Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The prevalence of depression is increased in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Little is known about the impact of effective control of inflammation on depressive mood in patients with PsA and the direct impact of therapies for PsA on depression. The aim of the study was to assess the effect of golimumab (TNFα blocker) and ustekinumab (IL-12/23blocker) on improving depressive symptoms in patients with PsA participating in clinical trials.
Methods: Data from three phase 3, randomized, double blinded placebo-control clinical trials assessing the efficacy of golimumab (GO-REVEAL) and ustekinumab (PSUMIT1 and 2) were analyzed. For each trial the analysis included all patients who were randomized to receive the study drug or placebo. The analysis included information collected during the double-blind portion of the trial (baseline, 14-16 and 24 weeks). The Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) mental component summary (MCS) score was used to assess the change in depressive symptoms over time in each treatment arm. A threshold of SF-36-MCS < 38 was used to define a state of depression (sensitivity of 87%, sensitivity of 80% and accuracy of 83%)1. The change in proportion of patients classified as being depressed was compared with baseline for each treatment arm using chi square test (Odds Ratio (OR)).
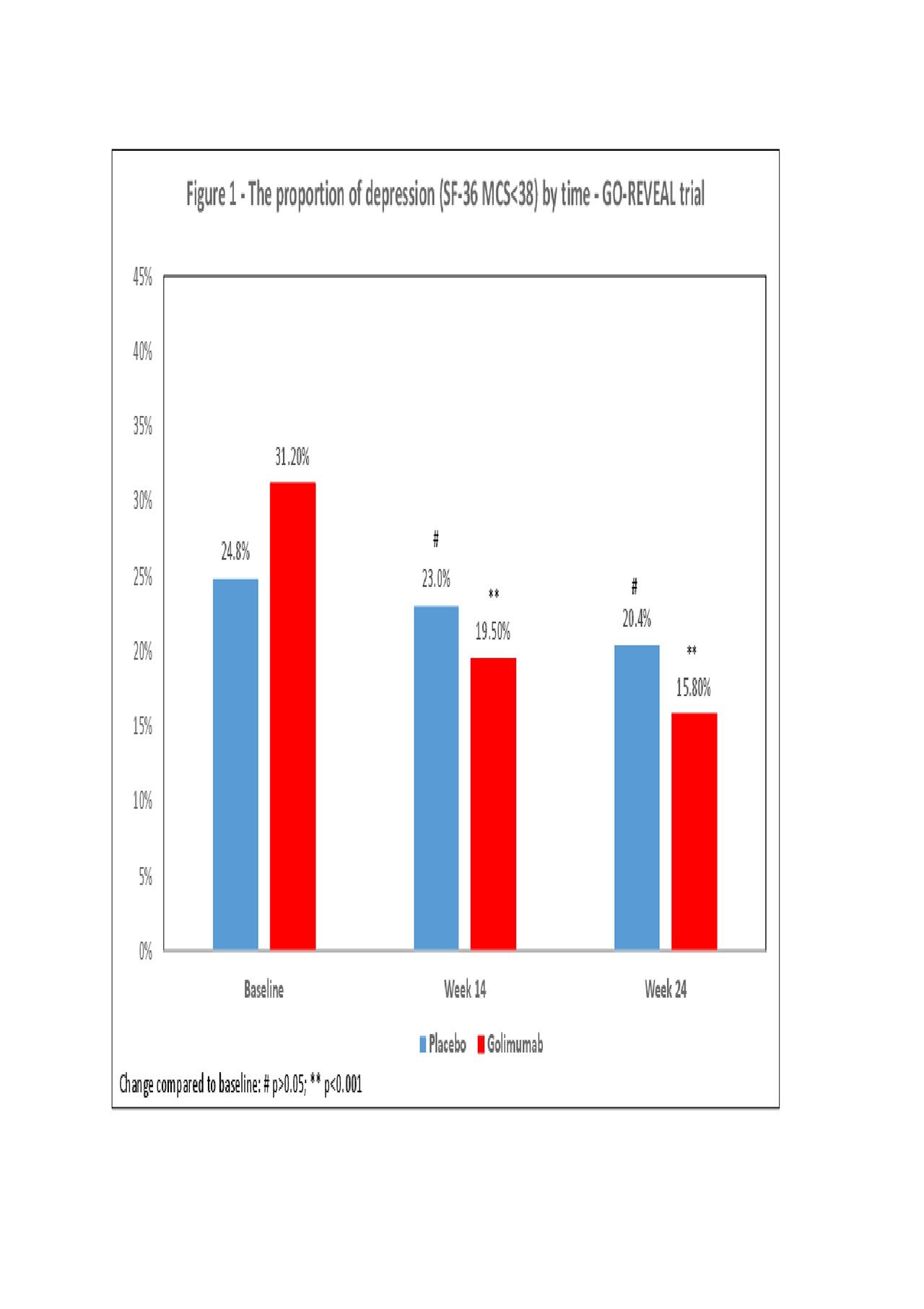
Results: A total of 1,332 patients were enrolled in the three trials (GO-REVEAL 405, PSUMIT1 615, PSUMIT2 312). The mean age was 47 years and the proportion of females ranged from 39.8% and 52.6%. The proportions of patients classified as being in depression at baseline were: 29.4% (GO-REVEAL), 34.9% (PSUMIT-1) and 38.8% (PSUMIT2). Overall, a significant decrease in the proportion of patients with depression was found in the treatment arms of all three studies. In the GO-REVEAL trial the proportion of depression reduced from 31.2% (baseline) to 19.5% (W14: OR 0.54; p=0.001) and 15.8% (W24: OR 0.41;p< 0.001, Figure 1) in the golimumab arm. In the PSUMIT1 trial the proportion of depression decreased from 36.2% (baseline) to 23.5% (W16: OR 0.54;p< 0.001) and 20.3% (W24: 0.45;p< 0.001, Figure 2) in the ustekinumab arm. In the PSUMIT2 trial the proportion of depression decreased from 37.5% (baseline) to 25.5% (W14: OR 0.57;p=0.009) and 21.2% (W24: OR 0.45;p< 0.001, Figure 3) in the ustekinumab. In general, minimal changes were seen in the proportion of depression in the placebo arm of all three studies.
Reference: Matcham F et al. Usefulness of the SF-36 Health Survey in screening for depressive and anxiety disorders in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2016;17:224
Conclusion: Blockage of TNFα and IL-12/23 was associated with a significant improvement in depressive symptoms in patients with PsA participating in clinical trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eder L, Ogdie A, Zhong Y. Blockage of TNFα and IL-12/23 Improves Depressive Symptoms in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis – Analysis of Clinical Trial Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/blockage-of-tnf%ce%b1-and-il-12-23-improves-depressive-symptoms-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-analysis-of-clinical-trial-data/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/blockage-of-tnf%ce%b1-and-il-12-23-improves-depressive-symptoms-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-analysis-of-clinical-trial-data/