Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) require effective treatment across all symptoms. Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody which selectively neutralizes interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F. During BE ACTIVE (NCT02969525), a phase 2b dose-ranging study in pts with PsA, BKZ demonstrated improved peripheral joint, skin, and extra-articular outcomes over 48 weeks (wks).1 The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)2 is a validated instrument for evaluating disease activity and symptoms in pts with axial spondyloarthritis. We use the BASDAI to assess the effect of BKZ treatment on fatigue and pain in pts with PsA.
Methods: In this randomized controlled trial, pts received BKZ or placebo (PBO).1 This post hoc analysis focuses on BASDAI over 48 wks. BASDAI data were collected prospectively from all pts as an efficacy variable. We report BASDAI50 (a 50% improvement on baseline [BL] BASDAI score), and mean change from BL (CfB) in BASDAI question scores (higher scores denote worse symptoms), for all BASDAI questions, with a focus on Question 1 (Q1; fatigue) and Question 2 (Q2; neck/hip/back pain). We also report the percentage (%) of pts who had a CfB in BASDAI Q1 or Q2 scores of ≥2 points.3,4 Observed data are reported for the Full Analysis Set (FAS) in pt subsets with a baseline (BL) BASDAI score of ≥4, and ≥4 for all individual questions. Treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) rates are reported per 100 pt-years (PY) for the Safety Set (SS; pts who received ≥1 dose BKZ).
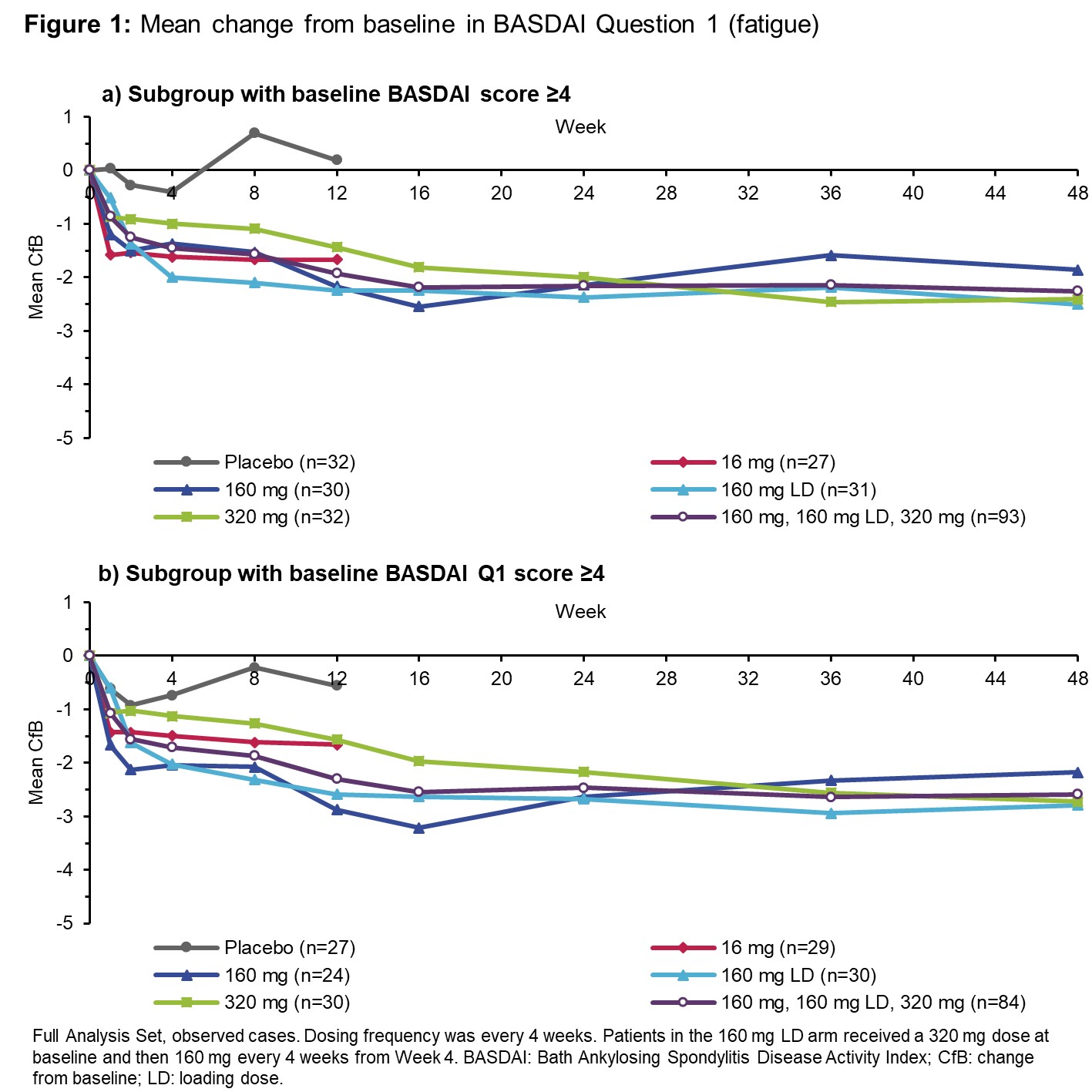
Results: 206 pts were randomized at BL (42 to PBO every 4 weeks [Q4W], 41 to each BKZ Q4W arm: 16 mg, 160 mg, 160 mg+320 mg loading dose [LD] and 320 mg). 152 pts had BASDAI ≥4 at BL (Table). 93 of these pts were in the 160–320 mg pool. Their mean (SD) BASDAI at BL was 6.20 (±1.42), and the BASDAI50 response rate was 43% (9% for PBO), and 56% at Wk 12 and Wk 48, respectively. 