Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Methods Replace the Conventional Sacroiliac Joint Magnetic Resonance Imaging?
ABSTRACT
Background/Purpose: The purpose of our study was to assess the diagnostic value of two-point Dixon method compared with conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including T1-weighted, T2-weighted, fat saturated (FS) T1-weighted, FS T2-weighted, and short tau inversion recovery (STIR) in diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis (SpA). Methods: A total of 67 patients with low back pain and suspected axial SpA who underwent sacroiliac joint MRI in our institution from September 2014 to October 2015 were retrospectively evaluated. Each with two data sets (modified Dixon images, conventional MRI), were independently reviewed by two radiologists as follows: 1) grading of both sacroiliac joints; 2) bone marrow edema; 3) erosion; 4) periarticular fat deposition; 5) ankylosis. Bone marrow edema was evaluated on FS T2-weighted, and STIR images. Structural change and fat deposition were evaluated on T1-weighted image. Erosion was evaluated on T1-weighted and FS T1-weighted images. All variables were determined in a thin slice 3D-Dixon images. Sensitivity, specificity, and intra- and interobserver reliabilities were calculated.
Results: Patients had a mean age of 31.7 ¡¾ 11.1 years and male were 44 (65.7%). 44 of 67 patients (65.7%) had positive HLA-B27. 62 patients were diagnosed with axial SpA based on laboratory and imaging information as well as the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) criteria. One patient was diagnosed with osteitis condensans ilii. Four patients were diagnosed with non-specific mechanical back pain. Sensitivities and specificities of Dixon method and conventional MRI are 97.4%, 14.3% and 94.6%, 10.7%. Both Dixon method and conventional MRI had a good to excellent intraobserver (mean intraclass correlation coefficient [ICC] = 0.680-0.953, 0.886-1.000) and interobserver agreement (mean ICC = 0.860-0.986, 0.792-0.953).
Conclusion: 3D-modified Dixon method might be another practical novel imaging technique as conventional MRI. The Dixon method is more intuitive than conventional MRI to evaluate sacroiliac joint, moreover, it takes less time.
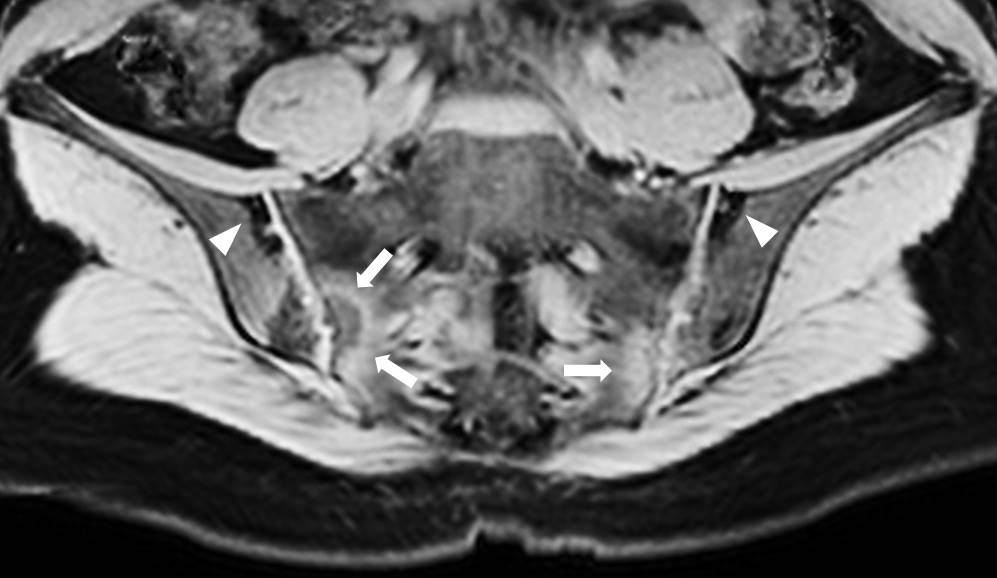
Figure 1. Bilateral sacroiliitis (grade 3) with periarticular fat deposition (arrow head), and edema (arrow) showed in 3D-Dixon methods.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Song Y, Lee S, Kim TH. Can the 3D-Modified Dixon Methods Replace the Conventional Sacroiliac Joint Magnetic Resonance Imaging? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/can-the-3d-modified-dixon-methods-replace-the-conventional-sacroiliac-joint-magnetic-resonance-imaging/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/can-the-3d-modified-dixon-methods-replace-the-conventional-sacroiliac-joint-magnetic-resonance-imaging/