Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Deucravacitinib (DEUC) is a novel, oral, selective TYK2 inhibitor with a unique allosteric mechanism of action that has demonstrated efficacy in patients with psoriasis1 and PsA.2 TYK2 mediates signaling of select immune cytokines, eg, IL-23, IL-12, and Type I IFN, whereas the related Janus kinases (JAK) 1/2/3 mediate signaling of a wider array of cytokines and mediators involved in inflammatory, developmental, metabolic, and hematopoietic pathways. DEUC reduced inflammatory markers associated with skin and joint manifestations but did not result in laboratory abnormalities associated with inhibition of JAK 1/2/3 in a PsA trial.3 The objective of this study was to identify baseline biomarkers that predict response to DEUC in patients with PsA in the phase 2 trial.
Methods: The double-blind phase 2 trial (NCT03881059) enrolled 203 patients with PsA randomized 1:1:1 to placebo (PBO), DEUC 6 mg once daily (QD), or 12 mg QD.2 Molecular profiling of serum samples collected at baseline and throughout the study were performed by immunoassays. Clinical response at week 16 was measured by ≥ 20% improvement from baseline in ACR Improvement Criteria (ACR 20) and ≥ 75% improvement from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 75) scores.
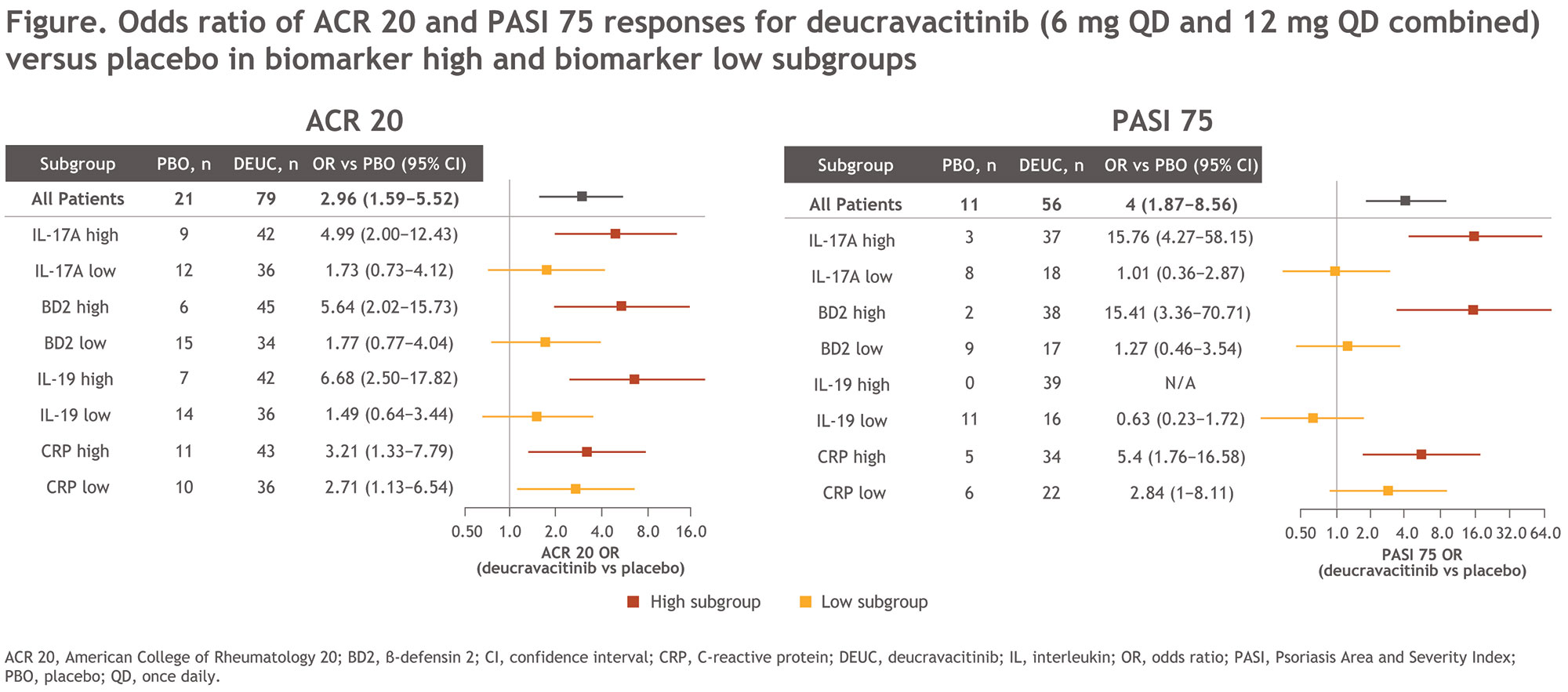
Results: Biomarkers of the IL-23/Th17 pathway, including IL-17A, IL-17‒induced β-defensin 2 (BD2), and IL-19, were associated with higher PASI but not Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Scores overall at baseline. PASI 75 responders at week 16 in the DEUC 12 mg QD treatment group had higher baseline levels of IL-17A and IL-19 compared with nonresponders. In contrast, PASI 75 responders in PBO-treated patients had lower baseline expression of IL-17A, BD2, and IL-19 compared with nonresponders. In patients treated with DEUC 12 mg QD, greater reductions in BD2 were observed in PASI 75 responders compared with nonresponders. When patients were dichotomized by median baseline biomarker level, higher clinical responses in both PASI 75 and ACR 20 were achieved in those with higher baseline overall biomarker levels in the DEUC-treated groups compared with the PBO group. Higher baseline expression of IL-17A, IL-19, and BD2 enriched PASI 75 and ACR 20 responses in patients treated with DEUC (both doses combined) compared with PBO; low-biomarker populations still manifested clinical responses, although not significant (Figure).
Conclusion: Although all PsA patient groups treated with DEUC benefited, those with higher expression of baseline serum IL-23 pathway biomarkers were more likely to benefit in their joint and skin manifestations with DEUC treatment compared with PBO. The potential value of IL-23-pathway markers in predicting higher responses to DEUC should be further explored in larger trials. These results reinforce the value of TYK2 inhibition in patients with IL-23‒mediated diseases.
References
1. Armstrong A, et al. Presented at AAD Virtual Meeting Experience 2021; April 23-25, 2021.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of selective TYK2 inhibitor, deucravacitinib, in a phase II trial in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:815-822.
3. FitzGerald O, et al. Presented at the 2021 ACR Convergence; Nov 3-9, 2021.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
FitzGerald O, Gladman D, Mease P, Ritchlin C, Smolen J, Gao L, Hu S, Nowak M, Banerjee S, Catlett I. Baseline Biomarkers Predict Better Responses to Deucravacitinib, an Oral, Selective Tyrosine Kinase 2 (TYK2) Inhibitor, in a Phase 2 Trial in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-biomarkers-predict-better-responses-to-deucravacitinib-an-oral-selective-tyrosine-kinase-2-tyk2-inhibitor-in-a-phase-2-trial-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-biomarkers-predict-better-responses-to-deucravacitinib-an-oral-selective-tyrosine-kinase-2-tyk2-inhibitor-in-a-phase-2-trial-in-psoriatic-arthritis/