Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: PsA has a substantial negative impact on patient (pt) health-related quality of life (HRQoL);1 symptom control, preventing structural damage, and normalizing physical and social function to maximize HRQoL are key treatment goals.2 Bimekizumab (BKZ), a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A, has demonstrated clinically relevant improvements in HRQoL measures to Week (Wk) 16 vs placebo (PBO) in pts with PsA in two phase 3 trials.3,4 In this study, the impact of BKZ treatment on HRQoL is reported up to 1 year.
Methods: The phase 3 BE OPTIMAL (NCT03895203) and BE COMPLETE (NCT03896581) trials, both with a 16-wk double-blind, PBO-controlled phase, assessed BKZ in pts with PsA who were biologic DMARD (bDMARD)-naïve or had intolerance or inadequate response to TNF-α inhibitors (TNFi‑IR), respectively. BE OPTIMAL pts were randomized 3:2:1 to subcutaneous (sc) BKZ 160 mg every 4 wks (Q4W), PBO, or reference (sc adalimumab 40 mg Q2W; data not reported). At Wk 16, PBO pts switched to BKZ (PBO/BKZ). BE COMPLETE pts were randomized 2:1 to sc BKZ 160 mg Q4W or PBO. Pts completing Wk 16 were eligible to enter an open‑label extension, BE VITAL (NCT04009499), when PBO pts switched to BKZ (PBO/BKZ). BE COMPLETE plus BE VITAL is referred to as ‘BE COMPLETE’ hereafter.
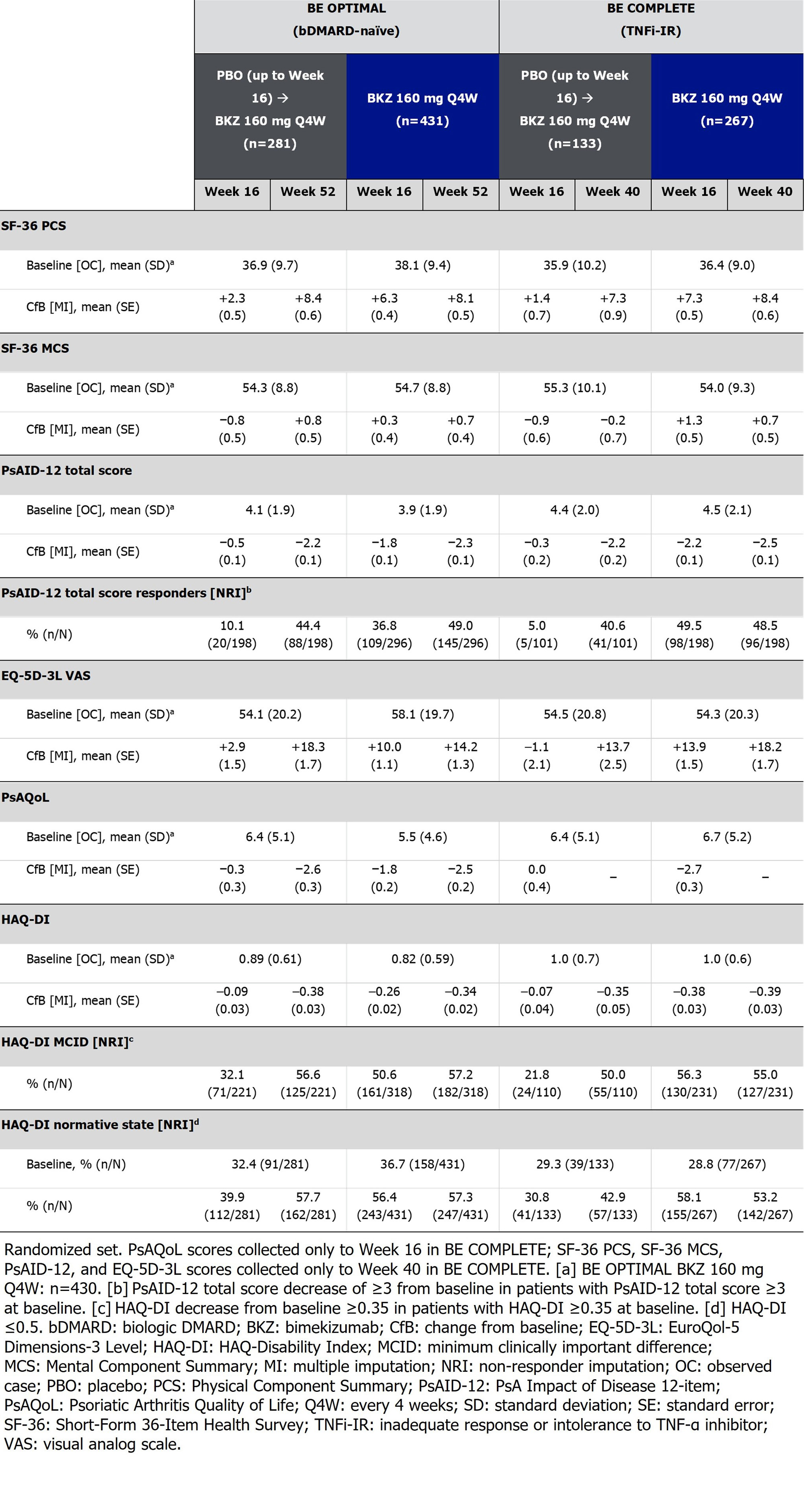
Endpoints reported for HRQoL, health status, and physical function included Short-Form 36-Item Health Survey (SF-36) Physical and Mental Component Summaries (PCS; MCS) and subscale norm-based scores; PsA Impact of Disease 12‑item (PsAID-12); EuroQol-5 Dimensions-3 Level Visual Analog Scale (EQ-5D-3L VAS); PsA Quality of Life (PsAQoL); HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI). BE COMPLETE outcomes were collected to Wk 40/52 as stated in the Table. Non-responder and multiple imputation (NRI; MI) were used for missing binary and continuous variables.
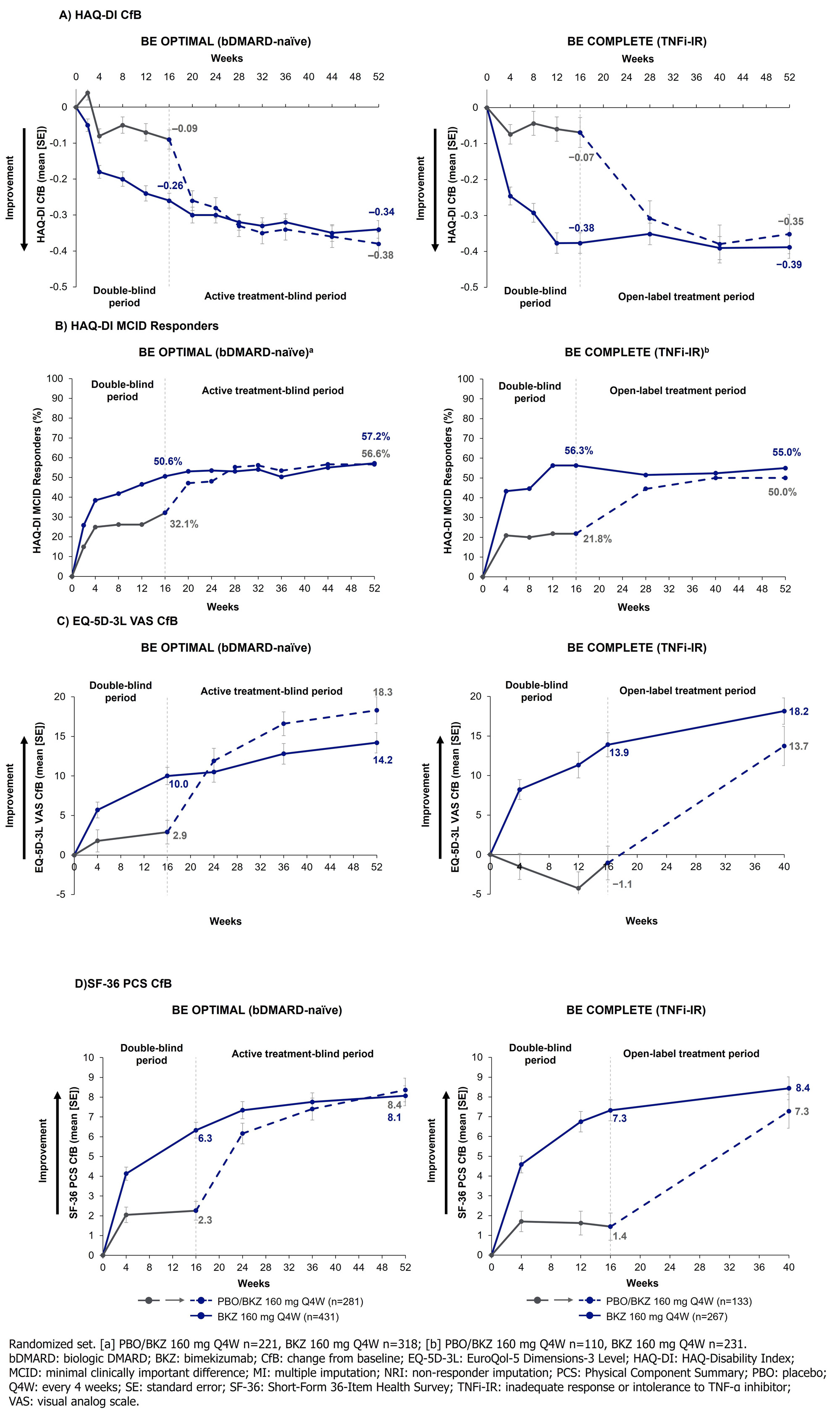
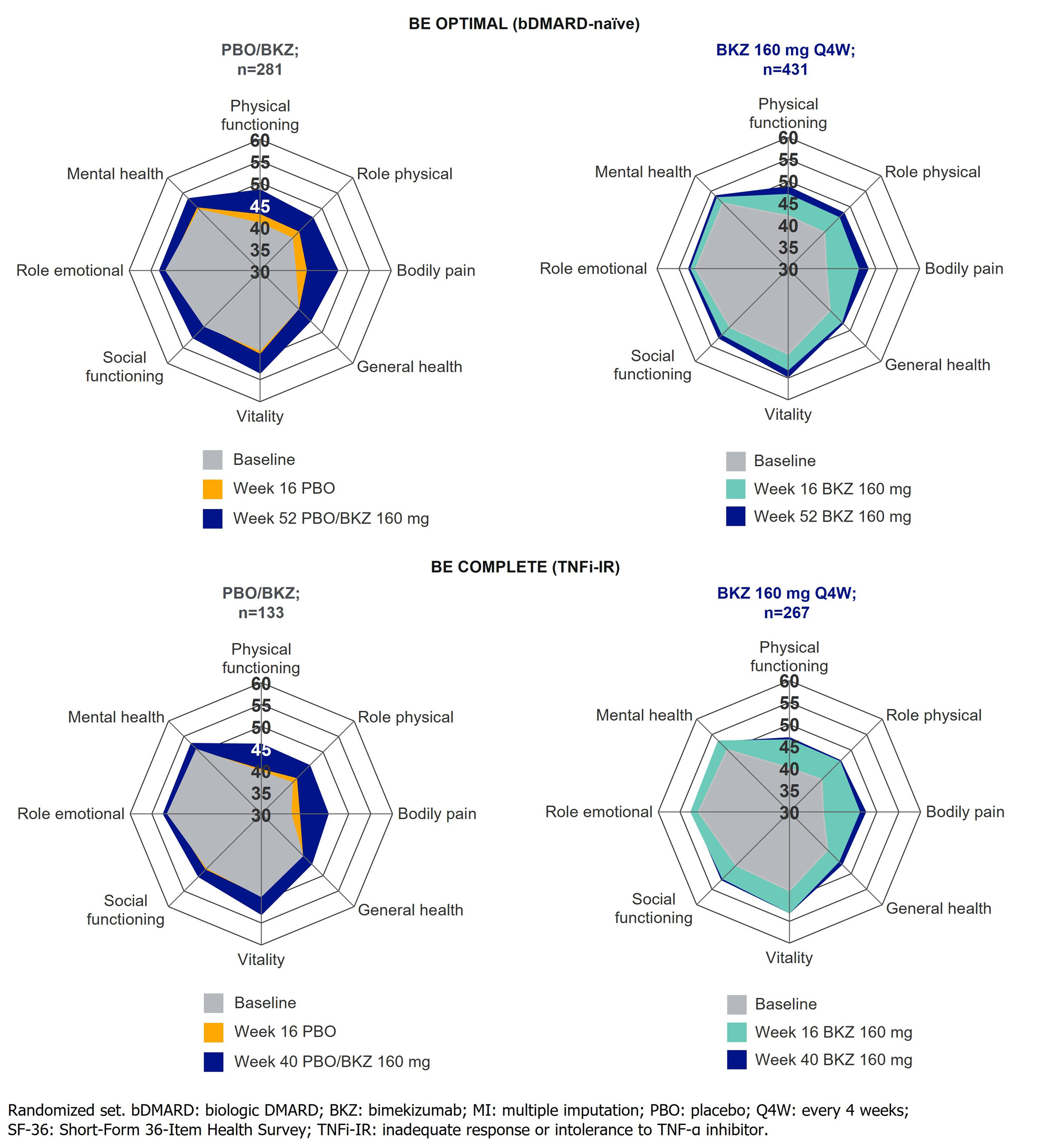
Results: Overall, 770/852 (90.4%) and 347/400 (86.8%) pts completed Wk 52 of BE OPTIMAL and BE COMPLETE. Across both trials, Wk 16 improvements in HRQoL, health