Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
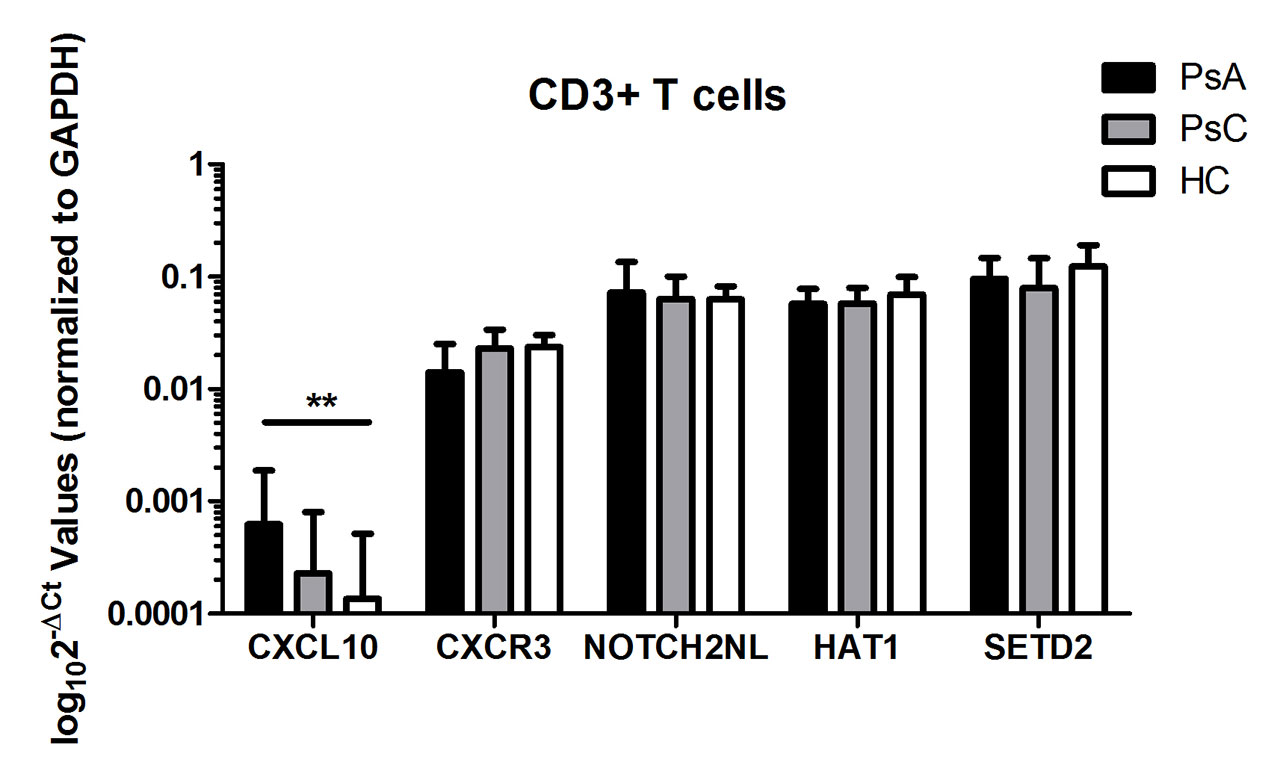
Background/Purpose: We previously identified CXCL10, NOTCH2NL, HAT1, and SETD2 as differentially expressed between psoriasis arthritis (PsA) and psoriasis patients without arthritis (PsC). This study aimed to validate these findings and determine their expression in leukocyte subsets in psoriatic disease.
Methods: Prospectively followed psoriasis patients without arthritis (PsC) were assessed yearly by rheumatologists for the presence of PsA. CXCL10, CXCR3, NOTCH2NL, HAT1, and SETD2 mRNA levels were measured in whole blood from 39 patients with early PsA (< 2 years disease duration), 38 PsC ( >10 years disease duration) and 39 healthy controls (HCs) as well as in T-cells (CD3+), monocytes (CD14+), and NK cells (CD56+) from PsA (n=25), PsC (n=23) and HCs (n=15). Gene expression was compared between groups using Mann-Whitney U tests.
Results: CXCL10 expression was elevated in PsA compared to PsC (2.4-fold, p=0.071) and HC (1.9-fold, p=0.407), although this was not statistically significant. Within T cells, CXCL10 was increased in PsA patients compared to HC (Figure 1; 4.9-fold, p< 0.01). CXCL10 expression was higher in monocytes as compared to T-cells (6.7-fold, p< 0.001) and NK cells (5.0-fold, p< 0.001) in all study subjects combined. CXCR3, HAT1 and SETD2 were higher in T cells (233.7-fold, 3.2-fold and 2.9-fold, respectively) and NK cells (168.2-fold, 2.3-fold and 2.6-fold, respectively) compared to monocytes (p< 0.001). Expression of NOTCH2NL was increased in T cells compared to monocytes (1.9-fold; p< 0.001).
Conclusion: Gene expression differences were identified in psoriatic disease that could provide insight into their role in driving the development of PsA and aid in developing targeted treatments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abji F, Muntyanu A, Pollock R, Machhar R, Ye J, Chandran V, Gladman D. C-X-C Motif Chemokine 10 (CXCL10) as a Transcriptomic Biomarker of Psoriatic Arthritis Susceptibility [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/c-x-c-motif-chemokine-10-cxcl10-as-a-transcriptomic-biomarker-of-psoriatic-arthritis-susceptibility/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/c-x-c-motif-chemokine-10-cxcl10-as-a-transcriptomic-biomarker-of-psoriatic-arthritis-susceptibility/