Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster II: Biomarkers and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Low disease activity (LDA) and remission are important goals in the treatment of patients (pts) with SLE.1,2 Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) is associated with reduced damage accrual,2 and has been shown to be a feasible clinical trial endpoint.3 In pts with high disease activity (HDA; SLEDAI-2K≥10) enrolled in the ADDRESS II study, atacicept improved SRI-6 response rates and flare prevention at Week 24 vs placebo (PBO).4 Atacicept was also shown to have an acceptable safety profile. We present a post-hoc analysis of data from ADDRESS II and its long-term extension describing 48-week LDA and remission rates in pts with HDA at Screening.
Methods: In ADDRESS II, pts were randomized (1:1:1) to weekly subcutaneous PBO or atacicept 75 or 150 mg for 24 weeks. Atacicept completers continued at the same dose in the extension study; PBO pts were switched to atacicept 150 mg (PBO/atacicept 150 mg). This post-hoc analysis assesses: LDA (SLEDAI-2K≤2), LLDAS (SLEDAI–2K≤4 without major organ activity, no new disease activity vs previous visit, Physician’s Global Assessment [PGA]≤1, prednisone-equivalent≤7.5 mg/day, and stable immunosuppressants),2 and remission (clinical SLEDAI-2K=0, PGA<0.5, prednisone≤5 mg/day), as proposed by the task force on definitions of remission in SLE (DORIS).1
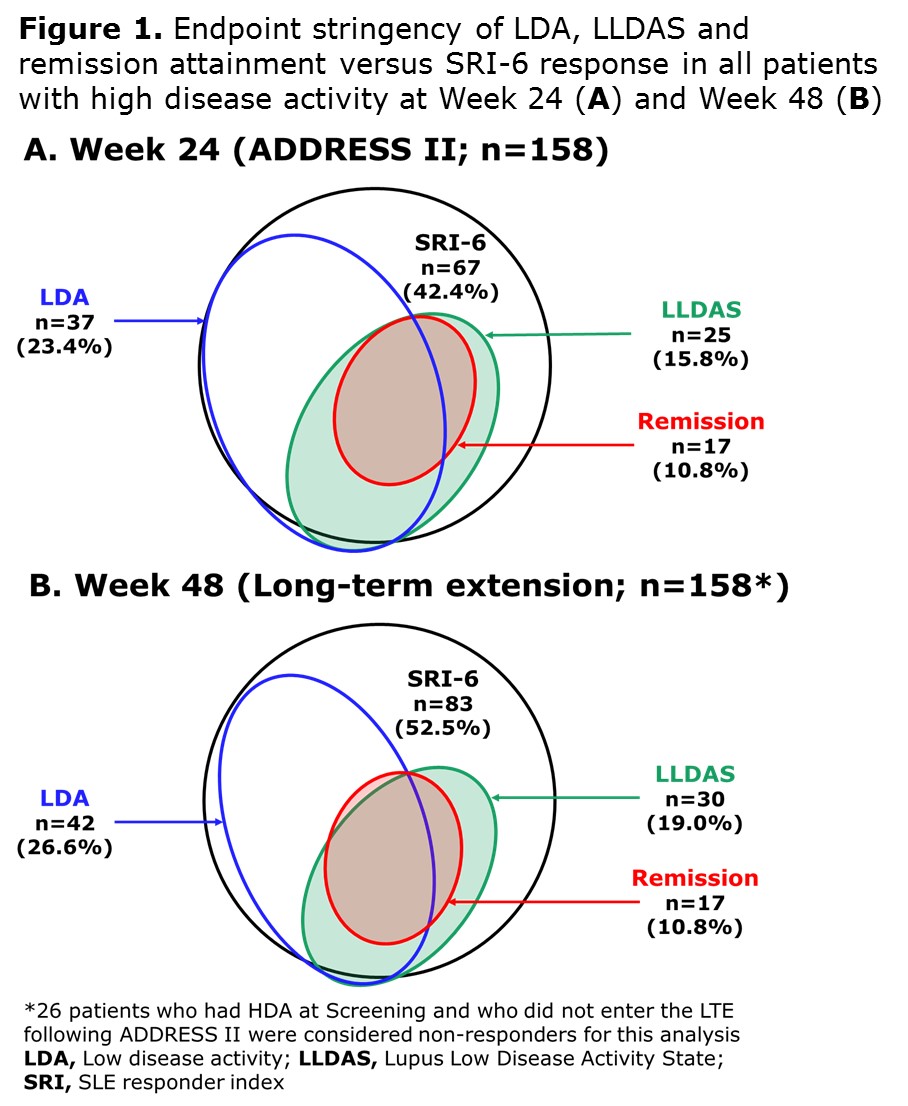
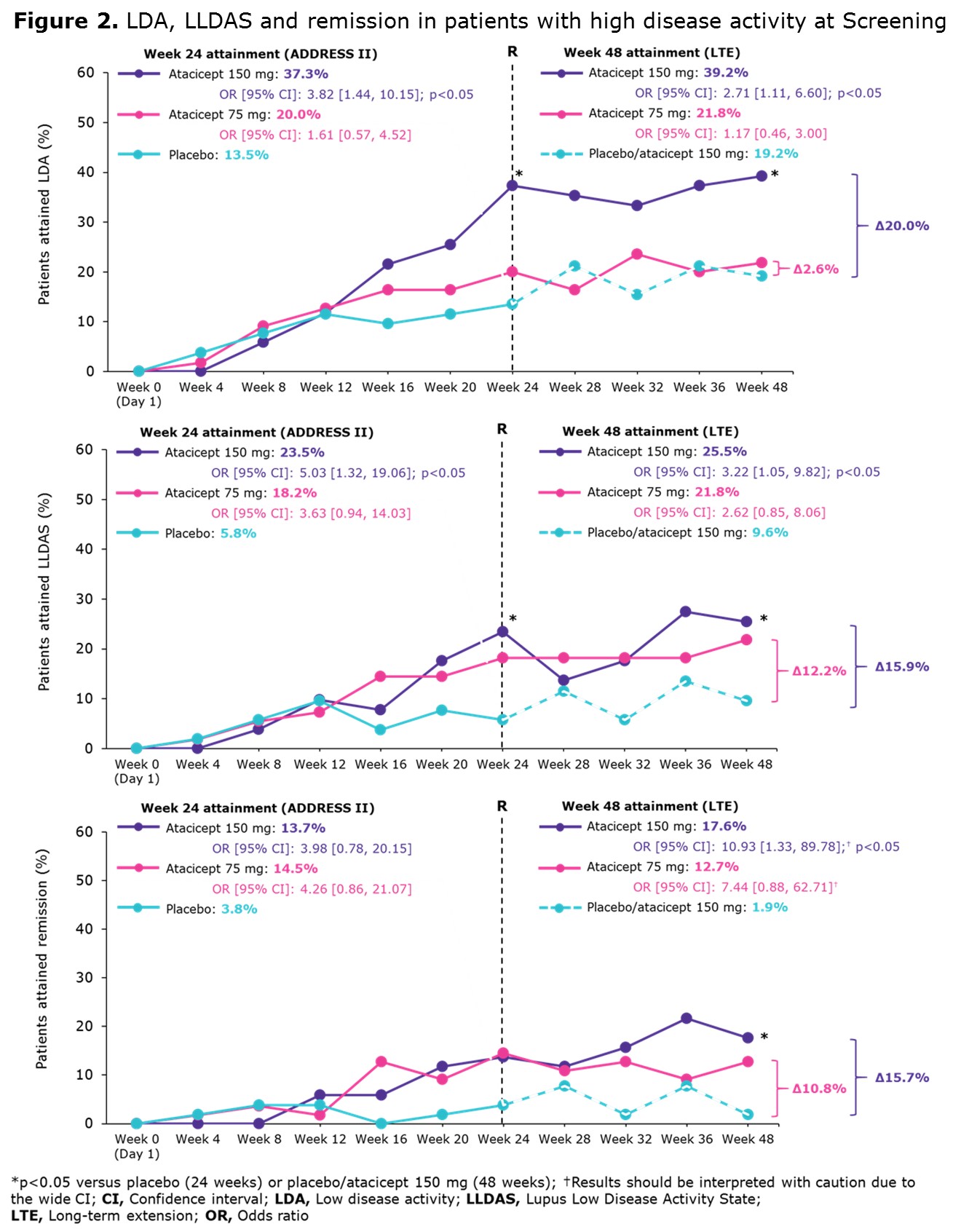
Results: A total of 158/306 (52%) ADDRESS II pts had HDA at study entry. At Week 24, 42.4% achieved SRI-6, 23.4% attained LDA, 15.8% LLDAS and 10.8% remission (Figure 1A). At Week 48, 52.5% achieved SRI-6, 26.6% attained LDA, 19.0% LLDAS and 10.8% remission (Figure 