84 pts in the 160–320 mg pool scored ≥4 for BASDAI Q1 (mean at BL: 6.19 [±1.59]; Wk 48: 3.58 [±2.67], a mean CfB of −2.59). 87 pts in this BKZ pool scored ≥4 for BASDAI Q2 at BL (mean 6.47 [±1.66]; Wk 48: 3.49 [±2.56], a mean CfB of −2.99). Across all 160–320 mg doses, clear improvements in BASDAI Q1 and Q2 scores were seen by Wk 12, continuing to Wk 48. This was also shown for pts with BASDAI Q1 and Q2 scores ≥4 at BL (Figures 1 and 2).
For pts in the 160–320 mg pool with a BASDAI Q1 or Q2 score ≥4 at BL, 58–66% and 63–68% had a ≥2-point reduction in their Q1 and Q2 scores, respectively, across Wks 12, 24, and 48. For the same pts on PBO, 26% and 43% had a ≥2-point reduction in their Q1 and Q2 scores at Wk 12, respectively. TEAEs were reported in 74% of BKZ-treated pts (exposure-adjusted event rate [EAER]: 294/100 PY). Serious TEAEs were reported for 3.9% (EAER: 4.52/100 PY).
Conclusion: In this exploratory analysis, BKZ treatment was associated with improvements in BASDAI total and single question scores related to fatigue and neck, back and hip pain in pts with PsA.
References: 1. Ritchlin C. Lancet 2020;395:427–40; 2. Garrett S. J Rheumatol 1994;21:2286–91; 3. Reilly M. Rheumatol 2010;49:812–9; 4. Braun J. ARD 2006;65:316–20.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar A, Gossec L, Mease P, Coarse J, Edens H, de Peyrecave N, Assudani D, Ink B, Ritchlin C. Bimekizumab Treatment Is Associated with Improvements in Back Pain and Fatigue in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: 48-Week Results from a Phase 2b Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-is-associated-with-improvements-in-back-pain-and-fatigue-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-48-week-results-from-a-phase-2b-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-is-associated-with-improvements-in-back-pain-and-fatigue-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-48-week-results-from-a-phase-2b-study/