Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A. BKZ treatment has demonstrated superior efficacy in joints and skin versus placebo (PBO) at Week (Wk) 16 in the phase 3 BE OPTIMAL study in biologic DMARD (bDMARD)-naïve patients (pts) with active PsA.1 Wk 52 efficacy and safety data are presented here.
Methods: BE OPTIMAL (NCT03895203) comprised 16 wks double-blind, PBO-controlled, and 36 wks treatment-blind. bDMARD-naïve pts were eligible if they had adult-onset, active PsA meeting the Classification Criteria for PsA for ≥6 months, ≥3 tender and ≥3 swollen joints, and ≥1 active psoriatic lesion and/or history of psoriasis. Pts were randomized 3:2:1 subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg every 4 wks:PBO:reference arm (adalimumab [ADA] 40 mg every 2 wks). From Wk 16, PBO pts received BKZ 160 mg Q4W (PBO/BKZ). Missing data imputed using non-responder imputation (discrete) or multiple imputation (continuous).
Results: 821/852 (96.4%) pts completed Wk 16; 761 (89.3%) completed Wk 52. Baseline (BL) characteristics were generally balanced between groups (randomized set): mean age 48.7 years; BMI 29.2 kg/m2; time since diagnosis 5.9 years; 46.8% male; 49.9% had psoriasis affecting ≥3% body surface area (BSA).
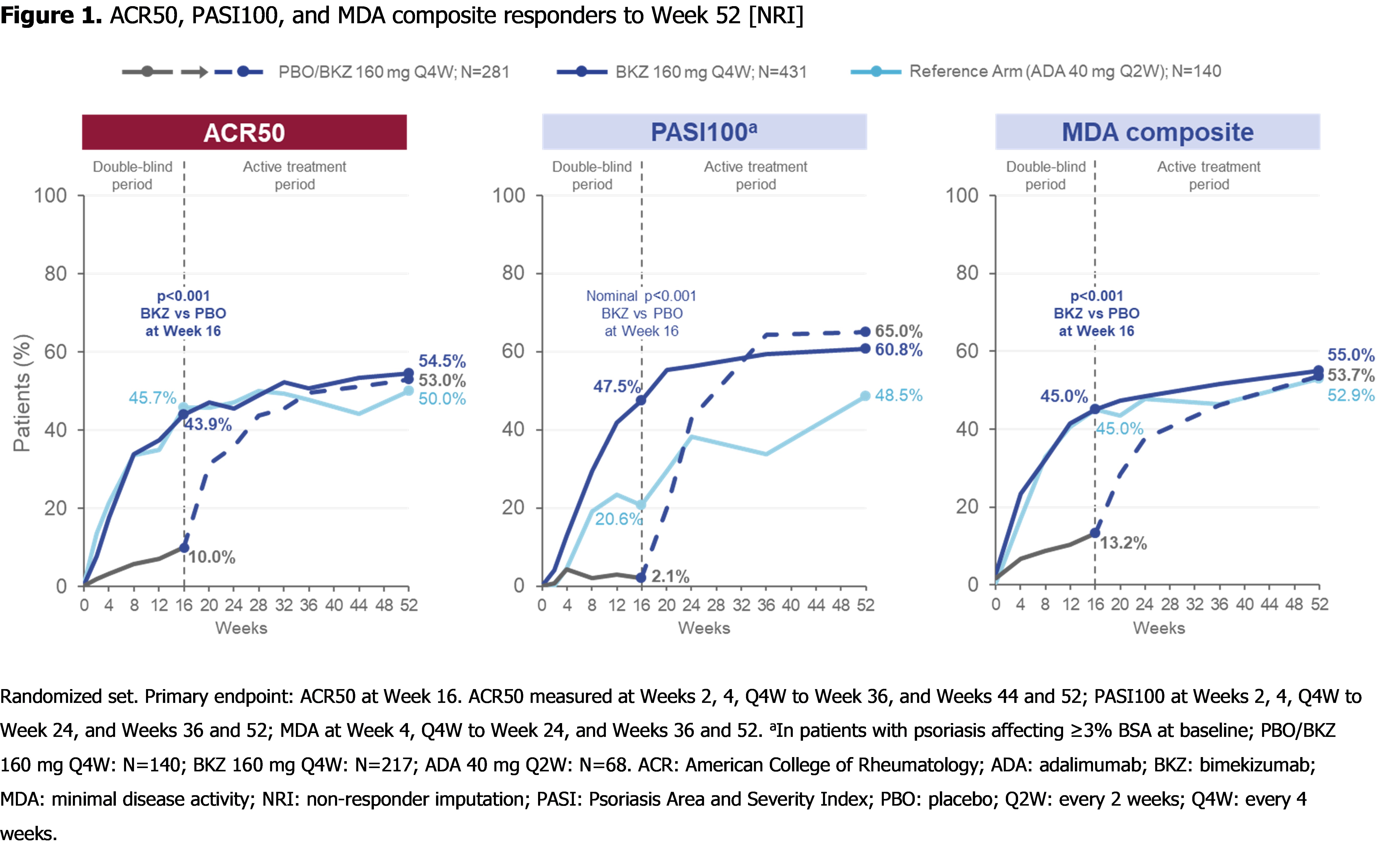
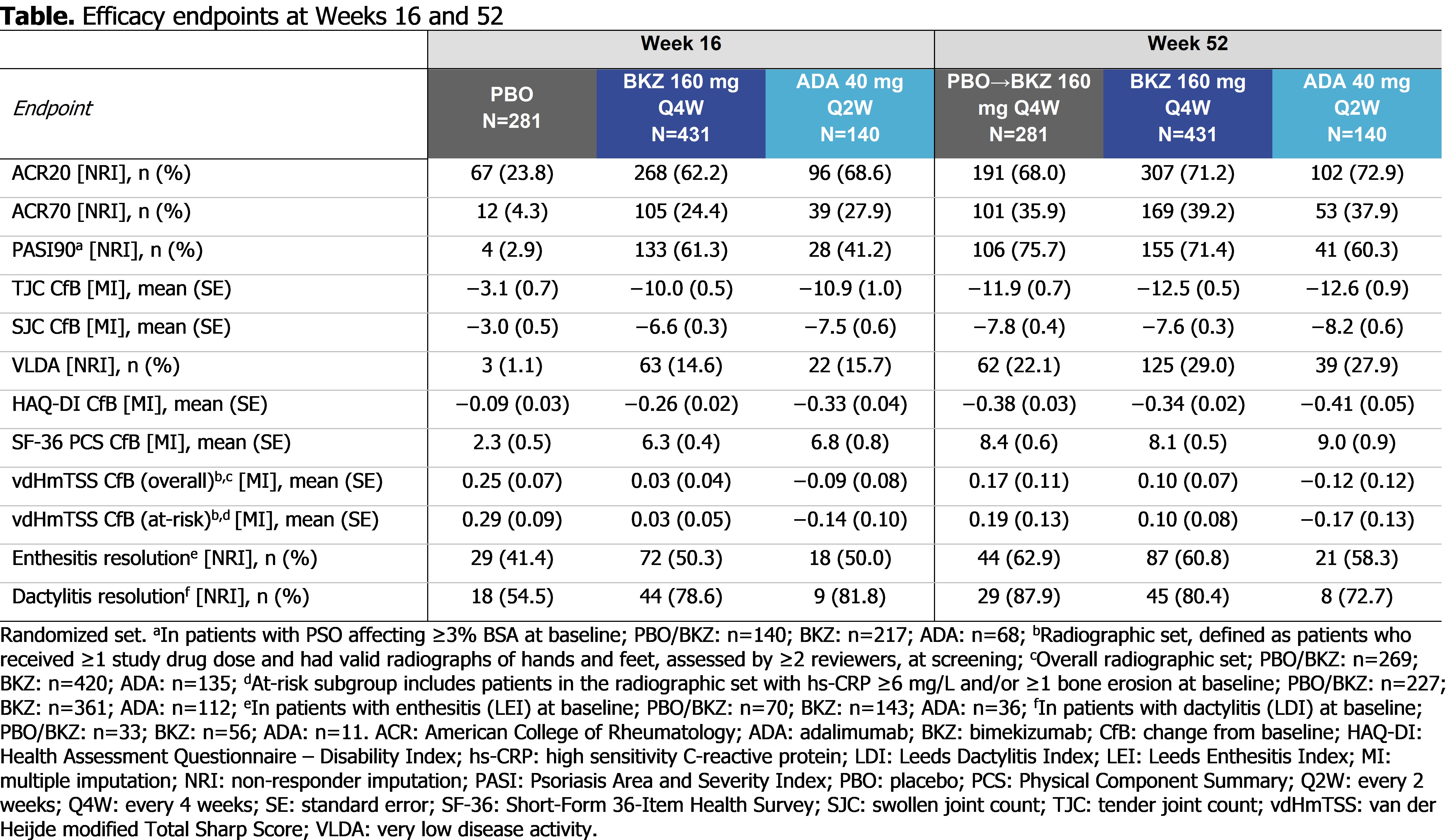
