Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a high-affinity monoclonal antibody that selectively targets interleukin (IL)-17A, has demonstrated efficacy in treating psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in Phase 3/4 clinical trials (Mease PJ et al. 2017; Nash P et al. 2017; Smolen JS et al. 2020). Here, we present interim data at baseline, Week (W) 4, and W12 in patients with active PsA treated with IXE or an IL 23p19 inhibitor (IL-23i) who enrolled in the prospective site-based Psoriatic Arthritis Real-World Study in US (PARTUS).
Methods: PARTUS is a non-interventional observational study enrolling adult patients with active PsA (clinical Disease Activity Index for PsA [cDAPSA] >4), who meet CASPAR criteria, and are initiating IXE or an IL-23i, guselkumab (GUS) or risankizumab (RZB), in accordance with the FDA labeling in a US clinical setting. The primary objective is to assess the real-world effectiveness in patients with PsA treated with IXE. This pre-specified interim analysis was carried out when approximately 50 patients treated with IXE completed W12. Disease activity (as measured by the cDAPSA), remission of disease activity (as measured by the proportion of patients achieving cDAPSA ≤4), low disease activity (as measured by the proportion of patients achieving cDAPSA ≤13, in patients with cDAPSA score >13 at baseline), and health-related quality of life (as measured by the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease [PsAID-12] score) were evaluated at W4 and W12. Descriptive statistics on observed data are presented. Mean and standard deviations (SD) are reported for continuous variables, while counts and percentages are reported for categorical variables.
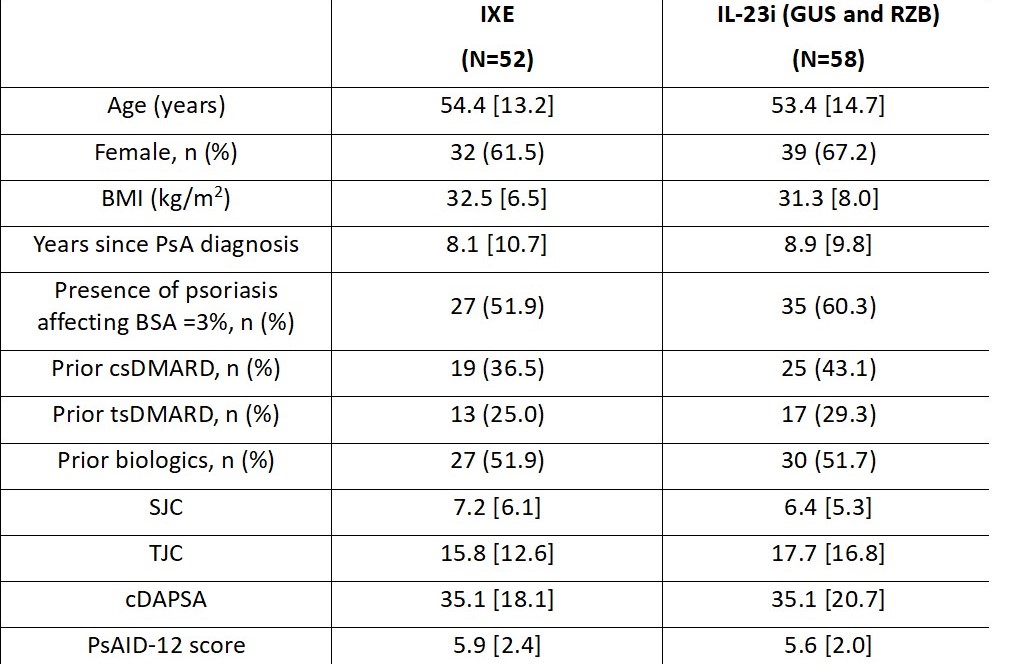
