Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1412–1441) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II: SpA
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To compare drug survival, effectiveness and safety of anti-IL17A with anti-TNF drugs as first line biologic therapy in patients (pts) with PsA using real life data from the Czech biologics registry ATTRA. ATTRA is a prospective observational cohort study that captures more than 90% of PSA patients treated with b/tsDMARDs in the Czech Republic (CZ). Anti-IL17A bDMARDs have been reimbursed in CZ since Jan 2016 with the same label and restrictions as anti-TNFs.
Methods: PsA pts who initiated their first bDMARD in Jan 2016–Mar 2022 with at least one year of follow-up were included. By the type of first bDMARD exposure patients were dichotomized to anti-IL17A and anti-TNF cohorts. Effectiveness was assessed every 3-6 months by DAS28-ESR and DAPSA, physician global assessment of psoriasis (PGApso) on numerical rating scale (1-5), and by EQ-5D utility. Incidence of reported AEs and SAEs per 1000 patient-years (p-yrs) was calculated. Propensity score (PS) matching was used to account for differences in baseline characteristics. Drug survival was visualized using Kaplan-Meier curves, and Cox proportional hazards models were used to calculate adjusted Hazard Ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for risk of discontinuing therapy.
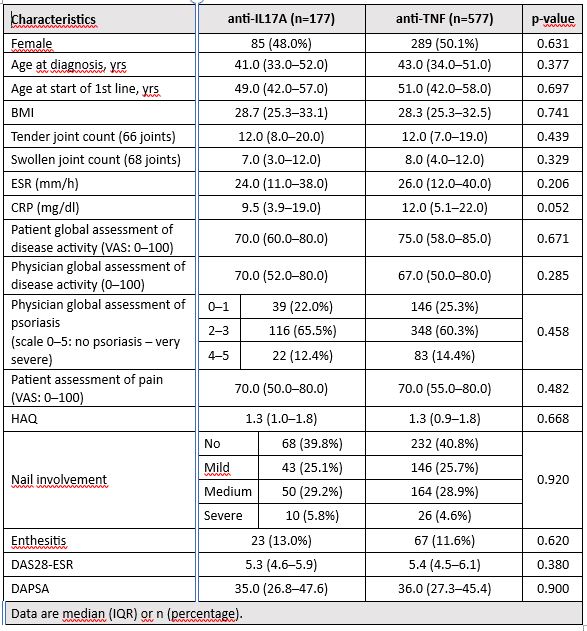
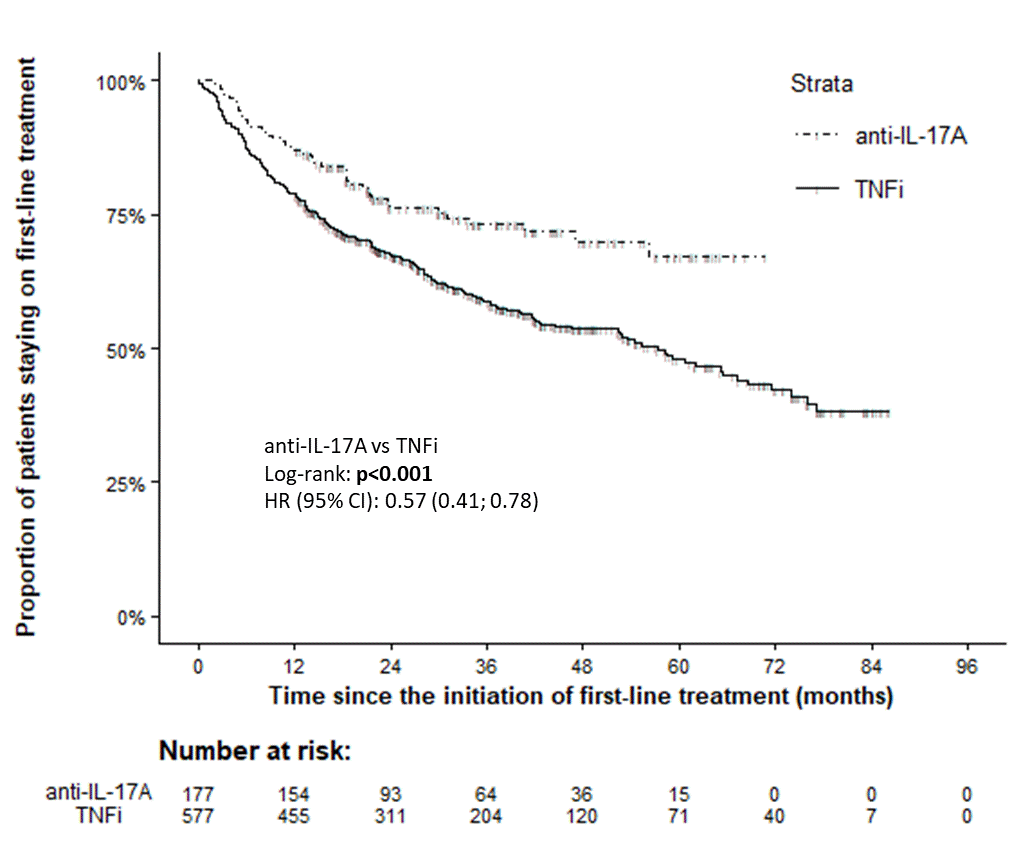
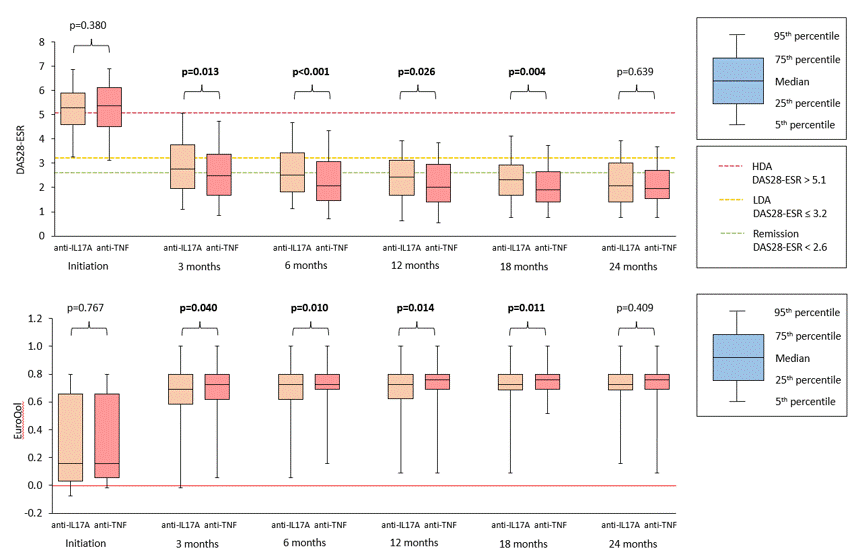
Results: 994 PsA pts started first-line anti-IL-17A (n=192) or anti-TNF (n= 802) therapy within period Jan 2016–Mar 2022, and 178 and 719 resp. had non-missing values for the outcomes of interest. Important baseline characteristics were similar between anti-IL17A and anti-TNF cohorts save for swollen joint counts (SJC), and after PS matching (using logistic model with 1 covariate: 68 SJC, matching ratio 1:4, caliper 0.1) 177 pts on anti-IL17A and 577 on anti-TNF were PS-matched and further analyzed. Baseline characteristics of PS-matched cohorts are in table 1. Drug retention on anti-IL7A was significantly better