At Wk 52, pts achieving ACR50: 53.0% PBO/BKZ, 54.5% BKZ, 50.0% ADA; pts with BL psoriasis (≥3% BSA) achieving complete skin clearance (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index [PASI]100): 65.0% PBO/BKZ, 60.8% BKZ, 48.5% ADA; pts achieving minimal disease activity: 53.7% PBO/BKZ, 55.0% BKZ, 52.9% ADA (Figure 1). Clinical joint and skin efficacy responses continued to increase or were sustained from Wk 16 to Wk 52 on BKZ; pts who switched to BKZ at Wk 16 demonstrated improvements in efficacy outcomes to Wk 52 (Table).
Overall radiographic progression was minimal to Wk 52. At Wk 52, pts with no radiographic progression (van der Heijde modified Total Sharp Score change from baseline ≤0.5): 87.3% PBO/BKZ, 89.3% BKZ, 94.1% ADA (radiographic set; observed case). Cumulative probability of radiographic progression is presented in Figure 2.
To Wk 52, 555/702 (79.1%) pts had ≥1 treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) while receiving BKZ; 113/140 (80.7%) on ADA. The three most frequent TEAEs on BKZ: nasopharyngitis (BKZ: 12.0% pts; ADA 8.6% pts), upper respiratory tract infection (BKZ: 7.1%; ADA: 5.7%), and urinary tract infection (BKZ: 6.1%; ADA: 3.6%). Pts who discontinued the study due to a TEAE: 21 (3.0%) BKZ; 7 (5.0%) ADA. Candida infections (high level term) reported in 7.7% BKZ, 0.7% ADA pts. All were mild/moderate; none systemic. 1 case of oral candidiasis led to discontinuation. To Wk 52, 3 BKZ‑treated pts had malignancies excluding non-melanoma skin cancers, 4 had adjudicated major adverse cardiac events, and 2 had definite IBD (ulcerative colitis); 1 death reported (motorcycle accident). No uveitis events were reported.
Conclusion: BKZ treatment demonstrated clinically meaningful improvements in efficacy outcomes in bDMARD-naïve pts with active PsA at Wk 16, which were sustained or continued to improve to Wk 52. BKZ was well tolerated; no new safety signals observed.2
References:
1. McInnes IB. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:206–7; 2. Coates LC. Arthritis & Rheum 2022;10.1002/art.42280.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ritchlin C, Coates L, McInnes I, Mease P, Merola J, Tanaka Y, Asahina A, Gossec L, Gottlieb A, Thaci D, Ink B, Assudani D, Bajracharya R, Shende V, Coarse J, Landewé R. Bimekizumab Treatment in Biologic DMARD-Naïve Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: 52-Week Efficacy and Safety Results from a Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Active Reference Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-in-biologic-dmard-naive-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-52-week-efficacy-and-safety-results-from-a-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-active-reference-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-in-biologic-dmard-naive-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-52-week-efficacy-and-safety-results-from-a-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-active-reference-study/