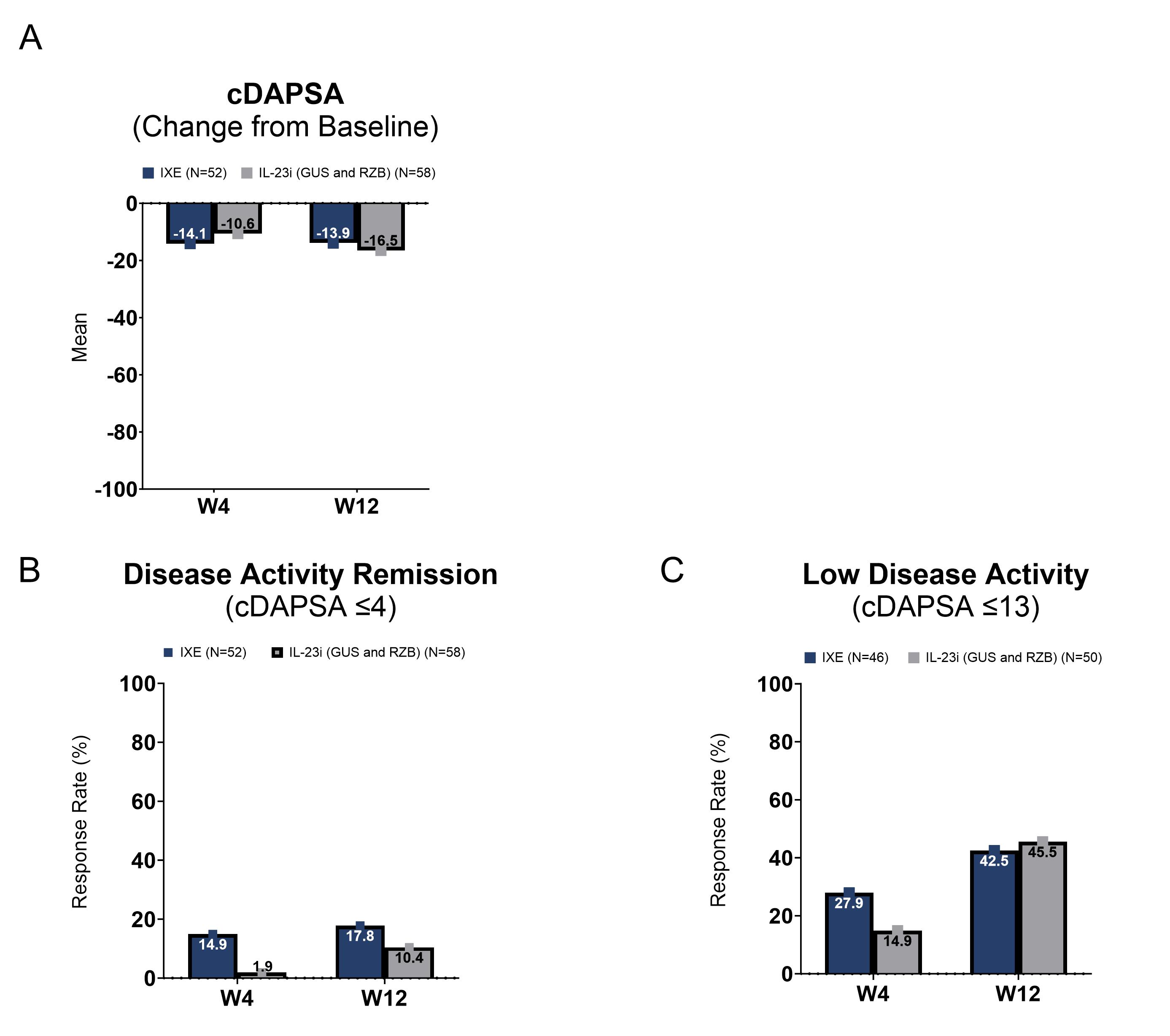
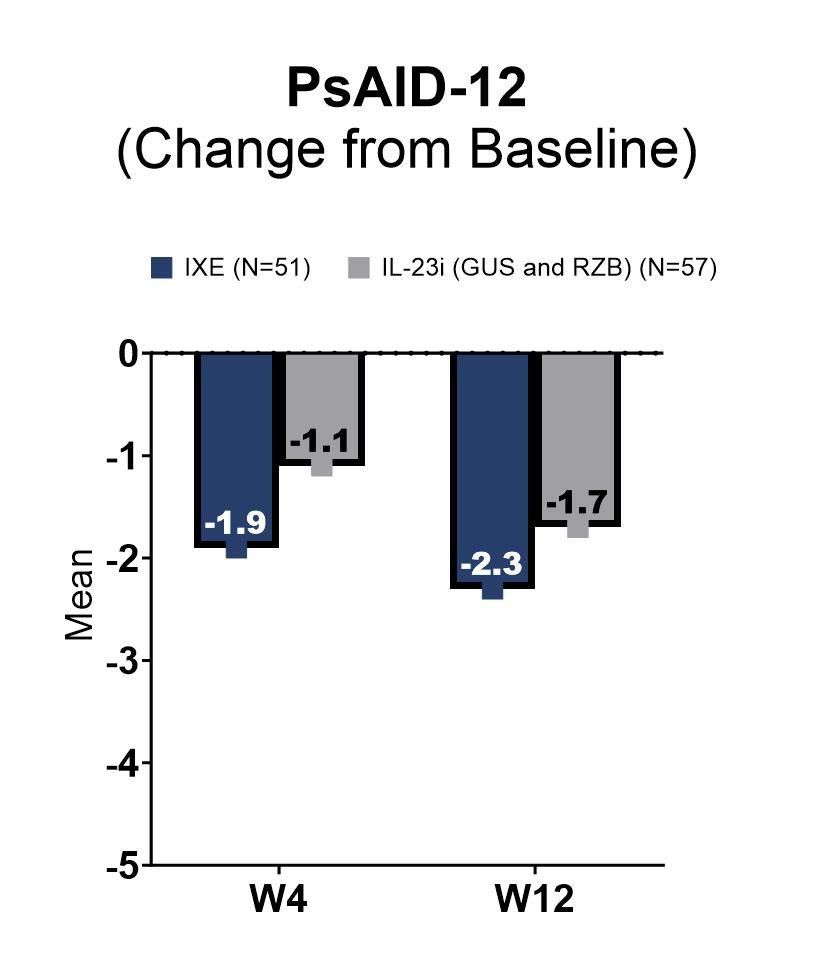
Results: At the time of this interim analysis, 52 patients in the IXE cohort and 58 patients in the IL-23i cohort completed W12. Baseline characteristics were balanced between the two cohorts of patients (Table 1). At W4, the mean (SD) change from baseline in the cDAPSA score was -14.1 (15.9) in the IXE cohort and -10.6 (18.3) in the IL-23i cohort. At W12, the mean (SD) change from baseline in the cDAPSA score was -13.9 (18.2) in the IXE cohort and -16.5 (22.4) in the IL-23i cohort (Figure 1A). At W4, the proportion of patients achieving remission of disease activity (cDAPSA ≤4) and low disease activity (cDAPSA ≤13) were 14.9% (n/Nx=7/47) and 27.9% (n/Nx=12/43) in the IXE cohort and 1.9% (n/Nx=1/53) and 14.9% (n/Nx=7/47) in the IL-23i cohort, respectively. These proportions increased by W12 in both cohorts of patients (Figure 1B, 1C). At W4, the mean (SD) change from baseline in the PsAID-12 score was -1.9 (2.2) in the IXE cohort and -1.1 (1.9) in the IL-23i cohort. Further improvements were reported by W12 in both cohorts of patients (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This interim analysis of the observational study PARTUS showed that IXE-treated patients with active PsA achieved early improvements by W4 in both disease activity and health-related quality of life with almost one-third of patients in low disease activity. Further improvements were observed by W12. Trends in improvement were also observed in the IL-23i-treated patients. The final results are pending study completion.
