Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: SLE – Treatment (0985–0989)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: No approved targeted therapies have been developed for cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE), a disfiguring autoimmune disease that severely impairs quality of life.1 BIIB059 is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds blood dendritic cell antigen 2 (BDCA2), a receptor uniquely expressed on plasmacytoid dendritic cells, leading to BDCA2 internalization and subsequent inhibition of inflammatory mediator production, most notably type I IFNs.2 LILAC (NCT02847598) was a 2-part, phase 2 study investigating the efficacy and safety of BIIB059. Part A enrolled SLE participants. Part B, presented here, is the largest interventional study to date in CLE participants.
Methods: To be eligible for enrollment, adults with histologically confirmed CLE must have had active CLE defined as a Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index-Activity (CLASI-A) score ≥8 despite prior use of or documented intolerance to topical CS and/or antimalarials and ≥1 lesion diagnostic of subacute CLE (CLASI-A erythema score ≥2) and/or chronic CLE (CLASI-A erythema score ≥2 and CLASI-Damage scarring score ≥1); all with or without systemic manifestations. Concomitant CLE/SLE therapy was allowed if doses were initiated ≥12 weeks and kept stable ≥4 weeks prior to randomization and throughout the treatment period; systemic CS doses could not exceed 15 mg/day of prednisone (or equivalent). BIIB059 (50, 150, 450 mg) or placebo was subcutaneously administered once every 4 weeks, with an additional dose at week 2, for 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was a multiple comparison procedure–modeling test of dose response in % change in CLASI-A score from baseline to week 16. Secondary endpoints included proportion of participants with a 50% improvement in CLASI-A score (CLASI-50 response rate) and ≥7-point reduction in CLASI-A score from baseline over time. Safety was assessed throughout the study.
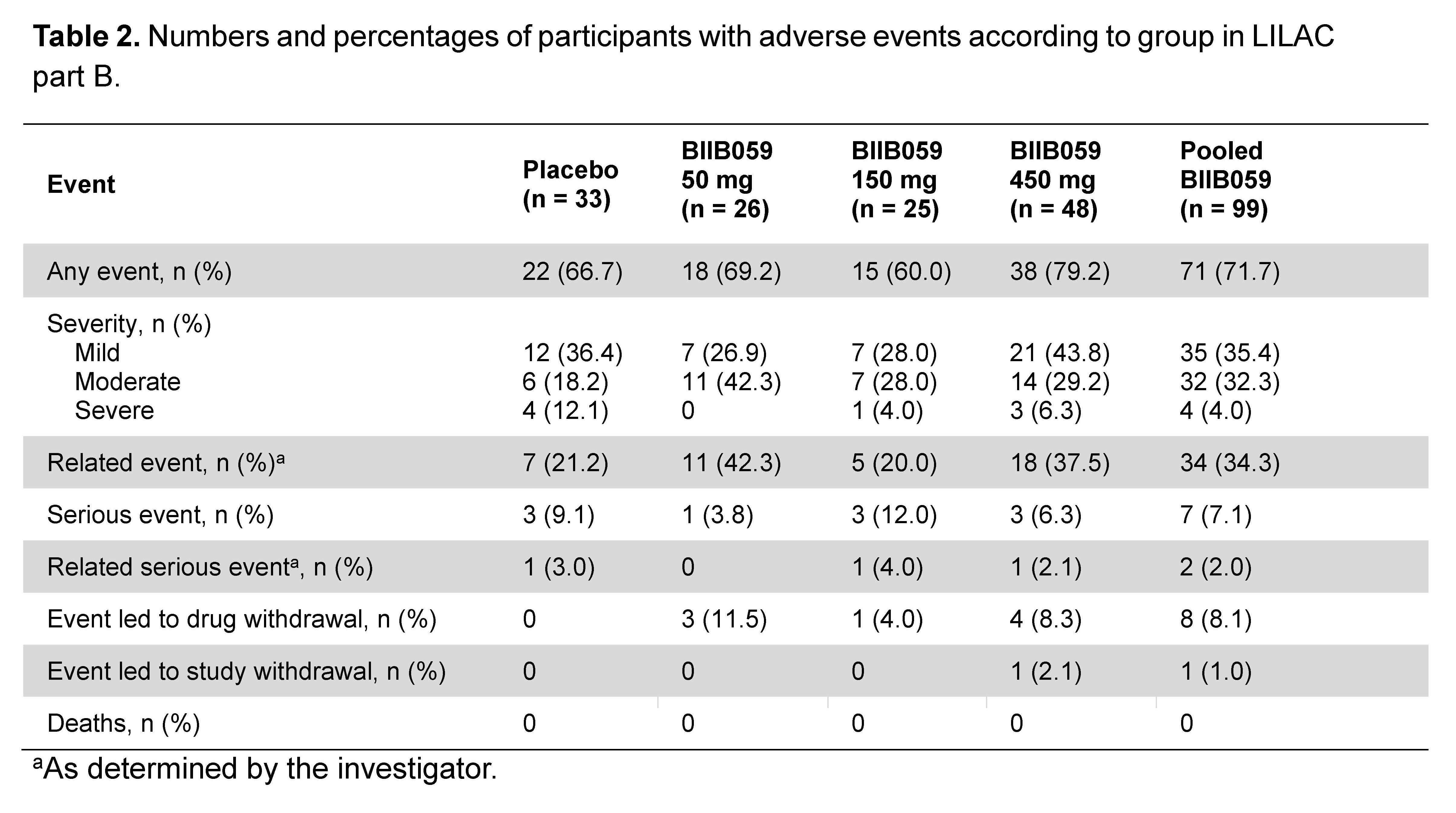
Results: Of 33, 26, 25, and 48 participants dosed in the placebo and BIIB059 50, 150, and 450 mg groups, respectively, 93.9%, 88.5%, 96.0%, and 87.5% completed treatment. The study met its primary endpoint, demonstrating a dose response (p=0.0005) and statistically significant differences in least squares mean % changes (SE) in CLASI-A score between the placebo vs. BIIB059-treated participants (Table 1). Meaningful clinical improvements in secondary skin-related efficacy endpoints were observed in the BIIB059 groups. AEs and serious AEs (SAEs) for the placebo and pooled BIIB059 groups occurred in 66.7% vs. 71.7% and 9.1% vs. 7.1%, respectively (Table 2). Three (3.0%) BIIB059 participants and no placebo participants had AEs of hypersensitivity. Herpes zoster meningitis was observed in 1 participant (BIIB059 50 mg) after study completion.
Conclusion: BIIB059 significantly reduced disease activity in CLE with an acceptable safety profile. Further development of BIIB059 for the treatment of CLE is warranted.
- Ogunsanya. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:52; 2. Pellerin. EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7:464
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Werth V, Furie R, Romero-Díaz J, Navarra S, Kalunian K, van Vollenhoven R, Nyberg F, Kaffenberger B, Sheikh S, Radunovic G, Huang X, Carroll H, Gaudreault F, Meyers A, Barbey C, Musselli C, Franchimont N. BIIB059, a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Blood Dendritic Cell Antigen 2 on Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells, Shows Dose-Related Efficacy in a Phase 2 Study in Participants with Active Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biib059-a-humanized-monoclonal-antibody-targeting-blood-dendritic-cell-antigen-2-on-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-shows-dose-related-efficacy-in-a-phase-2-study-in-participants-with-active-cutaneous/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biib059-a-humanized-monoclonal-antibody-targeting-blood-dendritic-cell-antigen-2-on-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-shows-dose-related-efficacy-in-a-phase-2-study-in-participants-with-active-cutaneous/