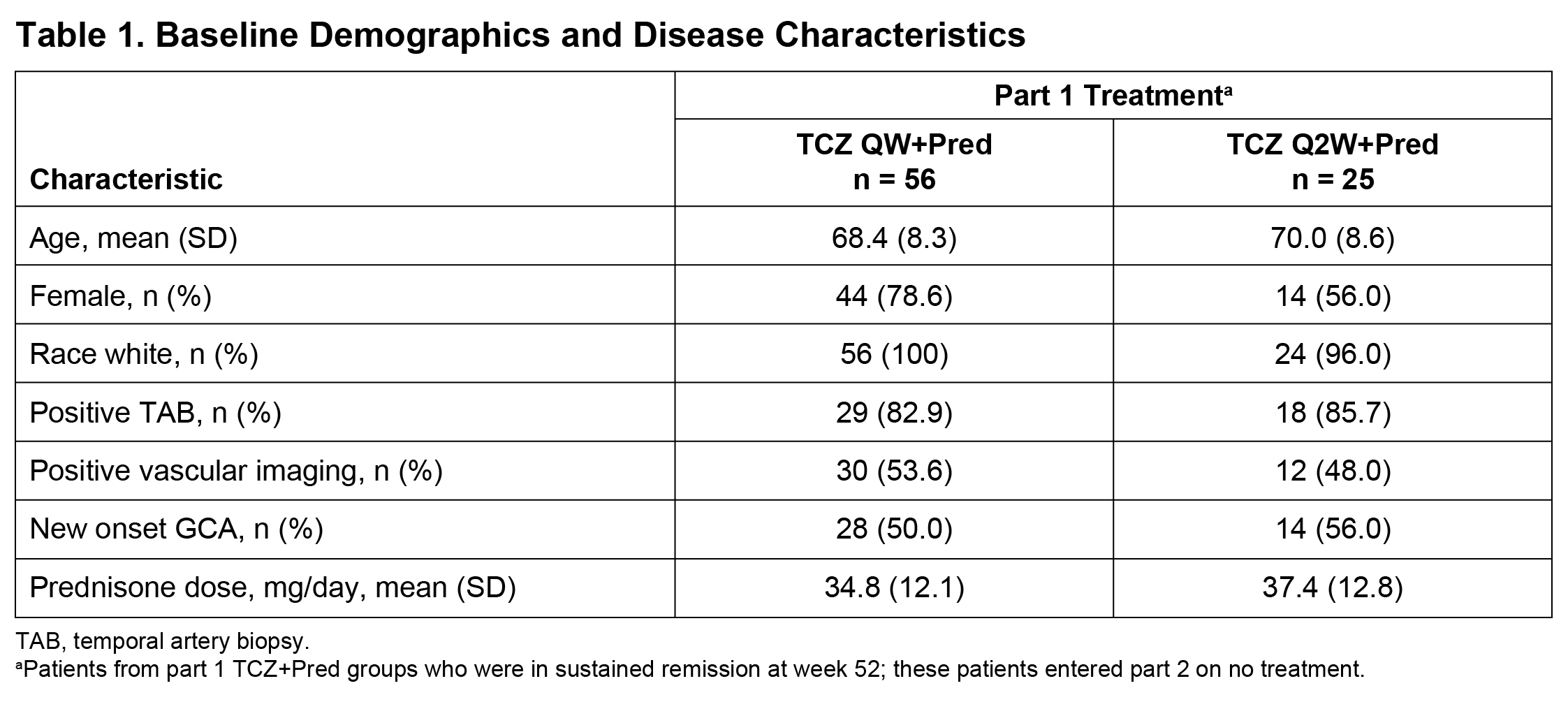
Methods: We performed a post hoc analysis of data from part 2 of the GiACTA trial. GiACTA consisted of a 52-week, double-blind, randomized controlled treatment period (part 1) and a 2-year long-term follow-up (part 2). In part 1, patients received TCZ 162 mg subcutaneously every week or every other week with a 26-week prednisone taper (TCZ+Pred) or placebo plus a 26-week or a 52-week prednisone taper. Patients who achieved the primary outcome of sustained remission through week 52 while adhering to the protocol prednisone taper entered part 2 on no treatment. Any treatment during part 2 was administered open-label at the investigator’s discretion. We analyzed the characteristics of first disease flare in patients originally assigned to the TCZ+Pred arms who were in sustained remission at the end of part 1 (week 52) and experienced flare in part 2. Flare was defined as the reappearance of cranial symptoms (headaches, jaw claudication, visual manifestations, scalp tenderness) or polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) symptoms or as the elevation of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) ≥30 mm/h that was attributable to GCA and necessitated treatment. ACR GCA classification criteria were fulfilled by 78% of patients
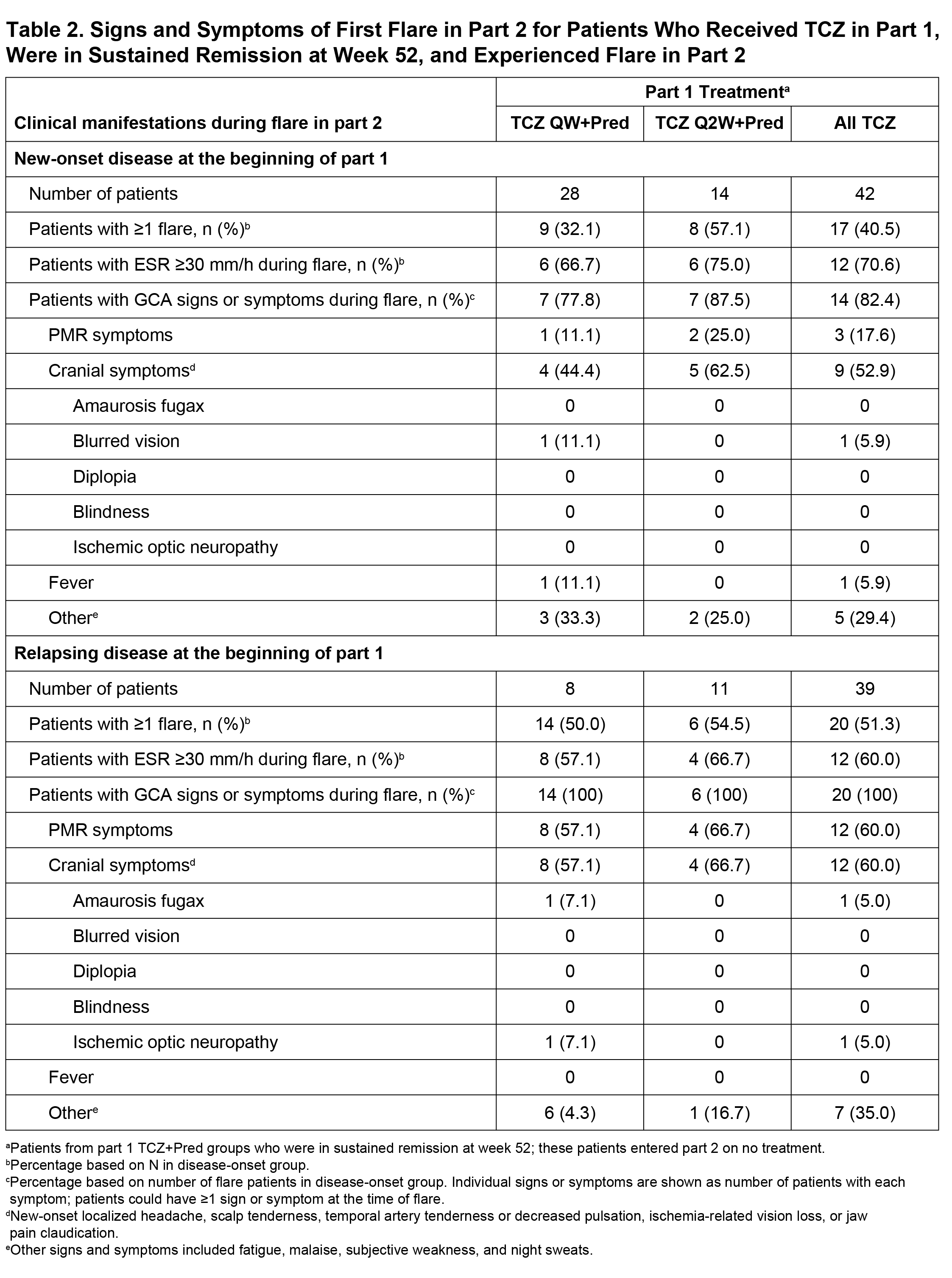
Results: Among 149 patients treated with TCZ+Pred in part 1, 81 (54%) were in sustained remission at week 52 upon entering part 2 (Table 1). Of these 81 patients, 37 (46%) experienced at least one flare during part 2, including 17 patients with new-onset GCA and 20 patients with relapsing GCA at the start of the trial. Flares among patients with new-onset GCA presented with