Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II: Basic and Translational Science
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Myositis specific antibodies (MSA) represent not only important diagnostic tools, but also help stratify myositis patients with particular clinical features, treatment responses and disease outcomes. These antibodies also have the potential to be used in classification criteria. Consequently, standardization of MSA is of high importance. Many laboratories rely on immunoprecipitation (IP) for the detection of MSA which, however, are met with logistic, standardization, and regulatory challenges. Therefore, reliable alternatives to IP are mandatory. The objective of this study was to compare the results obtained from different assays for the detection of anti-Mi-2 antibodies.
Methods:
The study included 82 patients (68 females/14 males), most of whom had dermatomyositis (DM, n=57), followed by polymyositis (PM, n=16) and juvenile DM (n=9). All samples were tested using a novel particle-based multi-analyte technology (PMAT, Inova Diagnostics, research use only; Mi-2b, OJ, TIF1y, PL-12, SAE, EJ, MDA5, HMGCR, PL-7, SRP, NXP2) in parallel with a line immunoassay (LIA, Euroimmun, not FDA approved; OJ, EJ, PL-12, PL-7, SRP, Jo-1, PM-75, PM-100, KU, SAE, NXP2, MDA5, TIF1y, Mi-2b, Mi-2a). To assess clinical specificity for the PMAT assay, a total of 775 disease controls and healthy individuals were tested.
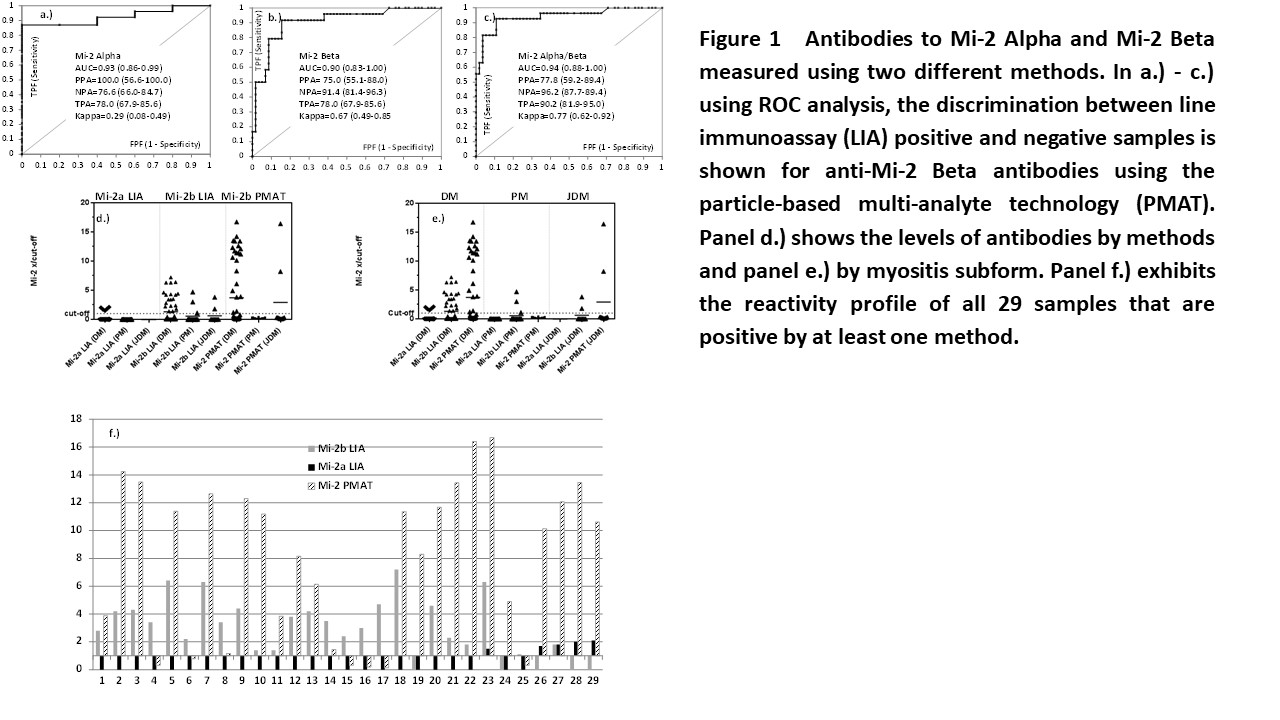
Results:
A total of 24 patients were positive for anti-Mi-2a and 5 patients for anti-Mi-2b antibodies by LIA. For PMAT, 23 patients tested positive for anti-Mi-2b antibodies. The comparison shows varying agreement between the different methods as shown by kappa statistics (0.27-0.77). When the results obtained from the LIA were used as reference for ROC analysis, good discrimination and high area under the curve values were found for both PMAT vs. LIA Mi-2 Alpha and LIA Mi-2 Beta. A total of 29 samples were positive by at least one test for anti-Mi-2 antibodies. Of those, 24 were positive by Mi-2b LIA, 5 by Mi-2a LIA and 23 by Mi-2 PMAT. When analyzing the results in the context of the myositis phenotype, LIA Mi-2 Alpha was positive in 5/57 (8.8%) DM, in 0/16 (0.0%) PM and 0/9 (0.0%) JDM patients. For LIA Mi-2 Beta, 19/57 (33.3%) DM, 2/16 (18.8%) PM and 2/9 (22.2%) JDM patients were positive. In addition, for PMAT Mi-2 Beta, 21/57 (0.0%) DM, 0/0 (0.0%) PM and 2/9 (22.2%) JDM patients were positive. Lastly, in the control group, 3 controls were positive for anti-Mi-2 antibodies resulting in a sensitivity and specificity of 28.1% and 99.6%, respectively.
Conclusion:
Overall good agreement was found between LIA and PMAT for anti-Mi-2 antibodies. Anti-Mi-2 Beta antibodies measured by PMAT tended to be more highly associated with the clinical phenotype of DM. Larger multi-center studies are needed to confirm the findings and to compare the results of LIA and PMAT to IP.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Richards M, Garcia-De La Torre I, Gonzalez-Bello Y, Vazquez-Del Mercado M, Andrade-Ortega L, Medrano-Rameriz G, Navarro-Zarza JE, Maradiaga M, Loyo E, Rojo-Mejía A, Gómez GN, Seaman A, Fritzler MJ, Koenig M, Mahler M. Autoantibodies to Mi-2 Alpha and Mi-2 Beta in Patients with Myositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibodies-to-mi-2-alpha-and-mi-2-beta-in-patients-with-myositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibodies-to-mi-2-alpha-and-mi-2-beta-in-patients-with-myositis/