Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1412–1441) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II: SpA
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In the phase 3 DISCOVER-2 study of biologic-naïve patients (pts) with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), guselkumab (GUS), a fully human, selective interleukin (IL)-23p19 subunit inhibitor significantly reduced the signs and symptoms of disease and radiographic progression vs placebo (PBO), with durable response across multiple disease domains through 2 years. GUS also significantly decreased serum levels of collagen turnover markers, which are elevated in PsA pts vs healthy controls. Furthermore, changes in these and other serum cytokine levels through Week 24 (W24) of GUS treatment are associated with clinical response through 2 years. Here, we further assessed effects of GUS on serum cytokine and collagen turnover biomarkers from W24 through W100 (2 years) and explored associations between biomarker levels and longer-term clinical response (W100).
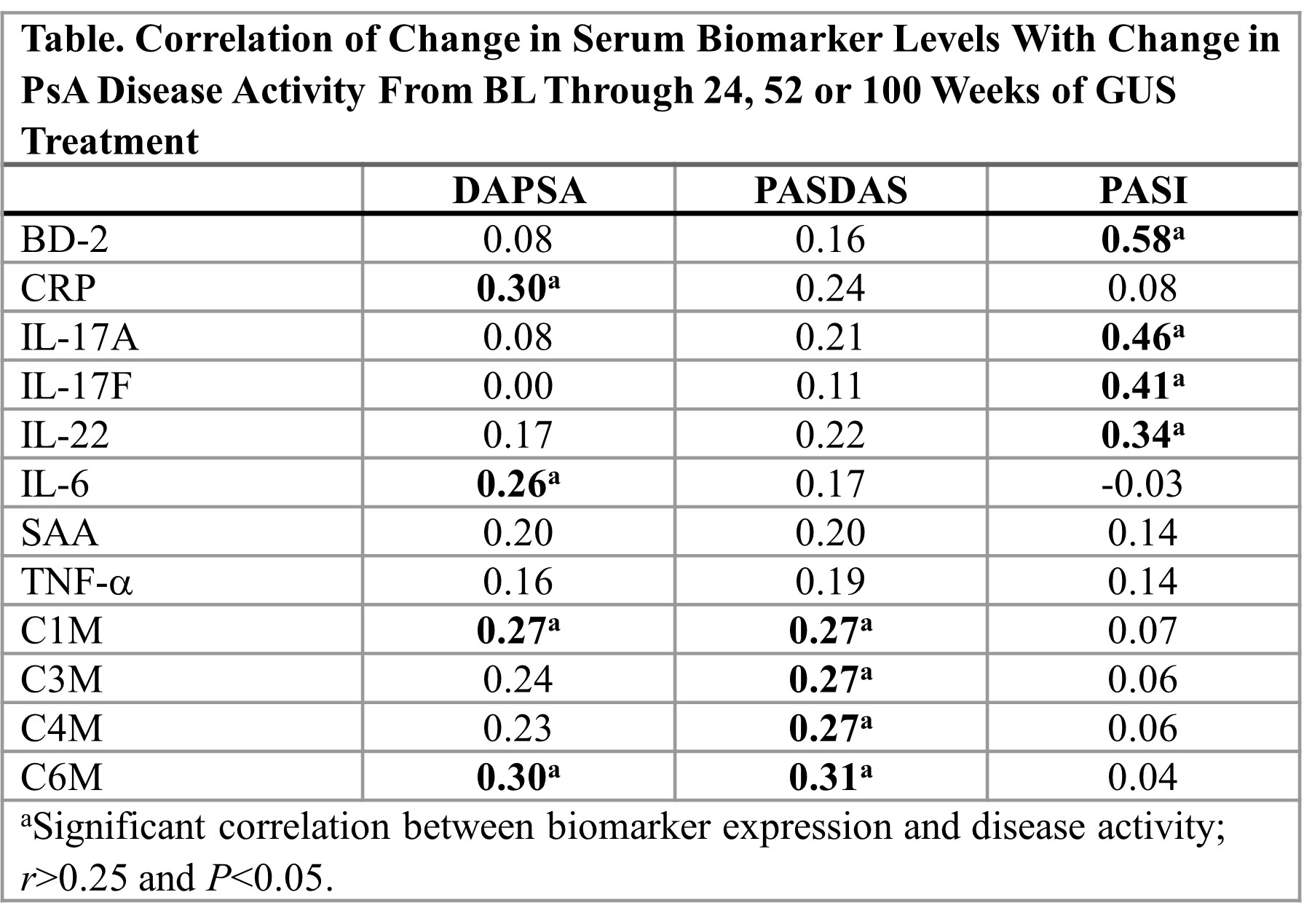
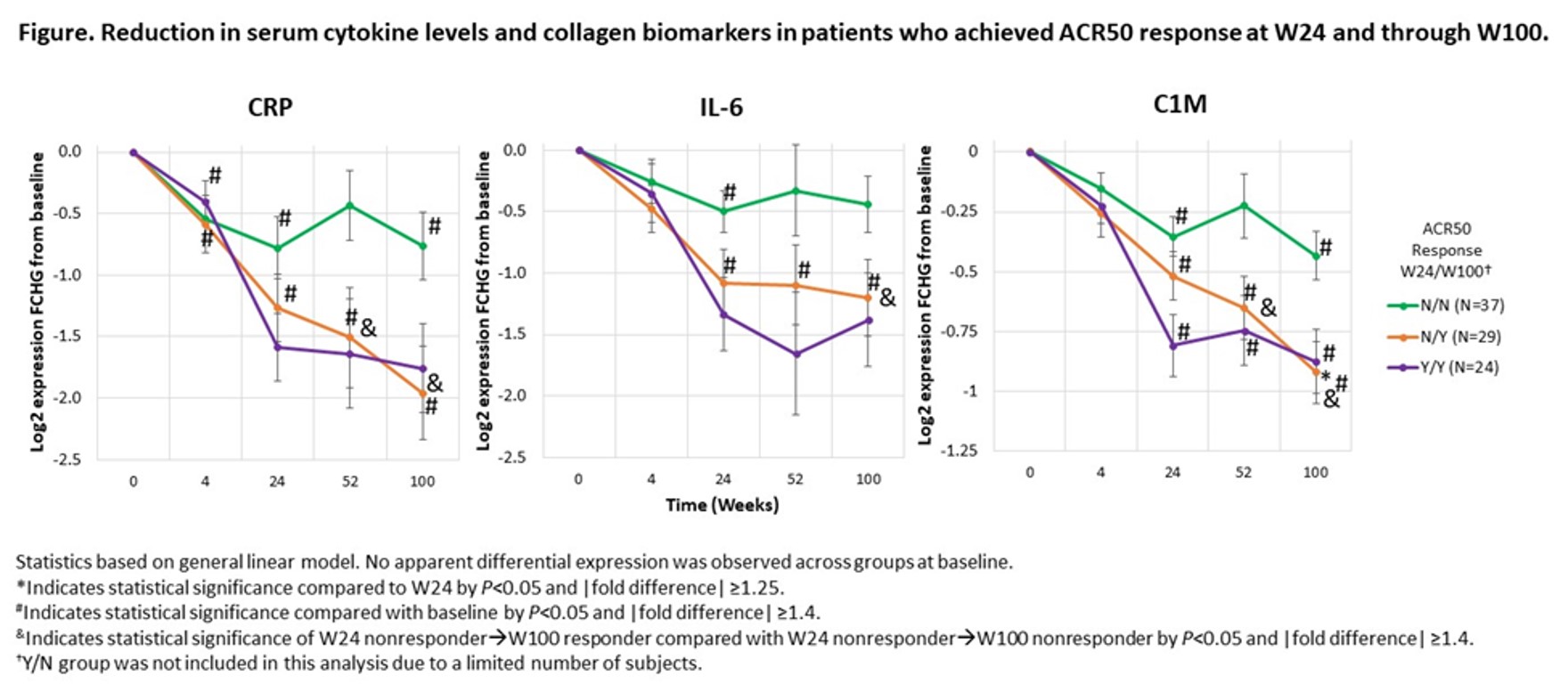
Methods: In DISCOVER-2, biologic-naïve adults with active PsA (swollen joint count ≥5, tender joint count ≥5, CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4 and then Q8W; or PBO with crossover to GUS Q4W at W24. Blood samples from consenting GUS-treated pts (Q4W and Q8W pooled) were assessed for serum cytokine levels (N=100), including Th17-related effector molecules (IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22), β-defensin 2 (BD-2), acute phase proteins (CRP, serum amyloid A [SAA], IL-6), and serum collagen turnover biomarkers (N=174; C1M, C3M, C4M, C6M). Using Spearman linear regression and general linear models, pooled changes from baseline (BL) in biomarkers during GUS treatment, correlations between changes in biomarker levels and reductions from BL at three time points (W24, W52, W100) in disease activity (measured by changes in Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis [DAPSA] score, Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score [PASDAS], Psoriasis Area and Severity Index [PASI] score) were assessed. Associations between biomarker changes and achievement of American College of Rheumatology (ACR)50 response at W100 were also assessed.
