Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: High BMI is associated with reduced remission rates with anti-TNF agents in RA.1,2 In ACQUIRE (NCT00559585), SC and IV abatacept (ABA) achieved similar ACR20 responses at 6 months (M)3 and therapeutic trough concentrations4 across body weight groups in patients (pts) with RA. This post hoc analysis explored clinical outcomes reflecting disease status and pharmacokinetics with SC (fixed dose) or IV (weight-tiered) ABA by BMI.
Methods: In ACQUIRE, pts with RA and MTX inadequate response were randomized (1:1) to SC (125 mg/week) or IV (~10 mg/kg/M) ABA plus MTX. Disease status over 6 M was assessed by DAS28 (CRP) (<2.6), SDAI (≤3.3) and CDAI (≤2.8) remission, mean change in Pt Global Assessment, TJC and SJC, and high-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP). Trough (Cmin) serum ABA concentrations were measured at 3 and 6 M. Data were analyzed by baseline BMI (underweight/normal, <25 kg/m2; overweight, 25–<30 kg/m2; obese, ≥30 kg/m2) and ABA administration route.
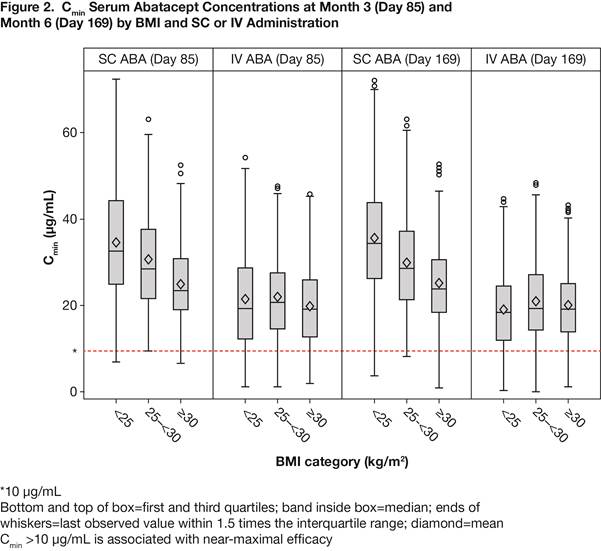
Results: 526 pts (SC 265, IV 261) were underweight/normal; 497 (SC 249, IV 248) overweight; 433 (SC 221, IV 212) obese. Baseline characteristics did not differ by administration route, and for the pooled SC/IV group were similar by BMI (Table 1). Clinical outcomes by BMI at 6 M were similar for SC and IV groups measured by the % of pts in DAS28 (Figure 1), SDAI (underweight/normal, 9.1 vs 10.6%; overweight, 12.0 vs 11.8%; obese, 11.9 vs 9.8%) and CDAI (underweight/normal, 9.0 vs 11.8%; overweight, 13.1 vs 13.7%; obese, 14.3 vs 11.8%) remission; 95% CIs overlapped at all time points. There were no differences in the other outcomes by BMI, except for hsCRP, but this had no impact on remission rates. Results were consistent for the pooled SC/IV group. Although SC ABA Cmin concentrations decreased with BMI increase, >90% of pts had concentrations >10 μg/mL (efficacy threshold) across BMI groups at 3 and 6 M for both SC and IV ABA (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The clinical efficacy of SC and IV abatacept was independent of BMI, even when stringent remission criteria were used. Across BMI groups, >90% pts achieved therapeutic trough concentrations, irrespective of SC or IV administration.
| Table 1. Baseline Characteristics by BMI Group (pooled SC and IV) | |||
|
Underweight/normal, <25 kg/m2 (n=526) |
Overweight, 25–<30 kg/m2 (n=497) |
Obese, ≥30 kg/m2 (n=433) |
|
| BMI, kg/m2 |
22.0 (2.1) |
27.4 (1.4) |
35.2 (5.2) |
| Age, years |
47.5 (14.4) |
51.3 (12.2) |
51.6 (11.2) |
| Females, % |
83.1 |
78.9 |
85.7 |
| Caucasians, % |
70.9 |
76.3 |
77.1 |
| RA duration, years |
8.3 (8.2) |
7.7 (7.5) |
6.9 (8.2) |
| TJC/68 |
28.5 (13.5) |
29.3 (13.6) |
31.2 (14.1) |
| SJC/66 |
19.7 (9.5) |
19.6 (8.7) |
20.5 (9.2) |
| hsCRP, mg/dL |
3.1 (3.4) |
2.5 (2.6) |
2.3 (2.5) |
| DAS28 (CRP) |
6.2 (0.9) |
6.2 (0.9) |
6.3 (0.8) |
| PGA, 100 mm VAS |
66.3 (19.5) |
64.9 (20.3) |
66.5 (20.9) |
| |
|||

To cite this abstract in AMA style:
D'Agostino M, Alten R, Mysler E, Le Bars M, Ye J, Murthy B, Heitzmann J, Vadanici R, Ferraccioli G. Body Mass Index Does Not Affect Response to Subcutaneous or Intravenous Abatacept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/body-mass-index-does-not-affect-response-to-subcutaneous-or-intravenous-abatacept-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/body-mass-index-does-not-affect-response-to-subcutaneous-or-intravenous-abatacept-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/
