Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Cytokines involved in lymphocyte development, function, and homeostasis signal through JAKs, and reductions in mean lymphocyte count over time have been reported in tofacitinib-treated patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis.1
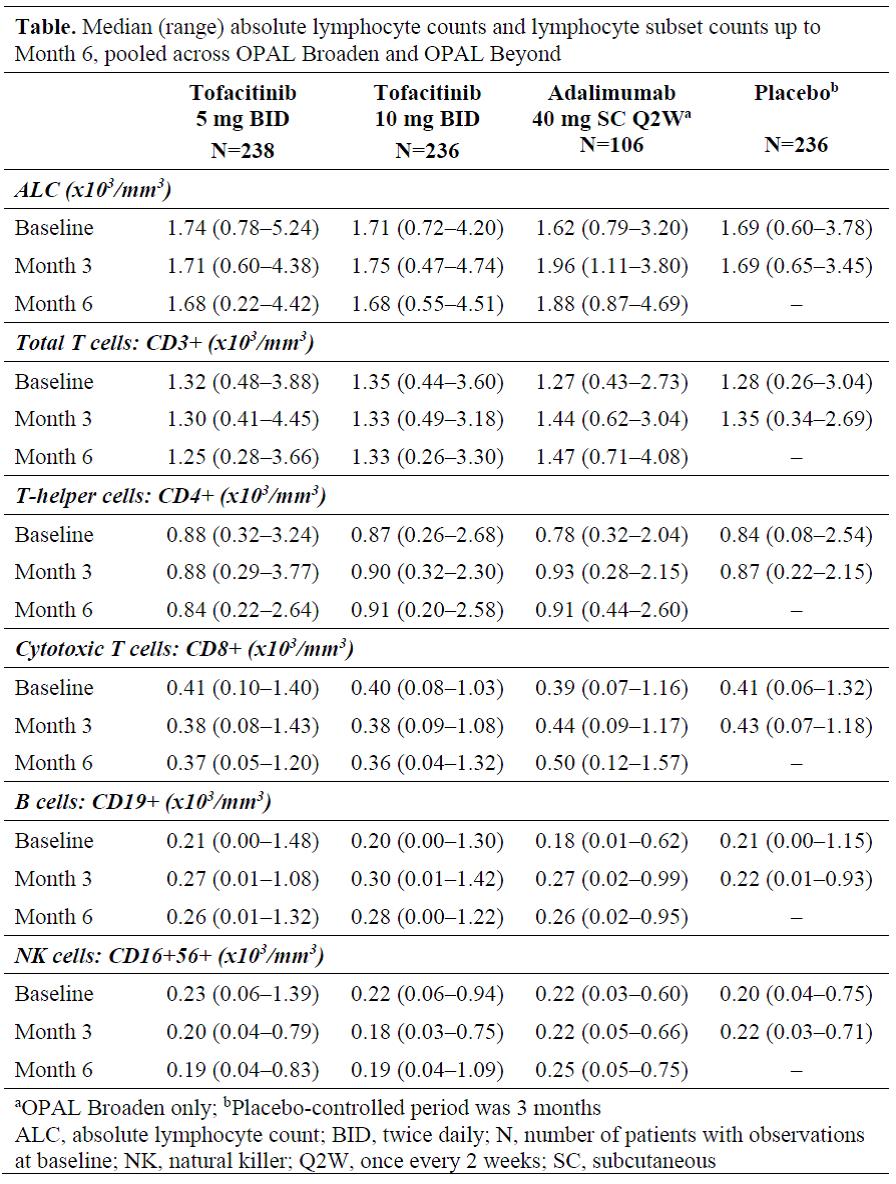
Methods: Data were pooled from 2 placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind, Phase (P)3 studies (OPAL Broaden [12 months; NCT01877668]; OPAL Beyond [6 months; NCT01882439]). Pts had active PsA and inadequate response to ≥1 conventional synthetic DMARD (OPAL Broaden) or to ≥1 tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (OPAL Beyond). Pts were randomized to tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID), tofacitinib 10 mg BID, adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneous injection once every 2 weeks (active control; OPAL Broaden only), or PBO. PBO pts advanced in a blinded manner to tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID at Month (M)3. Absolute lymphocyte counts (ALCs) and lymphocyte subset counts (LSCs) were assessed every 3 months as part of safety monitoring procedures in the P3 studies (any abnormalities were confirmed by retesting). Median ALCs and LSCs are reported up to M6. Incidence rates (pts with event/100 pt-years) for serious infections (SIs) were assessed by confirmed (2 sequential measurements) ALC categories (≥2.0, <2.0–1.5, <1.5–1.0, and <1.0–0.5×103/mm3) up to M12.
Results: The analysis included 816 pts: tofacitinib 5 mg BID, n=238; tofacitinib 10 mg BID, n=236; adalimumab, n=106; PBO, n=236. Up to M6, minimal decreases in median ALC were observed in pts who received tofacitinib 5 mg BID, tofacitinib 10 mg BID, and no change observed in PBO (up to M3 only) (Table). LSCs, including total T cells (CD3+), cytotoxic T cells (CD8+), and NK cells (CD16+56+), showed a similar trend to ALC for both tofacitinib doses (Table), with minimal decreases observed over 6 months. B cells (CD19+) showed numerical increases across treatments. Percentage changes from baseline in LSCs at M6 showed a generally similar pattern to absolute values. In adalimumab-treated pts, ALCs and all LSCs increased over 6 months. Up to M6, no pts receiving tofacitinib or adalimumab had confirmed ALC <0.5×103/mm3; 1 pt receiving PBO had a confirmed ALC <0.5×103/mm3 over 3 months, resulting in discontinuation from the study before advancing to active treatment. Up to M12, SIs were reported in 7 tofacitinib- (including 2 pts who advanced from PBO) and 1 adalimumab-treated pt; only 1 SI (PBO advanced to tofacitinib) occurred >6 months after treatment initiation. There was no trend that suggested an increased risk of SIs in any ALC category (data not shown).
Conclusion: Minimal changes in ALCs and LSCs were observed up to M6 in tofacitinib‑treated pts with active PsA. Incidence of SIs did not appear to be related to ALC in this clinical trial setting.
1. van Vollenhoven R et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 75: 258, abs
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burmester GR, Rigby WF, Choy E, Nash P, Winthrop K, Mease PJ, Young P, Hendrikx T, Wang C, Menon S, Graham D. Changes in Lymphocytes and Lymphocyte Subsets in Tofacitinib-Treated Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-lymphocytes-and-lymphocyte-subsets-in-tofacitinib-treated-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-lymphocytes-and-lymphocyte-subsets-in-tofacitinib-treated-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/