Results: Continued treatment with GUS led to significant and sustained reductions in serum cytokines from W24 through W100. Reductions in CRP and IL-6 were associated with changes in DAPSA score, with a similar trend observed for PASDAS. Reductions in BD-2, IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-22 from BL correlated with improvements in the PASI score, and reductions in collagen turnover biomarkers correlated with changes in the PASDAS (Table). Continued disease improvement with long-term GUS treatment, assessed clinically using ACR50 response, was supported by the further reductions in CRP, SAA, IL-6 and collagen turnover biomarkers in ACR50 responders at W100 who were ACR50 nonresponders at W24 (Figure). Among ACR50 responders at W24, mean reductions in CRP, SAA and IL-6 were sustained through W100.
Conclusion: These results provide molecular evidence that sustained reductions in serum acute phase proteins and collagen turnover biomarkers may contribute to the continuous, durable improvements in joint symptoms and that reductions in Th17-related effector molecules contribute to improvements in skin symptoms seen in PsA pts receiving GUS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Siebert S, Schett G, Raychaudhuri S, Guma M, Chen W, Gao S, Chakravarty S, Shawi M, Rahman P. Changes in Serum Cytokines and Collagen Proteins Correlate with Durability of Guselkumab Efficacy and Continued Disease Improvement Through 2 Years in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-cytokines-and-collagen-proteins-correlate-with-durability-of-guselkumab-efficacy-and-continued-disease-improvement-through-2-years-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-serum-cytokines-and-collagen-proteins-correlate-with-durability-of-guselkumab-efficacy-and-continued-disease-improvement-through-2-years-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/