than on anti-TNF drugs with HR (95% CI) 0.57 (0.41; 0.78), see fig. 1. More pts on anti-IL7A discontinued therapy because of primary failure (31% vs 16%), but less of them because of adverse events (9% vs 17%) or other unspecified reasons (13% vs 21%). In pts remaining on first line therapy, mean levels of DAS28-ESR and DAPSA were significantly lower and of utility EQ-5D significantly higher at each time point since month(M)3 until M18 after start of anti-TNF compared with anti-IL-17A therapy (Fig. 2). Skin involvement assessed by PGApso was significantly better in anti-IL17A treated pts at M3 and M12. Incidence of AEs and SAEs was lower in anti-17A than in anti-TNF treated group (93 vs 168/1000 p-yrs, p< 0.001; and 7 vs 18 /1000 p-yrs, p=0.079, resp.).
Conclusion: We have observed better drug retention on anti-IL17A compared to anti-TNF therapy despite its inferior effect on composite joint indexes and quality of life in pts with PsA. This discrepancy may be explained either by superior safety, tolerability, and effectiveness of anti-IL17A on skin involvement, limited possibility to switch between anti-L17A drugs, or lower confidence of physicians to switch from anti-IL17A to anti-TNF than vice versa.
Acknowledgements: Supported by project 00023728 of Ministry of Health, CZ.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zavada J, Baranová J, Pavelka K, Vencovsky J, Horak P, Klementová L, Senolt L. Better Drug Retention on anti-IL17A Compared to Anti-TNF Therapy Despite Its Inferior Effect on Composite Joint Indexes and Quality of Life in Patients with PsA–analysis from the Czech Biologics Registry ATTRA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/better-drug-retention-on-anti-il17a-compared-to-anti-tnf-therapy-despite-its-inferior-effect-on-composite-joint-indexes-and-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-psa-analysis-from-the-czech-biologi/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/better-drug-retention-on-anti-il17a-compared-to-anti-tnf-therapy-despite-its-inferior-effect-on-composite-joint-indexes-and-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-psa-analysis-from-the-czech-biologi/