Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Skeletal muscle, pulmonary and articular involvement in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) limit the mobility/self-sufficiency of patients, and can have a negative impact on body composition. The aim of this study was to assess body composition and physical activity of IIM patients and healthy controls (HC) and the association with chosen inflammatory cytokines/chemokines and laboratory markers of nutrition and lipid metabolism.
Methods: 54 patients with IIM (45 females; mean age 57.7; disease duration 5.8 years; polymyositis (PM, 22) / dermatomyositis (DM, 25) / necrotizing myopathy (IMNM, 7)) and 54 age-/sex-matched HC (45 females, mean age 57.7) without rheumatic/tumor diseases were included. PM/DM patients fulfilled Bohan/Peter criteria for PM/DM. We assessed body composition (densitometry: iDXA Lunar, bioelectric impedance: BIA2000-M), physical activity (Human Activity Profile (HAP) questionnaire, serum levels of 27 cytokines/chemokines (commercial multiplex ELISA kit, Bio-Rad Laboratories) and serum levels of chosen parameters of nutrition and lipidogram. Disease activity (MITAX and MYOACT activity score) and muscle involvement (manual muscle test, MMT-8, and functional index 2, FI2) were evaluated. Data are presented as mean±SD.
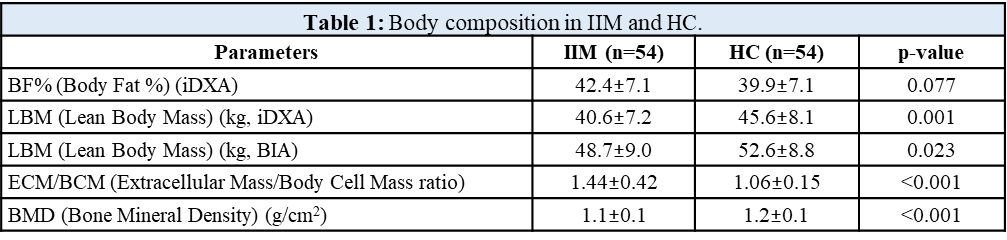
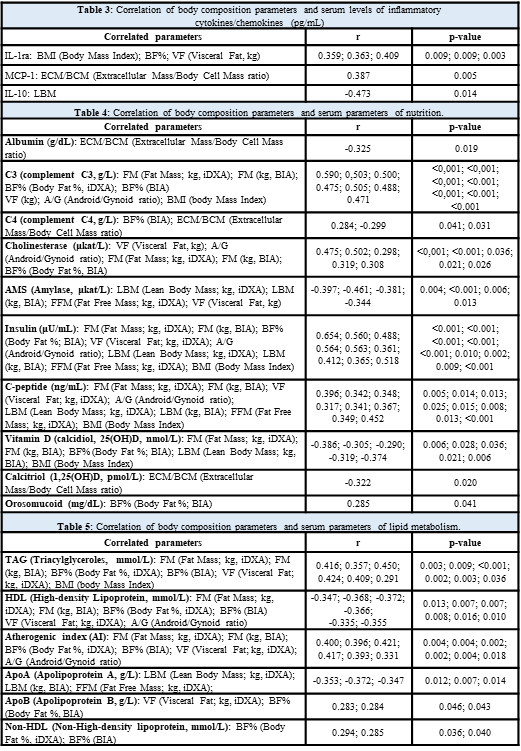
Results: Compared to HC, patients with IIM had a trend towards significantly increased body fat % (BF%) as assessed by iDXA, but significantly decreased lean body mass (LBM) as assessed both by iDXA and BIA, and increased extracellular mass/body cell mass (ECM/BCM) ratio reflecting worse muscle predispositions for physical exercise, aerobic fitness/performance, and deteriorated nutritional status. Compared to HC, IIM patients had significantly lower bone mineral density (BMD) (Table 1). Disease duration negatively correlated with BMD and LBM-BIA. Disease activity assessed by both MITAX and MYOACT positively correlated with LBM (by BIA and iDXA), similarly as with basal metabolic rate (BMR) and fat free mass (FFM). CRP was positively associated with BF% (by iDXA and BIA). Higher BF%-iDXA was associated with worse physical endurance (Function Index-2, FI-2) and worse ability to perform physical activity (HAP). MMT-8 score negatively correlated with ECM/BCM ratio (Table 2). Serum levels of several inflammatory cytokines/chemokines (Table 3) and markers of nutrition and lipid metabolism were associated with alterations of body composition (Table 4 and 5).
Conclusion: Compared to healthy age-/sex-matched individuals we found significant negative changes in body composition of our IIM patients, which are associated with their disease activity and duration, inflammatory status, skeletal muscle involvement, and physical activity. These data could reflect their impaired nutritional status and predispositions for physical exercise, aerobic fitness and performance. Serum levels of certain inflammatory cytokines/chemokines and markers of nutrition and lipid metabolism were associated with alterations of body composition in IIM patients.
Acknowledgement: Supported by AZV NV18-01-00161A, MHCR 023728 and GAUK 312218
cytokines/chemokines -pg/mL-;
Table 4: Correlation of body composition parameters and serum parameters of nutrition.
Table 5: Correlation of body composition parameters and serum parameters of lipid metabolism.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oreska S, Spiritovic M, Cesak P, Marecek O, Storkanova H, Hermankova B, Kubinova K, Klein M, Vernerová L, Ruzickova O, Pavelka K, Senolt L, Mann H, Vencovský J, Tomcik M. Body Composition in Myositis Patients Is Negatively Changed Compared to Healthy Controls and the Changes Are Associated with Disease Activity and Duration, Skeletal Muscle Involvement and Physical Activity and Nutritional Status [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/body-composition-in-myositis-patients-is-negatively-changed-compared-to-healthy-controls-and-the-changes-are-associated-with-disease-activity-and-duration-skeletal-muscle-involvement-and-physical-act/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/body-composition-in-myositis-patients-is-negatively-changed-compared-to-healthy-controls-and-the-changes-are-associated-with-disease-activity-and-duration-skeletal-muscle-involvement-and-physical-act/