1B). Among 83 SRI-6 responders with HDA at Screening, 49.4% (n=41) attained LDA, 34.9% (n=29) LLDAS and 20.5% (n=17) remission at Week 48. At 48 weeks, LDA, LLDAS and remission rates were higher in pts treated with atacicept 150 mg vs PBO/atacicept 150 mg and vs atacicept 75 mg (Figure 2).
Conclusion: ADDRESS II pts with HDA at Screening receiving atacicept 150 mg were more likely to attain LDA, LLDAS and remission at Week 48 than those treated with atacicept 75 mg or PBO/atacicept 150 mg. These endpoints were more stringent and discriminatory than SRI-6, confirming LLDAS, LDA, and remission to be robust and meaningful endpoints for SLE trials. In addition, these data further support future studies of atacicept in SLE.
References (1) Van Vollenhoven et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2017. (2) Franklyn et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2016. (3) Morand et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2018. (4) Merrill et al, Arthritis Rheum 2018.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Morand E, Merrill JT, Isenberg DA, Kao AH, Vazquez-Mateo C, Wax S, Chang P, Pudota K, Aranow C, Wallace DJ. Attainment of Low Disease Activity and Remission in SLE Patients Who Started with High Disease Activity in the Atacicept Phase IIb Address II Study and Its Long-Term Extension [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/attainment-of-low-disease-activity-and-remission-in-sle-patients-who-started-with-high-disease-activity-in-the-atacicept-phase-iib-address-ii-study-and-its-long-term-extension/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/attainment-of-low-disease-activity-and-remission-in-sle-patients-who-started-with-high-disease-activity-in-the-atacicept-phase-iib-address-ii-study-and-its-long-term-extension/