Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: BI 695501 is a proposed adalimumab biosimilar
currently in development and was evaluated for pharmacokinetic (PK) similarity to
both US-licensed and EU-approved reference products.
Methods: Healthy male
subjects aged 18 to 55 years (N = 327) were randomized to receive one dose of
either BI 695501 40 mg/0.8 mL, or US-licensed adalimumab or EU-approved adalimumab
40 mg/0.8 mL (NCT02045979). In each treatment group, 108 subjects received the
trial medication, which was administered by subcutaneous injection. Primary and
secondary PK endpoints included were total drug exposure as measured by the area
under the concentration–time curve (AUC) from time zero to infinity (AUC0-inf),
AUC from time zero to the last measurable concentration (AUC0-tz),
and maximum observed plasma concentration (Cmax), as well as several
time truncated AUCs. Statistical PK similarity of BI 695501 vs. US‑licensed
and vs. EU‑approved adalimumab was assessed by an ANCOVA model on the
log-transformed primary PK parameters (with fixed effects for treatment and
trial site as well as age and body weight as continuous covariates) for the
ratios of the geometric means for each treatment and compared with the pre-specified
boundaries of 80% to 125%. Safety and immunogenicity were also evaluated.
Results: Demographics and baseline characteristics
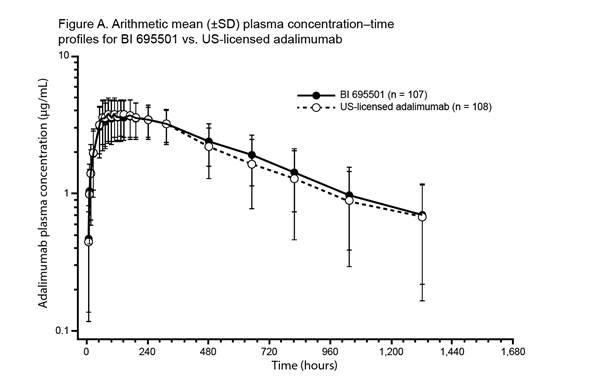
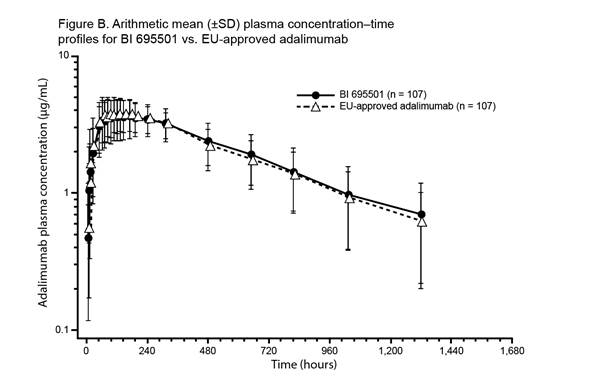
were similar between the three treatment groups. Mean plasma concentration–time
profiles for BI 695501, US-licensed and EU‑approved adalimumab were similar
over the entire profiling interval (See figures). Body weight at baseline was a
statistically significant predictor of Cmax and AUC (P < 0.0001
for all pairwise analyses). Subject age was a statistically significant
predictor of Cmax (P < 0.026 for all pairwise analyses)
but not for AUC (P > 0.149 for all pairwise analyses). Based on the
predefined hypothesis test, the primary and secondary endpoints were met. PK parameters
were similar for all comparisons of BI 695501 vs. US-licensed and vs.
EU-approved adalimumab. Single subcutaneous doses of BI 695501, US-licensed or
EU-approved adalimumab were generally well tolerated, and there were no notable
differences in safety between the three treatment groups. Immunogenicity was
also comparable and will be reported elsewhere.
Conclusion: BI 695501,
US-licensed, and EU‑approved adalimumab are bioequivalent and have
similar safety and tolerability profiles.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wynne C, Petkova M, Rombout F, Czeloth N, Altendorfer M, Lang B, Frapaise FX, Ellis-Pegler R. BI 695501, a Proposed Biosimilar for Adalimumab, Shows Bioequivalence to Adalimumab Reference Products in a Randomized, Double-Blind Phase I Trial in Healthy Subjects [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bi-695501-a-proposed-biosimilar-for-adalimumab-shows-bioequivalence-to-adalimumab-reference-products-in-a-randomized-double-blind-phase-i-trial-in-healthy-subjects/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bi-695501-a-proposed-biosimilar-for-adalimumab-shows-bioequivalence-to-adalimumab-reference-products-in-a-randomized-double-blind-phase-i-trial-in-healthy-subjects/