Note: For Figures 1A and 1B, the total number of patients at W4 and W12, respectively, was 47 and 45 in the IXE cohort and 53 and 48 in the IL_23i (GUS and RZB) cohort. For Figure 1C, the total number of patients at W4 and W12, respectively, was 43 and 40 in the IXE cohort and 47 and 44 in the IL_23i (GUS and RZB) cohort.
Abbreviations: cDAPSA, clinical Disease Activity Index for PsA; GUS, guselkumab; IL_23i, interleukin 23p19 inhibitor; IXE, ixekizumab; N, number of patients in each cohort; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; RZB, risankizumab; SD, standard deviation; W, week.
Note: PsAID_12 score ranges from 0 to 10, where 10 represents the worst health score.
Note: The total number of patients at W4 and W12, respectively, was 46 and 44 in the IXE cohort and 52 and 47 in the IL_23i (GUS and RZB) cohort.
Abbreviations: GUS, guselkumab; IL_23i, interleukin 23p19 inhibitor; IXE, ixekizumab; N, number of patients in each cohort; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; PsAID_12, Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease; RZB, risankizumab; W, week.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
OELKE K, Edson Heredia E, Ross S, Lisse J, Pustizzi J, Sheikhi Mehrabadi A, Bello N, Murphy F, Singla S, Raychaudhuri S. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Ixekizumab or Interleukin-23 Inhibitors and Interim Effectiveness Results from an Observational Study in the US [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-characteristics-of-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ixekizumab-or-interleukin-23-inhibitors-and-interim-effectiveness-results-from-an-observational-study-in-the-us/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-characteristics-of-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ixekizumab-or-interleukin-23-inhibitors-and-interim-effectiveness-results-from-an-observational-study-in-the-us/