Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I: Biomarkers and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by involvement of different organs in the body. The cardiovascular (CVD) involvement in SLE is responsible for high morbidity and is often the leading cause of death. Despite that, little is known about the risks of development of different CVDs in SLE. We aimed to determine the rate of different echocardiographic findings and their risks and clinical correlates in SLE patients.
Methods:
SLE patients (n=59), fulfilling 4 or more ACR criteria for SLE, attending outpatient Rheumatology clinics, were recruited. Demographic data, disease characteristics and current medication use were gathered from the patients. Clinical evaluation with SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI), echocardiography, anthropometric measurements and routine laboratory tests were done. Mann-Whitney U test, Chi-square test, Fisher exact test and logistic regression analysis were used for statistical analysis as appropriated.
Results:
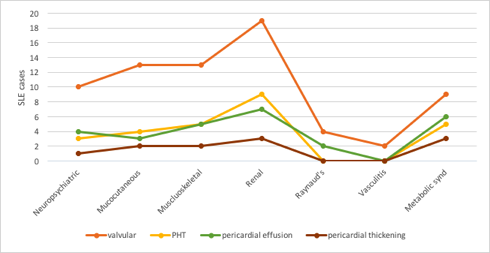
The mean age of the patients was 31.4±10.5, and 86.4% of the patients were females. The rate of different echocardiographic findings was as follow: overall valve lesions (47.5%), pulmonary hypertension (PHT) (18.6%), pericardial effusion (13.6%) and pericardial thickening (6.8%). The most common valve abnormalities were: mitral regurge (33.9%), tricuspid regurge (32.2%), mitral thickening (18.6%), and aortic thickening (13.6%) but less common were aortic regurge (6.8%) and pulmonary regurge (5.1%). The least common were pulmonary stenosis, mitral stenosis, and tricuspid and pulmonary thickening representing only (1.7%) each. The frequency of occurrence of different echocardiographic findings with different SLE features is shown in fig1. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed a significant association of PHT with age (OR=1.095, p=0.023, CI=1.013 – 1.184), mucocutaneous disease was a negative predictor of mitral regurge (OR=0.227, p=0.03, CI=0.059 – 0.868) and mitral thickening, (OR=0.046, p=0.032, CI=0.003 – 0.765), unlike Raynaud phenomenon which is a positive predictor of mitral thickening (OR=14.614, p=0.036, CI=1.199 – 178.1). Levels of HDL were associated with aortic thickening (OR= 0.907, p=0.05, CI =0.823 – 1). The use of prednisolone reduced the risk of developing aortic thickening (OR= 0.054, p=0.012, CI=0.006 – 0.53). Pericardial effusion was associated with metabolic syndrome (OR=12.4, p=0.025, CI=1.367 – 112.5) and high triglycerides levels (OR=1.012, p=0.028, CI=1.001 – 1.023). The echocardiographic findings showed no association with SLEDAI scores.
Conclusion:
Different laboratory and clinical correlates with different echocardiographic findings reflect the complexity of CVD mechanisms and warrant further studies to unravel disease pathogenesis.
Fig.1 The frequency of different echocardiographic findings in different SLE features
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hammam N, EL zohri MH, Mohamed AAA. Characteristics of Cardiac Diseases in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Risk Factors of Different Echocardiographic Features [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-cardiac-diseases-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-risk-factors-of-different-echocardiographic-features/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-cardiac-diseases-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-risk-factors-of-different-echocardiographic-features/