cranial symptoms (53%) more often than PMR symptoms (18%). In contrast, the incidence of cranial (60%) and PMR (60%) symptoms was balanced in patients with relapsing GCA. Visual manifestations occurred in two patients (5%) who experienced flare (Table 2). ESR and CRP were elevated in 68% and 36% of patients, respectively, at the time of flare. Median ESR and CRP values around the time of flare were 37.0 mm/h and 5.44 mg/L, respectively, in patients with new-onset GCA and 35.0 mm/h and 8.6 mg/L, respectively, in patients with relapsing GCA. Only three (8%) of the flares were identified as ESR elevation without cranial or PMR symptoms.
Conclusion: Overall, 46% of GCA patients successfully treated with TCZ for 12 months experienced disease flare within the following 2 years. Flares in patients with new-onset disease at the time of TCZ initiation occurred more often with cranial symptoms than PMR symptoms. Visual manifestations were rare at the time of flare, and no cases of blindness occurred. ESR was within the normal range in one-third of the patients who experienced flare.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Unizony S, Mohan S, Han J, Stone J. Characteristics of Giant Cell Arteritis Flares After Successful Treatment with Tocilizumab: Results from the Long-Term Extension of a Randomized Controlled Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-giant-cell-arteritis-flares-after-successful-treatment-with-tocilizumab-results-from-the-long-term-extension-of-a-randomized-controlled-phase-3-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-giant-cell-arteritis-flares-after-successful-treatment-with-tocilizumab-results-from-the-long-term-extension-of-a-randomized-controlled-phase-3-trial/