Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment III: AxSpA
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: The EULAR task force recently published the difficult-to-treat (D2T) RA definition1, however, a definition of D2T axSpA is still lacking. To date, we have little data concerning D2T axSpA, especially in real-world. One of the limitations of the D2T RA EULAR definition is the lack of a temporal criterion. The primary endpoint of this work was to study the characteristics of D2T axSpA patients using the EULAR definition applied to axSpA. The second endpoint was to study a sub-group of patients with a predefined more stringent definition including a temporal criterion.
Methods: A retrospective multicentric study was performed. Patients with axSpA (radiographic or non-radiographic) ≥18 years old starting a b/tsDMARDs with at least 2-year follow-up were included. D2T axSpA was defined as failure of ≥ 2 b/tsDMARDs with different mechanism of action (MoA) among TNF inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors. Very D2T axSpA was defined as failure of ≥ 2 b/tsDMARDs in strictly less than 2 years. D2T and Very D2T axSpA patient’s characteristics were compared with non-D2T patients.
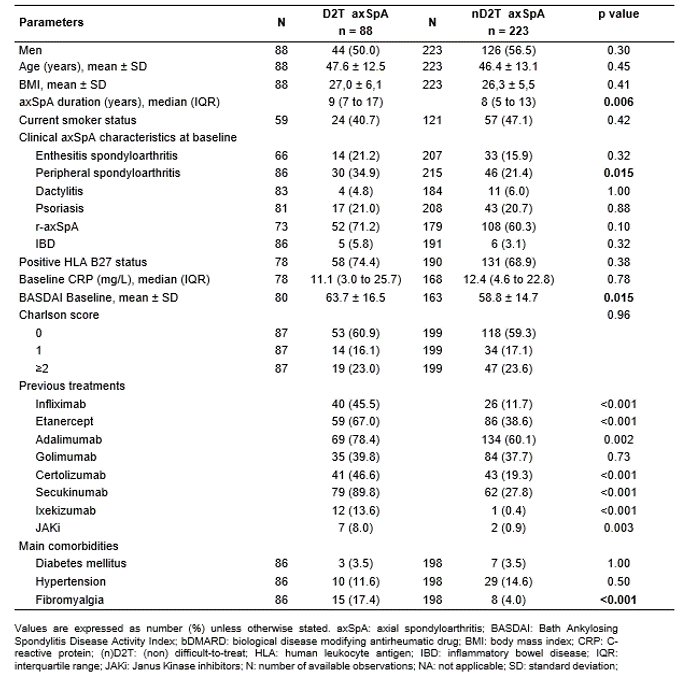
Results: 311 axSpA patients were included: 88 D2T axSpA (28.3%) and 223 non-D2T (nD2T) axSpA (71.7%) (Table 1). Proportion of r-axSpA patients was 71.2% in the D2T group and 60.3% in the nD2T group (p=0.10). Disease duration was significantly higher in the D2T group (p=0.006). Peripheral involvement was more prevalent in the D2T group with 34.9% of patients vs. 21.4% in the nD2T group (p=0.015). BASDAI level at baseline was higher in the D2T group with a mean of 63.7 vs 58.8 in the nD2T group (p=0.015). Fibromyalgia was found to be more frequent in the D2T group vs nD2T group (p < 0.001). Among D2T patients, 12 (14%) presented a contraindication to TNF or IL-17 inhibitors (multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, recurrent uveitis, solid cancer < 5 years).
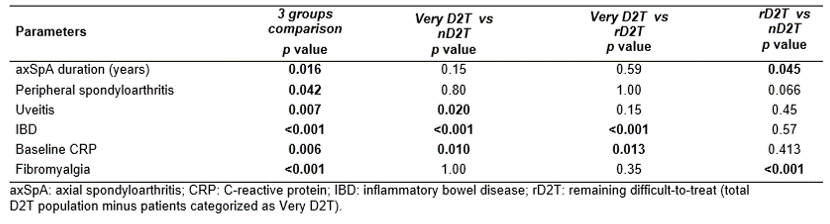
12 patients (3.8%) were categorized as very D2T axSpA. axSpA patient’s characteristics were compared between the three groups (Very D2T, remaining D2T and nD2T) and in case of significant result, pairwise comparisons were performed (Table 2). When compared to nD2T, Very D2T patients had a higher CRP level at baseline (42.0 ± 31.3 vs 17.8 ± 23.1; p=0.010). Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) prevalence at baseline was higher in the Very D2T group with 41.7% vs 3.1% in the nD2T group (p< 0.001). Uveitis at baseline was more frequent (45.5% vs 11%; p=0.020). None of the Very D2T patients had a diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
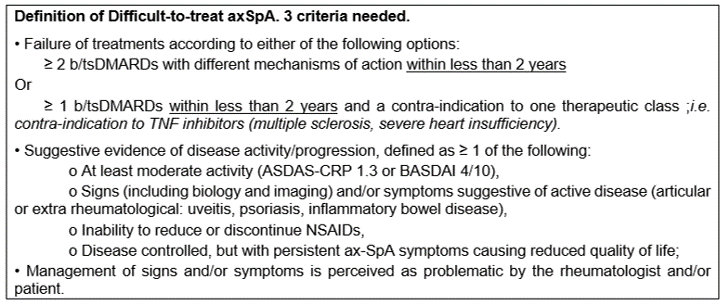
Conclusion: D2T axSpA was associated with a longer disease duration, higher BASDAI at baseline, higher prevalence of peripheral involvement and more frequent fibromyalgia. Very D2T patients represented a minim proportion of patients after applying a more stringent definition and might be independent from fibromyalgia, with higher CRP level at baseline and higher prevalence of IBD and uveitis. This study highlights some characteristics that may help practitioners better identify D2T axSpA patients. Pending a consensual definition by the European and American societies, we propose a definition of D2T axSpA (Figure 1).
1 Nagy G et al. EULAR definition of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:31–5.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
PHILIPPOTEAUX C, DELEPINE T, Cailliau E, Philippe P, TAISNE N, Pascart T, Paccou J, Cortet B, Flipo R, Letarouilly J. Characteristics of Difficult-To-Treat Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results of a Multicentric Retrospective Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-difficult-to-treat-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-of-a-multicentric-retrospective-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-difficult-to-treat-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-of-a-multicentric-retrospective-study/