Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
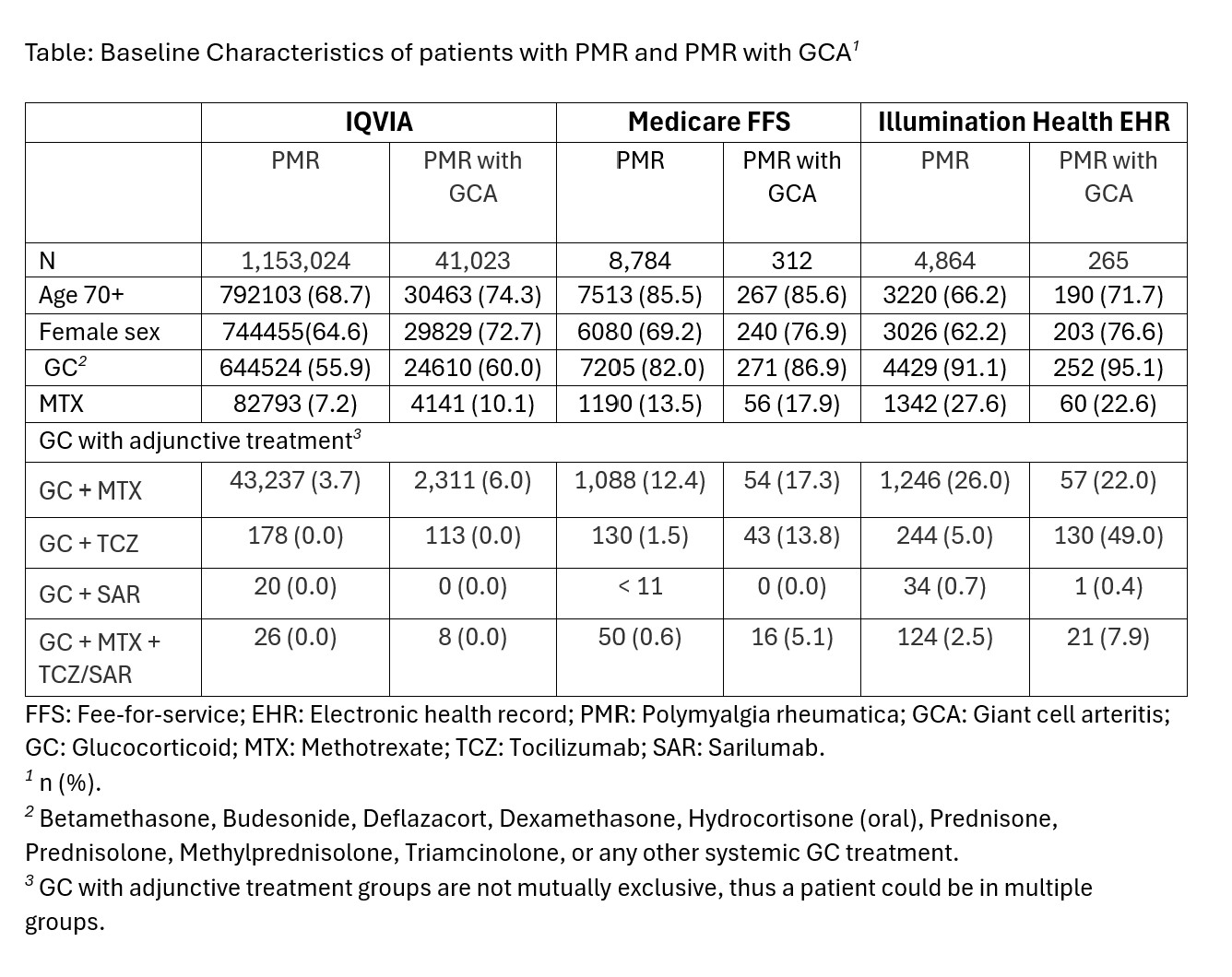
Background/Purpose: Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic condition that affects approximately 800,000 people in the U.S., occurring almost exclusively after age 50. Moreover, many patients with PMR also have associated giant cell arteritis (GCA), potentially leading to additional complications. We conducted a baseline evaluation of electronic health records (EHR) and claims data to examine PMR prevalence and glucocorticoid (GC) prescribing patterns.
Methods: We queried the IQVIA open claims database from 1/1/2015-12/31/2021, claims data (Medicare fee-for-service [FFS] from the 100% sample of Medicare beneficiaries) from 1/1/2011-12/31/2021, and community rheumatology EHR data from the Excellence Network in Rheumatology (ENRGY) from 1/1/2014-12/31/2021. The different study identification periods allowed for at least 2 years of follow-up based on the limitations of the individual datasets. PMR and PMR with GCA were defined as ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM codes 725 or M35.3 (PMR) and 446.5 or M31.5 (PMR with GCA), with any PMR with GCA diagnosis placing the patient in the PMR with GCA cohort. Drug use was defined as any oral GC use, Methotrexate (MTX), Tocilizumab (TCZ), Sarilumab (SAR), or combination (GC + MTX, GC+TCZ, GC+SAR, GC+MTX+(TCZ or SAR)).
Results: Across all three data sources disease distribution for PMR with GCA cohort was greatest in those over 70 years old compared to other age categories. The data consistently demonstrated that more women than men were diagnosed with PMR and PMR with GCA (Table). The prevalence of PMR and PMR with GCA was consistent throughout the 3 databases: PMR with GCA IQVIA 3% (41,023/1,153,024), U.S. Medicare 3% (312/8,784), and EHR 5% (265/4,864). Methotrexate was utilized by 7.2%, 13.5%, and 27.6% of patients with PMR in IQVIA, FFS, and EHR data, and 10.1%, 17.9%, and 22.6% of patients with PMR with GCA, respectively. Across the 3 sources we saw low levels of adjunctive treatment with methotrexate plus sarilumab, tocilizumab, or combination therapy.
Conclusion: Steroid sparing agents (e.g., methotrexate; sarilumab and tocilizumab for GCA) were underutilized in this cohort. However, long-term use of GCs can lead to negative health outcomes. Surveying health professionals with the gathered data and identifying educational needs can help with treatment optimization for PMR and PMR with GCA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stradford L, Venkatachalam S, Gavigan K, Degrassi A, Holladay E, xie F, Su Y, Daigle S, Curtis J. Baseline Evaluation of Diagnoses and Prescribing Patterns in Polymyalgia Rheumatica [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-evaluation-of-diagnoses-and-prescribing-patterns-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-evaluation-of-diagnoses-and-prescribing-patterns-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica/