Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can help to identify those with more rapid erosive disease.1,2 Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. In this post hoc analysis, we explored whether anemia was a predictor of radiographic progression in patients with RA who were treated with tofacitinib.
Methods: Data were from two 24-month, Phase 3 randomized controlled trials in methotrexate (MTX)-naïve (ORAL Start [NCT01039688]) or MTX-inadequate responder (IR) patients (ORAL Scan [NCT00847613]). Patients received either tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (as monotherapy or with background MTX), placebo or MTX. Radiographic progression was evaluated by modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) at baseline (BL), Month (M)6, M12, and M24. Anemia was defined as lower normal hemoglobin limits of 12 g/dL for women or 13 g/dL for men. We used a linear mixed model with repeated measure analysis to analyze the impact of BL anemia on change in radiographic joint damage (ΔmTSS), adjusting for treatment, age, gender, disease duration, and BL mTSS, autoantibody status, DAS28, corticosteroid, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use. Analyses were performed on observed data without linear extrapolation on missing data.
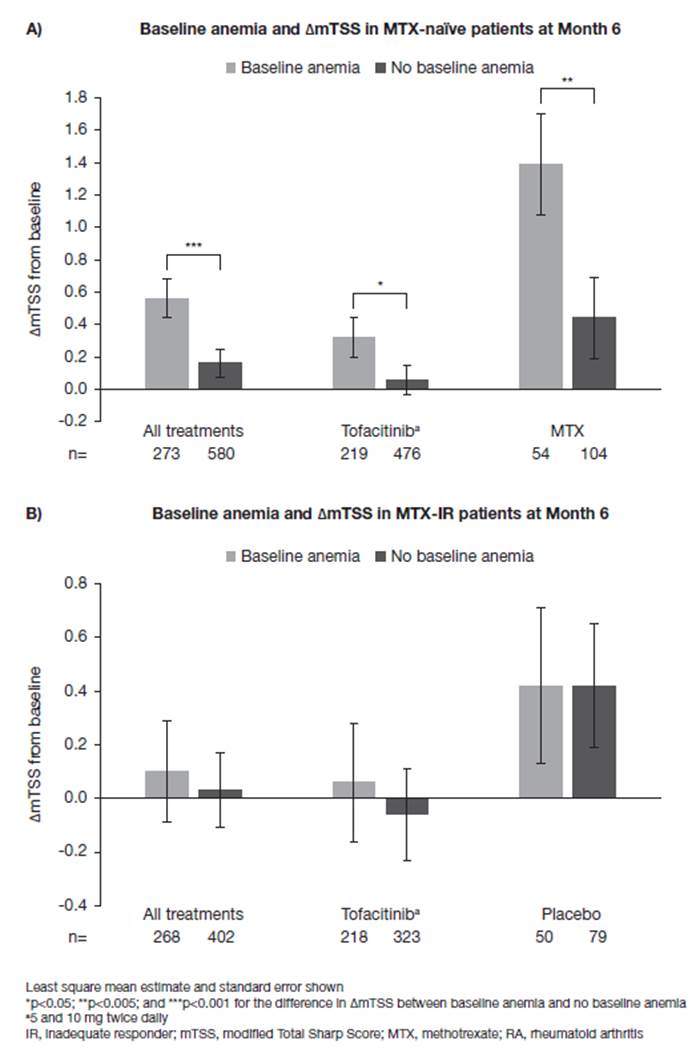
Results: Anemia was present at BL in 312/956 MTX-naïve patients (32.6%), RA duration ranged from 2.7–3.4 (mean) and from 0.7–0.8 (median) years, and in 321/797 MTX-IR patients (40.3%), RA duration ranged from 8.9–9.2 (mean) and from 6.0–7.7 (median) years. In MTX-naïve patients, anemia at BL was significantly associated with additional ΔmTSS from BL to M6 only (difference in ΔmTSS with and without BL anemia = 0.40; p<0.001) and increased ΔmTSS was also observed at M6 for patients receiving tofacitinib (0.25; p<0.05) or MTX monotherapy (0.95; p<0.005) (Figure 1A). There were no differences in ΔmTSS observed at M12 or M24 for either treatment group according to anemia status (data not shown). No associations between BL anemia and ΔmTSS were observed for MTX-IR patients overall or in either treatment group at M6 (Figure 1B), M12, or M24.
Conclusion: BL anemia was associated with radiographic progression at M6 in MTX-naïve patients, regardless of treatment received (tofacitinib or MTX monotherapy) but not at later time points (M12/M24). These data support the evidence that anemia at BL is a predictive parameter for joint damage progression in MTX-naïve patients, at least up to M6.
References:
1. Moller B et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73: 691-696.
2. van Steenbergen HW et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2013; 72: e16.
Figure 1. Association between baseline anemia and change in radiographic progression at Month 6 in A) MTX-naïve and B) MTX-IR patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moeller B, Finckh A, Scholz G, Shi H, Connell CA, Strengholt S. Baseline Anemia As a Predictor of Radiographic Progression in Tofacitinib-Treated Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Post Hoc Analyses from Two Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-anemia-as-a-predictor-of-radiographic-progression-in-tofacitinib-treated-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-post-hoc-analyses-from-two-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-anemia-as-a-predictor-of-radiographic-progression-in-tofacitinib-treated-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-post-hoc-analyses-from-two-phase-3-trials/