Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Anti-TNF therapy for RA is associated with antinuclear (ANAs) and
anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) autoantibodies.1,2 The effect
of biologics on autoantibody-positive patients is unknown. We explored ANA and
anti-dsDNA antibody development during abatacept (ABA) and anti-TNF treatment
(ATTEST/AMPLE trials) and effects of switching to ABA in patients with
ANA/anti-dsDNA (ATTEST).
patients had active RA, were biologic naïve and MTX inadequate responders.
ATTEST: patients were randomized to IV ABA (∼10mg/kg
q4w), infliximab (IFX; 3mg/kg q8w) or placebo, on background MTX. At Month 6,
placebo-treated patients started ABA (blinding maintained); ABA- and
IFX-treated patients continued treatment. Patients completing the 1-year DB
period were eligible to receive ABA (open-label long-term extension [OLE]).
AMPLE (2-year head-to-head trial): patients were randomized to SC ABA (125mg
weekly) or SC adalimumab (ADA; 40mg biweekly), on background MTX. Serum ANA and
anti-dsDNA were measured at baseline, Month 6, Year 1 and 2 in ATTEST, and at
baseline, Year 1 and 2 in AMPLE.
Results: In the ATTEST DB period, 156
patients received IV ABA and 165 received IFX; 132 and 136 patients received IV
ABA in the OLE, respectively. In AMPLE, 318 patients received SC ABA and 328
received ADA. At baseline in ATTEST, 69 patients (32 IV ABA/37 IFX) were ANA+
and 26 (11 IV ABA/15 IFX) were anti-dsDNA+; AMPLE: 166 were ANA+ (72 SC ABA/94
ADA) and 6 anti-dsDNA+ (1 SC ABA/5 ADA). In both studies, a higher percentage
of patients seroconverted (negative–positive, baseline–Year 1) with anti-TNFs
versus ABA (Table); this difference continued during AMPLE Year 2. In ATTEST,
48.5% (ANA) and 48.3% (anti-dsDNA) of IFX-treated patients who entered the OLE
seroconverted (negative–positive, baseline–Year 1), falling to 22.4% and 13.3%,
respectively, at Year 2 after switching to ABA. The percentage of patients who
seroreverted (baseline positive–negative) increased from 12.1% to 20.6% on
switching from IFX to ABA (Table).
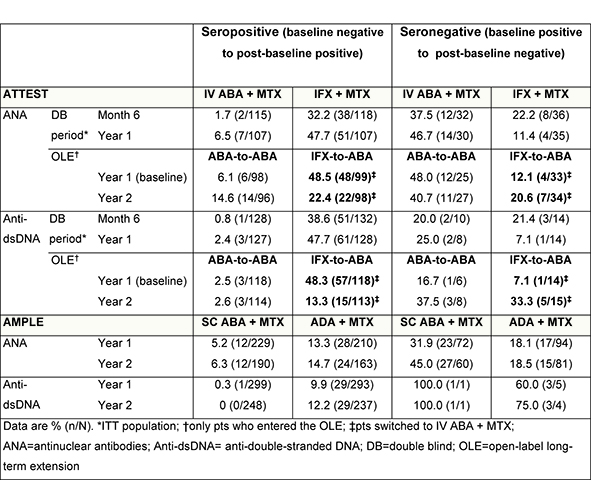
ATTEST, switching from infliximab to abatacept seemed to reverse autoantibody
induction observed with anti-TNF treatment. In both trials, anti-TNF therapy
was associated with greater autoantibody induction than abatacept. These data
imply an effect of T-cell co-stimulation blockade on B-cell function and
autoantibody production.3
1.
Charles PJ, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2000;43:2383–90.
2. Eriksson
C, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:403–7.
3. This abstract was first presented at the EULAR Congress, 10–13 June
2015, Rome, Italy (AB0469) and published in the corresponding supplement of Ann
Rheum Dis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Buch MH, Johnsen A, Wong D, Schiff M. Can Anti-TNF-Induced Autoantibody Conversion be Reversed By Switching to Abatacept Therapy in Patients with RA on Background MTX? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/can-anti-tnf-induced-autoantibody-conversion-be-reversed-by-switching-to-abatacept-therapy-in-patients-with-ra-on-background-mtx/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/can-anti-tnf-induced-autoantibody-conversion-be-reversed-by-switching-to-abatacept-therapy-in-patients-with-ra-on-background-mtx/
