Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Apremilast (APR) is a PDE4 inhibitor that helps regulate the immune response. PALACE 1, 2, and 3 assessed the efficacy and safety of APR in pts with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) despite prior DMARDs and/or biologics. We evaluated weight change from BL in PALACE 1, 2, and 3.
Methods: Pts were randomized (1:1:1) to PBO, APR 20 mg BID (APR20), or APR 30 mg BID (APR30) stratified by baseline DMARD use (yes/no). Patients whose swollen and tender joint counts had not improved by ≥20% at Wk 16 were considered non-responders and were required to be re-randomized (1:1) to APR20 or APR30 if initially randomized to placebo, or continued on their initial apremilast dose. At Wk 24, all remaining PBO patients were re-randomized to APR20 or APR30. The pooled analysis comprises data for the PBO-controlled period (Wks 0 to 24) and the APR-exposure period (Wks 0 to ≥52) up to cutoff date, 3/1/2013.
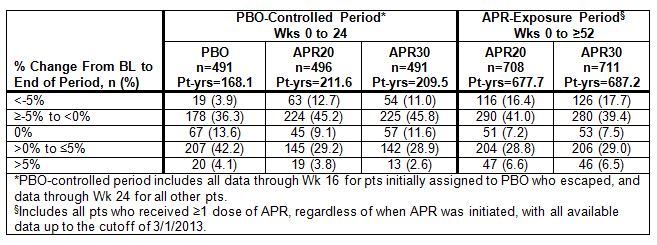
Results: During the PBO-controlled period, 495 pts received PBO, 501 received APR20, and 497 received APR30. At cutoff, 720 pts had received APR20 and 721 had received APR30. At BL, mean/median weight was 86.4/84.0 (PBO), 86.1/84.0 (APR20), and 84.5/83.0 (APR30) kg. Weight decrease was spontaneously reported as an AE in a small proportion of pts during both the PBO-controlled (PBO: 0.4%; APR20: 1.0%; APR30: 1.4%) and APR exposure (APR20: 1.4%; APR30: 1.8%) periods. No pts in the PBO-controlled and 2/1,441 pts (APR20: 1; APR30: 1) in the APR-exposure period discontinued due to weight decrease. An additional analysis using observed weight measurements collected at selected visits assessed changes from BL weight. In the PBO-controlled period, most pts remained within 5% of their BL weight (PBO: 92.1%; APR20: 83.5%; APR30: 86.4%). A larger proportion of APR-treated pts experienced any weight loss (APR20: 57.9%; APR30: 56.8%) vs PBO (40.1%). Weight loss >5% was experienced by 3.9% (PBO), 12.7% (APR20), and 11.0% (APR30) (Table). At the end of the PBO-controlled period, mean/median weight change from BL was 0.09/0.0 (PBO), -1.16/-0.60 (APR20), and -0.96/-0.60 (APR30) kg. In the APR-exposure period (Wks 0 to ≥52), most pts remained within 5% of BL weight (APR20: 77.0%; APR30: 75.8%); 57.3% (APR20) and 57.1% (APR30) experienced weight loss. Weight loss did not lead to any overt medical sequelae or manifestations through the APR-exposure period. In an analysis to determine the relationship between weight loss and GI AEs, weight loss was not associated with diarrhea or nausea/vomiting.
Conclusion: APR was associated with a small rate of weight decrease reported as an AE. The incidence of observed weight loss was higher with APR vs PBO, although most pts remained within 5% of their BL weight. Observed weight loss did not appear to be dose-dependent and did not lead to overt clinical sequelae. No association between weight loss and incidence of other AEs, including GI AEs, was apparent.
Disclosure:
P. J. Mease,
Research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene, Crescendo, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Vertex,
2,
Consulting fees from: AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene, Covagen, Crescendo, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Vertex,
5,
Speakers’ bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Crescendo, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, and UCB,
8;
D. D. Gladman,
AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Novartis, and UCB,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Novartis, and UCB,
5;
A. Kavanaugh,
Abbott, Amgen, Astra-Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Centocor-Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and UCB,
2;
A. O. Adebajo,
None;
J. Gomez-Reino,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Schering-Plough, and UCB SA,
9,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Schering-Plough, and Wyeth,
9,
Roche and Schering-Plough,
2;
J. Wollenhaupt,
Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer Inc, and UCB,
2,
Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer Inc, and UCB,
5;
G. A. Schett,
Abbott, Celgene Corporation, Roche, and UCB,
2,
Abbott, Celgene Corporation, Roche, and UCB,
5;
K. Shah,
Celgene Corporation,
1,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
C. Hu,
Celgene Corporation,
3,
Celgene Corporation,
1;
R. M. Stevens,
Celgene Corporation,
1,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
C. Edwards,
Celgene Corporation, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and Samsung,
2,
Celgene Corporation, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and Samsung,
5,
Abbott, Glaxo-SmithKline, Pfizer Inc, and Roche,
8;
C. A. Birbara,
Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Eli Lilly, Merck, and Pfizer Inc,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-weight-from-baseline-with-apremilast-an-oral-phosphodiesterase-4-inhibitor-pooled-results-from-3-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trials/