Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The purpose of this study was to describe biologic initiation patterns over a 1-year follow-up period in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with moderate or high disease activity (M/HDA) while on conventional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (cDMARDs).
Methods: Biologic-naïve RA patients on cDMARD were selected in a US national observational cohort (Corrona RA registry) between 1/1/2006 and 1/31/2016. All patients selected were in M/HDA based on the Clinical Disease Activity index (CDAI >10) and had ≥ 1 year of follow-up and no change in the treatment during 3 months prior to the index date. Index date was the earliest visit the patient met the inclusion criteria. Patients were excluded if their age of RA onset was <18y, or they were exposed to biologics prior to the index date. Patients’ demographics, RA disease characteristics, and biologic initiation patterns were described. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were compared, using descriptive statistics, between patients who initiated a biologic during the follow-up vs. those who did not.
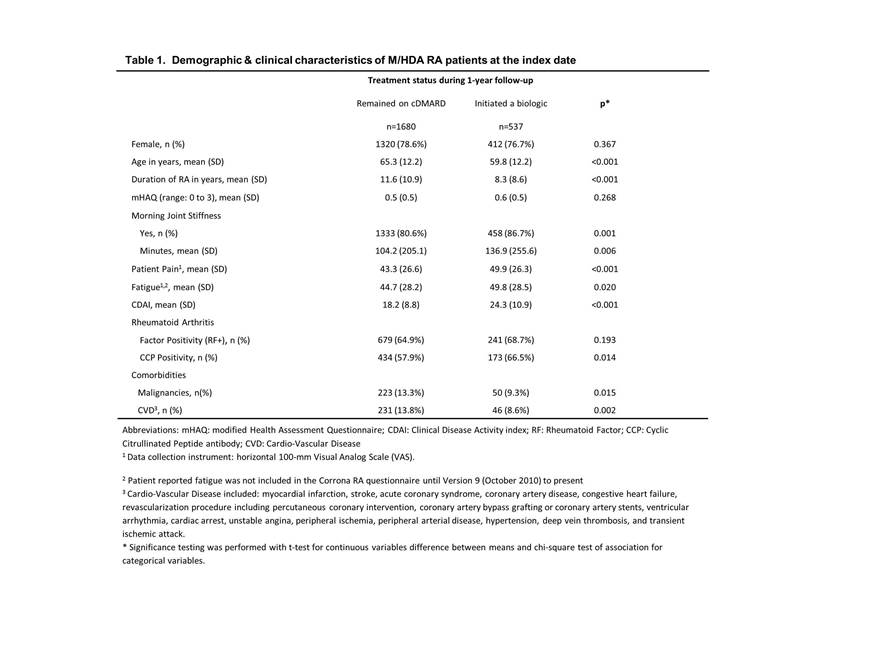
Results: Out of 11874 cDMARD users in Corrona, 3345 (28%) were in M/HDA and 2217 (19%) met the study inclusion/exclusion criteria. Most patients were female (78%), white (88%) and 64 years of age on average [SD=12]. The mean duration of RA was about 11 years [SD=10] with mean CDAI score of 20 [SD=10] at the index date. About a quarter (n=537) of the patients initiated a biologic, on average, 4 months [SD=3] after the index date. Of biologic initiators, most (85%) received a TNF-inhibitor as their first biologic. There were significant differences between the biologic initiators and non-initiators in baseline demographic and clinical characteristics (Table 1). The initiators were younger, had shorter duration of RA, had fewer comorbidities, but had higher CDAI scores and a higher proportion reported morning joint stiffness. Other RA disease baseline characteristics indicated more severe RA for the initiator group (Table 1). Most (92%) of these patients had M/HDA at the time of the biologic initiation. Among those who did not initiate a biologic, two-thirds remained on their index cDMARD therapy. Of the non-initiators, 11% had unknown disease activity status during the follow-up; among those who had disease activity reported, 53% had achieved LDA and 16% had achieved remission on at least 1 visit during the follow-up; 32% remained in M/HDA.
Conclusion: A minority (24%) of cDMARD users in M/HDA initiated a biologic therapy during the 1 year follow-up. Factors associated with biologic initiation were younger age, shorter duration of RA, less cancer and cardiovascular disease, more severe RA at baseline and higher disease activity during the follow-up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Boytsov N, Reed GW, Harrold LR, Zhang X, Gaich CL, Larmore CJ, Shan Y, Rebello S, Araujo AB. Biologic Initiation Patterns Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Moderate or High Disease Activity While Using Conventional Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biologic-initiation-patterns-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-moderate-or-high-disease-activity-while-using-conventional-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biologic-initiation-patterns-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-moderate-or-high-disease-activity-while-using-conventional-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs/