Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Although available data has suggested successful withdrawal of a monoclonal antibody TNF blocker after achieving low disease activity (LDA) or remission over the short-term for a large proportion of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA), longer term follow-up data are needed to predict maintenance of biologic-free disease control. The purpose of this study was to identify the factors associated with maintenance of disease control for 2 years of adalimumab (ADA) discontinuation after treatment with ADA plus methotrexate (MTX) in patients with early RA.
Methods: In the HOPEFUL-1 study, patients with early RA were randomized to receive ADA 40 mg every other week (EOW) plus weekly MTX 6-8 mg , or only MTX 6-8 mg every week for 26 weeks. Thereafter, all patients received open-label ADA 40 mg EOW plus weekly MTX for 26 weeks. At week 52, patients could enroll in HOPEFUL-2, an observational follow-up study, where they received ADA plus MTX (ADA-continued group) or MTX alone (ADA-withdrawn group) for 52 weeks based on investigator and/or patient decision. At week 104, patients could enroll in HOPEFUL-3, a 104-week follow-up extension. Data at week 156 were used in this interim analysis. Using multivariate analysis, factors associated with remaining in ADA-withdrawn group as well as sustaining LDA in the ADA-withdrawn group at week 156, were analyzed. The 28-joint disease activity score based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and modified total Sharp score (mTSS) were also examined.
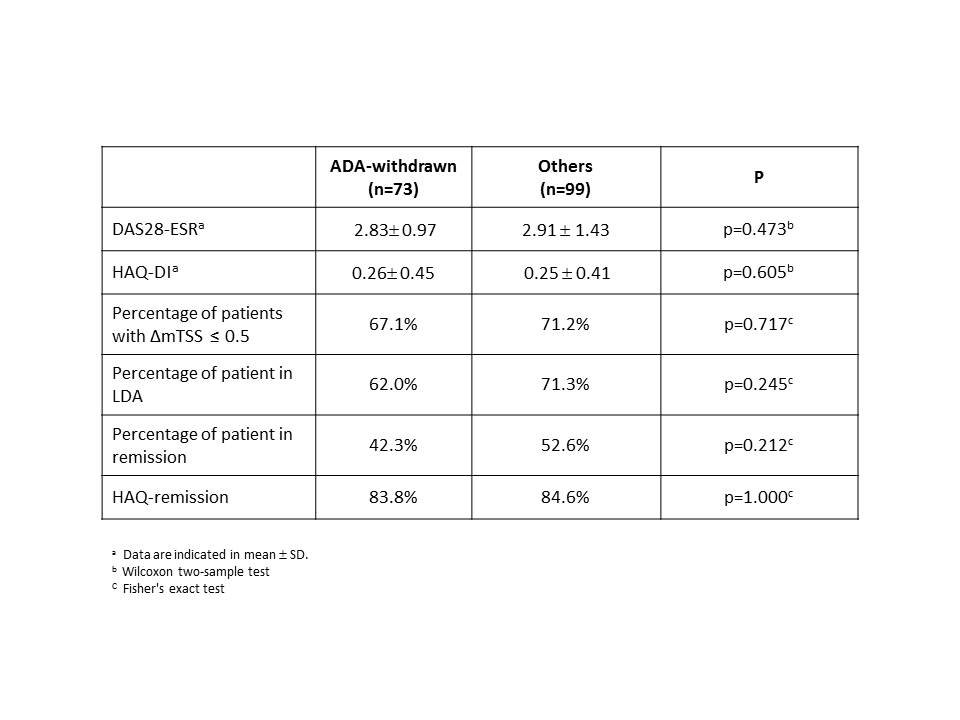
Results: Among the 220 HOPEFUL-2 patients, 172 were enrolled in the HOPEFUL-3 study, 79 from ADA-continued and 93 from ADA-withdrawn. Patient characteristics at the baseline of HOPEFUL-2 were similar in the ADA-continued and -withdrawn groups, except for SJC, which was significantly higher in the former group. At week 156, 73 patients out of 93 (78%) remained in the ADA-withdrawn group, with the remainder of patients either discontinuing from the study or continuing/restarting treatment with ADA. At week 156, there were no differences in clinical, functional, and structural outcomes between the patients in ADA-withdrawn group and the remainder of patients. (table). The predictive factors for remaining in the ADA-withdrawn group at week 156 were level of CRP at week 0, as well as SJC, CRP, and titer of rheumatoid factor at week 52 (cut-offs =week 0 CRP, 2.04; week 52 CRP, 0.21; week 52 SJC, 0). Moreover, DAS28-ESR 2.6 at week 52 distinguished 44 patients, those who were able to sustain LDA without using ADA at week 156.
Conclusion: The attainment of low disease activity based on serological markers at the onset and at the time of ADA withdrawal was the key determinant for maintenance of biologic-free disease control for up to 2 years in early RA patients.
Disclosure:
Y. Tanaka,
BMS, MSD, Chugai, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Astellas, Abbvie and Daiichi-Sankyo,
2,
UCB, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Abbott, Abbvie, Eisai, Chugai, Janssen, Pfizer, Takeda, Astellas, Daiichi-Sankyo, GSK, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Quintiles, MSD and Asahi Kasei,
5,
UCB, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Abbott, Abbvie, Eisai, Chugai, Janssen, Pfizer, Takeda, Astellas, Daiichi-Sankyo, GSK, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Quintiles, MSD and Asahi Kasei,
8;
H. Yamanaka,
Abbott, AbbVie, Asahikasei , Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squib, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, MSD, Nippon Kayaku, Pfizer, Santen, Taishotoyama, Takeda, Teijin,
2,
Abbott, AbbVie, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squib, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Nippon Kayaku, Pfizer, Takeda, Teijin Speakers bureau: Abbott, AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squib, Chugai, Eisai, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer, T,
5;
N. Ishiguro,
AbbVie, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer and Takeda.,
5,
AbbVie, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer and Takeda.,
8;
N. Miyasaka,
Abbvie GK, Astellas Pharma, Banyu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, and Teijin Pharma Limited,
2;
K. Kawana,
Abbvie,
3;
K. Hiramatsu,
Abbvie,
3;
A. Kuroki,
Abbvie,
3;
T. Takeuchi,
Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma, Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., Sanofi–Aventis K.K., Santen Pharmaceutica,
2,
Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co,. Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma, Diaichi Sankyo Co.,Ltd.,
8,
Astra Zeneca K.K., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Asahi Kasei Medical K.K., Abbivie GK, Daiichi Sankyo Co.,Ltd.,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/attainment-of-low-disease-activity-is-predictive-of-maintenance-of-disease-control-upon-adalimumab-discontinuation-for-two-years-following-combination-therapy-in-japanese-patients-with-early-rheumatoi/