Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), an IL-17A inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials1-3 but real-world effectiveness data are limited.4 This study describes changes in disease activity and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) at 6 and 12 months follow-up among psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients initiating IXE in a real-world setting.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients from the OM1 PsA Registry (OM1, Boston, MA), a linked electronic medical record and administrative claims dataset with over 50,000 patients. Eligible patients had ≥1 prescription for IXE (first considered index), were ≥18 years old at index, had ≥1 diagnosis code for PsA in the 12 months before or on index, and had ≥12 months of baseline and ≥6 months of follow-up data as of June 2021. For patients with baseline and follow-up measures available, changes in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), PROs, and other clinical outcomes from baseline to 6 and 12 months were described. For patients on IXE monotherapy, change in CDAI score from baseline to 6 and 12 months was assessed using mixed effects linear models adjusted for age, sex, and baseline CDAI score.
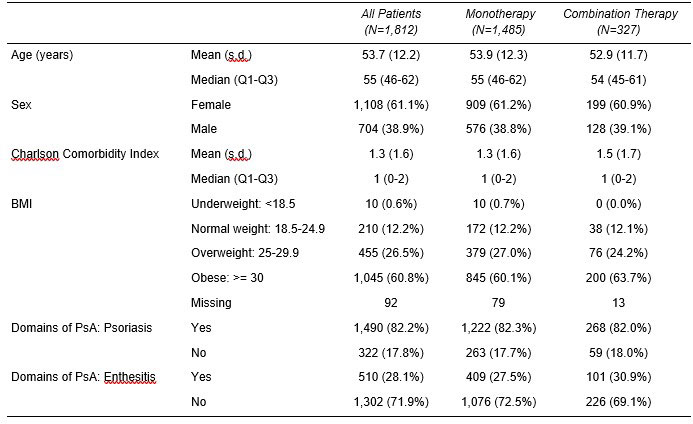
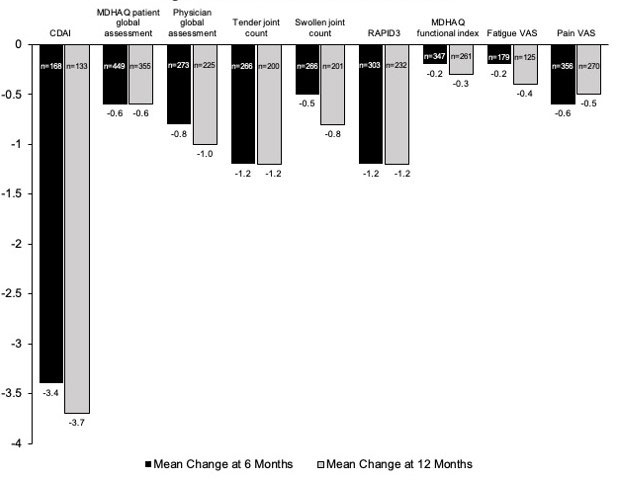
Results: The study population included 1,812 patients with a mean age of 53.7 years (Table 1). For all patients, domains of PsA included psoriasis (82%) and enthesitis (28%). Over 60% of patients were obese, and the mean Charlson Comorbidity Index was 1.3. Of 291 patients with a baseline CDAI score, 61% had moderate or severe disease activity. Most patients (84%) had prior treatment with a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) and 40% with a targeted synthetic DMARD (tsDMARD). The mean number of prior bDMARDs and tsDMARDs used during all available prior history was 2.3 and 1.1, respectively. The most common prior b/tsDMARDs were secukinumab (n=428, 24%) and adalimumab (n=245, 14%). For all patients, CDAI scores improved (decreased) by an average of 3.4 and 3.7 points at 6 and 12 months, respectively, from a baseline mean of 15.4. All disease activity measures and PROs improved from baseline to 6 and 12 months (Figure 1). In patients persistent with IXE, 35.3% and 33.7% were in CDAI remission or low disease activity at 6 and 12 months after initiation, respectively. For IXE monotherapy users (82% of patients), at baseline, patients had a mean CDAI of 14.3 (n=131) and 15.1 (n=105) for the 6 and12 month analyses, respectively. Adjusted mean changes in CDAI from baseline to 6 months (-3.6 points, p < 0.0001) and 12 months (-4.9 points, p < 0.0001) were statistically significant.
Conclusion: In this cohort of biologic-experienced, difficult to treat PsA patients with high comorbidity burden, improvements in disease activity and PROs were observed at 6 and 12 months after initiating treatment with IXE. Improvements were observed in patients overall and in the monotherapy subgroup. More real-world research on IXE and other bDMARDs may inform the effect of treatment choices on clinical and PROs in both bDMARD-naive and experienced PsA patients.
References:
[1] Mease PJ. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017;76(1):79-87.
[2] Nash P. Lancet. 2017;389(10086):2317-2327.
[3] Mease PJ. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020;79(1):123-131.
[4] Berman J. Biologics. 2021 Nov 18;15:463-470.<
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tillett W, Birt J, Cavanaugh C, Jung Y, Vadhariya A, Ross S, Paulus J, Sprabery A, Lubrano E. Changes in Disease Activity and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Treated with Ixekizumab in a Real-World US Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-disease-activity-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-treated-with-ixekizumab-in-a-real-world-us-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-disease-activity-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-treated-with-ixekizumab-in-a-real-world-us-cohort/