status, and physical function were sustained to Wk 52 on BKZ (Table). PBO/BKZ pts achieved comparable improvements to BKZ-randomized pts by Wk 52/40, including PsAID-12 total score response (decrease from baseline ≥3; bDMARD-naïve/TNFi-IR BKZ: 49.0/48.5%, PBO/BKZ: 44.4/40.6%), HAQ-DI minimal clinically important difference (MCID; decrease from baseline ≥0.35; BKZ: 57.2/55.0%, PBO/BKZ: 56.6/50.0%; Figure 1), and reaching HAQ-DI normative state of ≤0.5 (BKZ: 57.3/53.2%, PBO/BKZ: 57.7/42.9%). SF-36 PCS improved to a greater extent at Wk 16 in BKZ vs PBO pts (Figure 1); responses were sustained to Wk 52 on BKZ. SF-36 physical functioning, role physical, and bodily pain subscales showed the most improvement over the other subscales (Figure 2). Similar improvement trends were seen in EQ-5D-3L VAS (Table; Figure 1).
Conclusion: Clinically meaningful improvements in measures of HRQoL, health status, and physical function were observed up to 1 year with BKZ treatment, irrespective of prior bDMARD use.
References:1.Gudu T. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2018;14:405–17; 2. Gossec L. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:700–12; 3.McInnes IB. Lancet 2023;401:25–37; 4. Merola JF. Lancet 2023;401:38–48.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gladman D, Gossec L, Husni M, Erik L, Gisondi P, Gottlieb A, Thaçi D, Ink B, Bajracharya R, Lambert J, Lyris N, Coarse J, Tillett W. Bimekizumab Impact on Health-Related Quality of Life and Physical Function in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis Who Were Biologic DMARD‑Naïve or Had Inadequate Response or Intolerance to TNF-α Inhibitors: 1-Year Results from Two Phase 3, Randomized Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-impact-on-health-related-quality-of-life-and-physical-function-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-who-were-biologic-dmard%e2%80%91naive-or-had-inadequate-response-or-intolerance-t/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-impact-on-health-related-quality-of-life-and-physical-function-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-who-were-biologic-dmard%e2%80%91naive-or-had-inadequate-response-or-intolerance-t/