Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Golimumab (GLM) is the latest anti-TNFα to be indicated for treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). The post-registration GO-PRACTICE study was performed at the request of the French Health Authorities, for the reevaluation of GLM in real-life.
Methods: The primary objective was to estimate GLM persistence at 2 years from initial prescription which was defined as the time to GLM discontinuation. This abstract focuses on a post-hoc analysis of the factors linked to GLM discontinuation in axSpA patients.
Observational, prospective, multicenter study, that consecutively recruited adult patients with RA, PsA and axSpA who were newly prescribed GLM. Patients were followed-up for 2 years and outcomes data were collected at baseline, 1 and 2 years. Patients’ sociodemographic characteristics, disease history, comorbidities and treatment history were also collected at baseline. Persistence was estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method. Cox proportional hazard models were used to assess factors associated with persistence. Selected baseline characteristics were studied in univariate models, where those associated with p-value < 0.20 were included in multivariate analysis. Significance level was set at p < 0.05.
Results: Patients with axSpA (n=478) were included from Jan 2015 to Mar 2016. Mean age was 43 years and 55% were female; 61% of patients were biologic-naïve (BN, n=291) and 39% (n=187) were biologic-pretreated (BP). Median time-elapsed in years since axSpA diagnosis was 1.7 (range 0–45.1) and 6.9 (range 0.2–51.8) in BN and BP patients, respectively (P < 0.001); 97% patients were prescribed 50 mg GLM monthly and co-treatments included DMARD (34%), corticosteroids (17%) and NSAIDs/analgesics (90%).
The cumulative persistence probability of GLM at 2-years was 52.6% (Fig 1). Table 1 details the binary variables associated with GLM discontinuation at p < 0.20. Among continuous variables, baseline CRP level was associated with p < 0.20. A multivariate analysis of these factors revealed that being female (Hazard Ratio 1.59, 95%CI 1.14–2.23, P = 0.0065) and being BP (Hazard ratio 1.63, 95%CI (1.18–2.26), P = 0.0034) were risk factors for earlier GLM discontinuation (Table 1).
Conclusion: The persistence of golimumab at 2-years was 52.6% in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Females and those who were biologics-pretreated were at greater risk for earlier golimumab discontinuation.
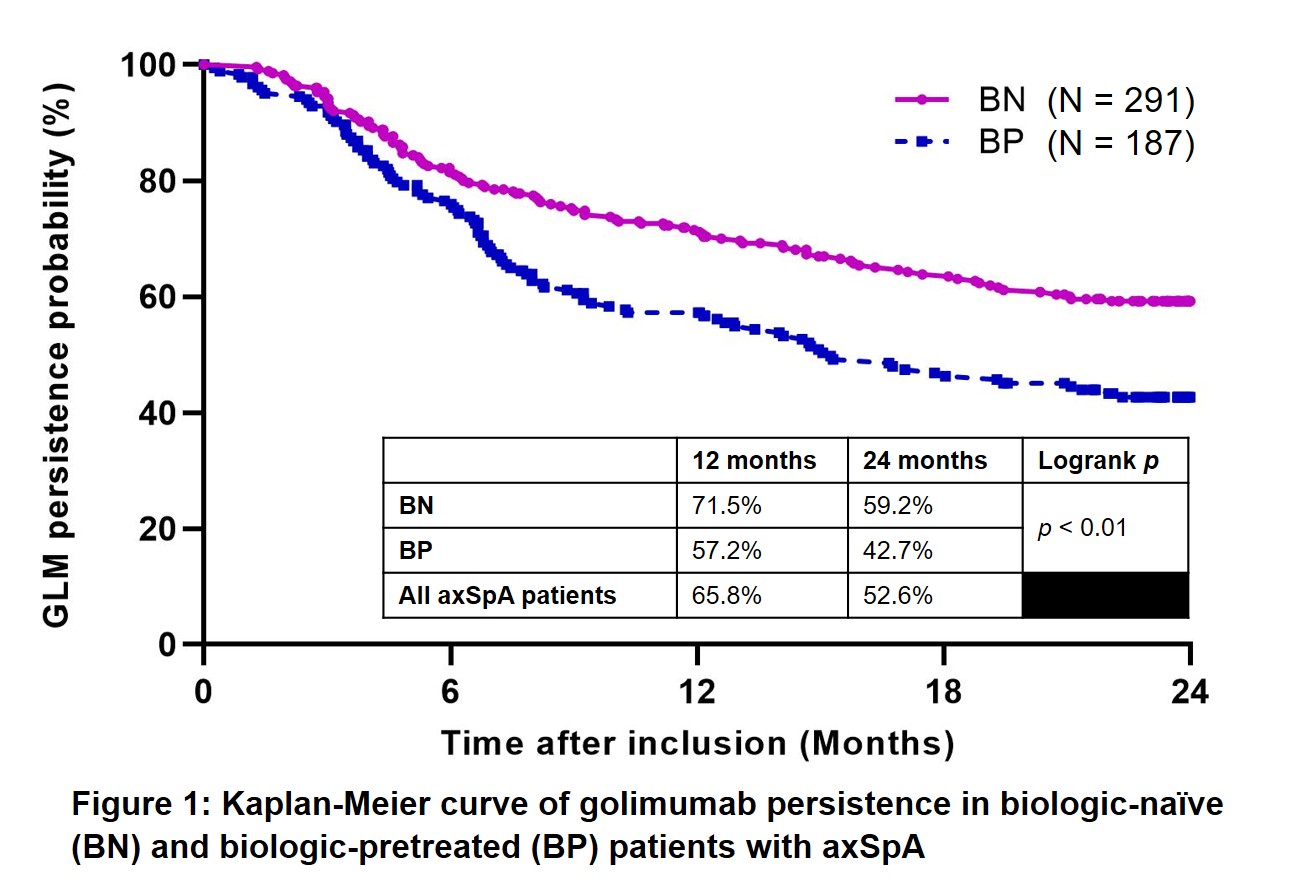 Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier curves of golimumab persistence in biologic-naïve and biologic-pretreated patients with axSpA
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier curves of golimumab persistence in biologic-naïve and biologic-pretreated patients with axSpA
 Table 1: Cox proportional hazard model results for variables of interest and their link to golimumab discontinuation in axSpA
Table 1: Cox proportional hazard model results for variables of interest and their link to golimumab discontinuation in axSpA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bertin P, Goupille P, Tubach F, Lespessailles E, Harid N, Sequeira S, Fayette J, Fautrel B, Flipo R. Biologics History and Sex Are Linked to Golimumab Discontinuation in Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Sub-Analysis of the Post-Registration GO-Practice Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biologics-history-and-sex-are-linked-to-golimumab-discontinuation-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-sub-analysis-of-the-post-registration-go-practice-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biologics-history-and-sex-are-linked-to-golimumab-discontinuation-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-sub-analysis-of-the-post-registration-go-practice-study/
