Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
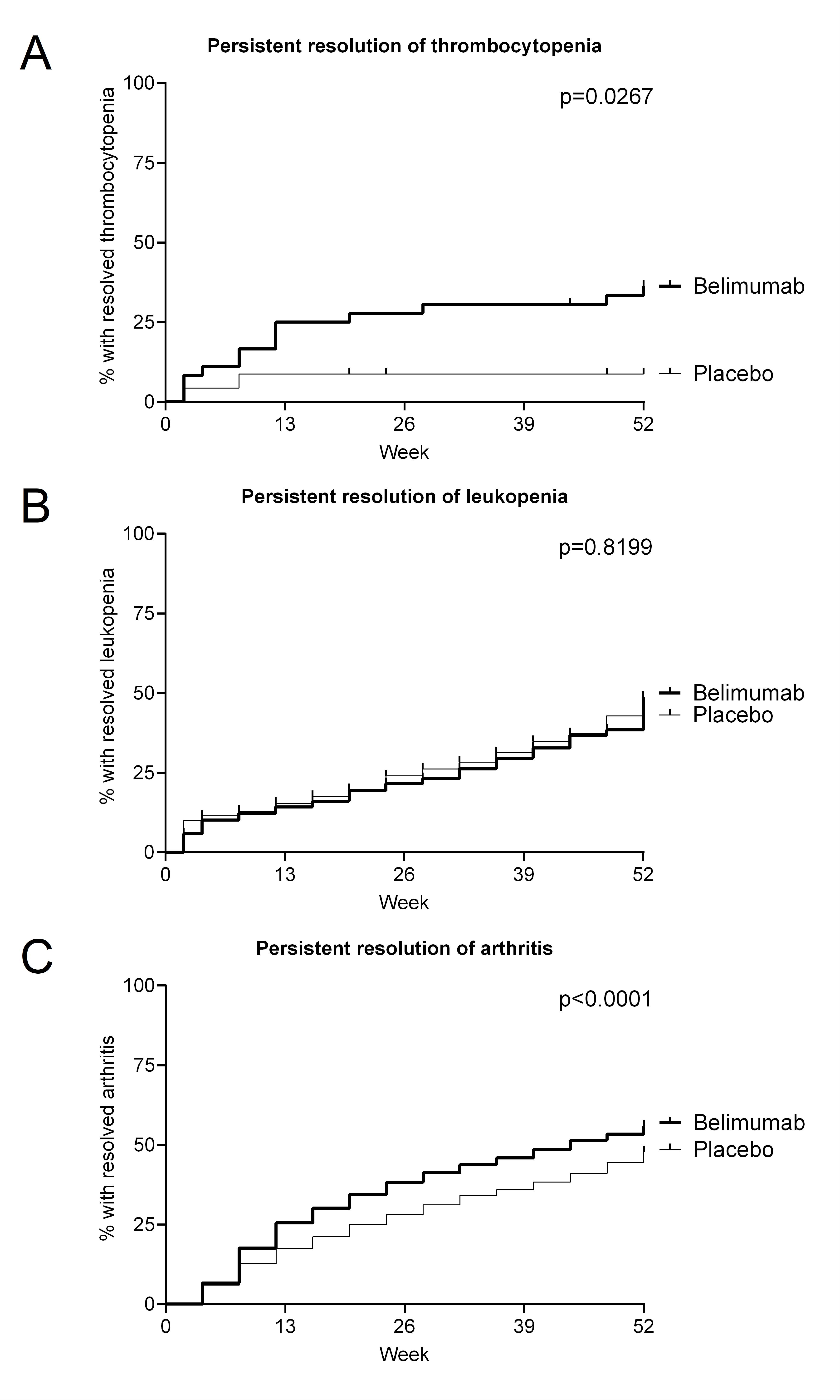
Background/Purpose: Belimumab has well-established efficacy in improving overall SLE disease activity and in preventing flares and organ damage. In clinical routine, however, the primary goal often is resolution of SLE activity in specific organ systems. For musculoskeletal manifestations, published data show efficacy, while belimumab efficacy in hematological manifestations remains unclear. We therefore investigated the efficacy of belimumab in resolving thrombocytopenia and leukopenia in patients with SLE and compared this to belimumab efficacy in lupus arthritis.
Methods: Anonymized data on musculoskeletal and hematological parameters from the five large belimumab randomized controlled clinical trials BLISS-52 (NCT00424476), BLISS-76 (NCT00410384), BLISS-NEA (NCT01345253), BLISS-SC (NCT01484496), and EMBRACE (NCT01632241), were provided by GSK based on a Data Sharing Agreement from 6th November 2019. These datasets included 1,869 patients treated with an approved dose of belimumab (10 mg /kg i.v. days 0, 14, 28, and every 4 weeks, or 200 mg s.c. weekly) and 1,217 patients on placebo, all on top of standard of care. For each manifestation under investigation, we selected patients with activity at baseline (thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, or, in absence of joint counts, lupus arthritis BILAG A, B, or C) and compared sustained resolution of symptoms (defined as normal cell counts or absence of arthritis by BILAG, i.e. BILAG D from the time of resolution through the end of one year) by means of Log-rank tests.
Results: At baseline, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and lupus arthritis were present in 39, 346, and 1,427 belimumab patients, and 25, 203, and 956 placebo patients, respectively. Thrombocytopenia resolved more quickly (Figure 1A), starting from 2 weeks of therapy, and in a higher proportion of patients under belimumab (p=0.0267), with one third (13/39) of the belimumab and 8% (2/25) of the placebo patients reaching persistent resolution. In contrast, there was no separation between belimumab and placebo regarding resolution of leukopenia (Figure 1B). As expected, a significant (p < 0.0001) effect of belimumab on lupus arthritis was seen, with separation of the belimumab and placebo lines starting as early as 8 weeks of treatment (Figure 1C). Lupus arthritis showed sustained resolution in 55.9% (797/1,427) of the belimumab-treated and 47.8% (457/956) of the placebo-treated patients.
Conclusion: This post-hoc analysis of complete data from five large belimumab phase 3 RCTs for the first time shows a clear effect of belimumab on thrombocytopenia. Belimumab was superior to placebo in resolving lupus arthritis, with separation observed from 8 weeks on treatment. These data further substantiate the role of belimumab in lupus arthritis and provide evidence for efficacy in lupus thrombocytopenia, but not leukopenia.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leuchten N, Parodis I, Brinks R, Aringer M. Belimumab Induces Early and Sustained Resolution of Lupus Thrombocytopenia and Lupus Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-induces-early-and-sustained-resolution-of-lupus-thrombocytopenia-and-lupus-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-induces-early-and-sustained-resolution-of-lupus-thrombocytopenia-and-lupus-arthritis/