Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
We hypothesized that increased dietary intake of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids (FA) prior to disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) initiation may associate with superior response to anti-rheumatic treatments. On the other hand, high dietary folate intake may be associated with worse response to methotrexate (MTX). The aim of this study was to investigate the association between dietary intakes of vitamin D, omega-3 FA, and folate and treatment results of DMARDs in patients with early RA.
Methods:
This study included 727 early RA patients from Epidemiological Investigation of Rheumatoid Arthritis (EIRA) study linked with the Swedish Rheumatology Quality register (SRQ). Data on dietary vitamin D, omega-3 FA and folate intake based on food frequency questionnaires were linked with data on response to DMARDs using European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) response criteria at 3-month follow-up. Associations between dietary intakes of vitamin D, omega-3 FA, and folate and EULAR response, respectively, were analyzed with binary logistic regression adjusting for potential confounders.
Results:
The majority of the patients were initially treated with monotherapy of MTX (n=653 [89.9%]) and more than half of the patients had combined DMARD(s) with glucocorticoids (n=414 [56.9%]). Higher intakes of vitamin D and omega-3 FA were associated with good EULAR response. Folate intake around the recommended dose (300 µg/day), but not higher, was associated with EULAR response (Table). Similar associations were observed in the subgroup of patients who were initially treated with MTX monotherapy at baseline. 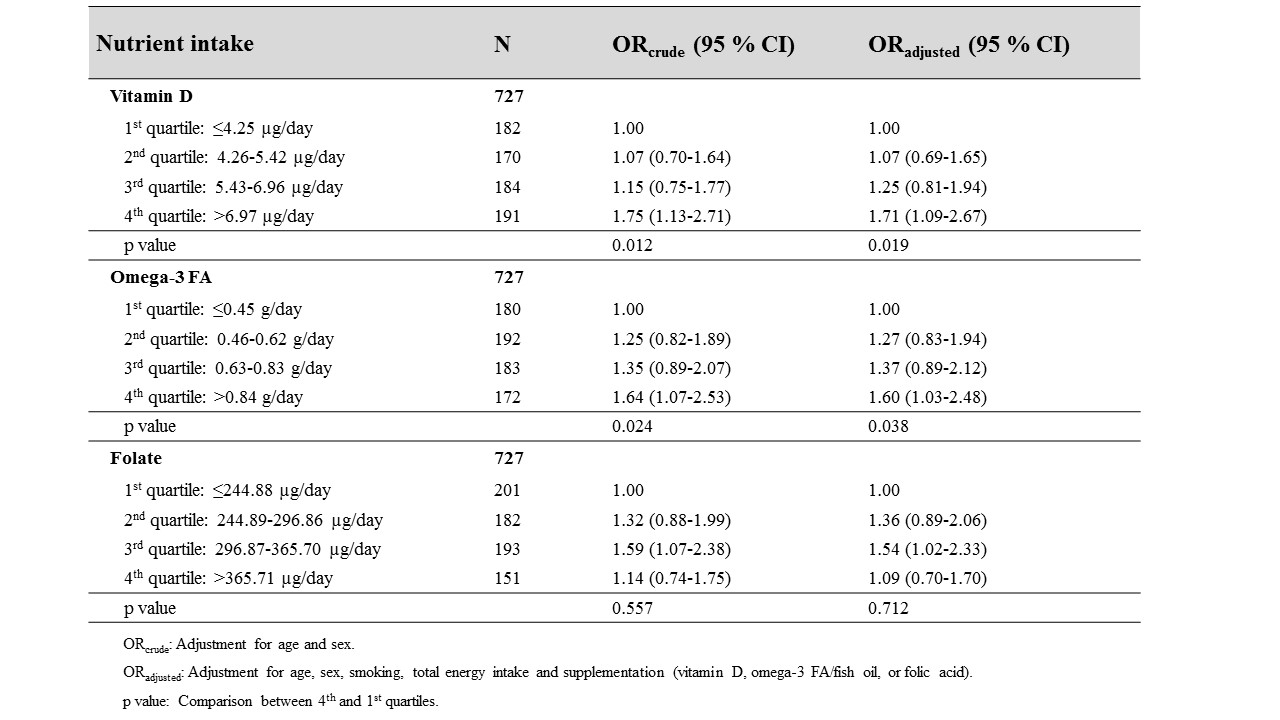
Conclusion:
Increased intake of dietary vitamin D and omega-3 FA during the year preceding DMARD initiation may associate to better treatment results in early RA patients. Moderate dietary folate intake, but not lower or higher, was associated with better response to treatment. Our results suggest that several specific nutrients may associate with enhanced treatment results in early RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lourdudoss C, Wolk A, Nise L, Alfredsson L, van Vollenhoven RF. Associations Between Dietary Intake of Vitamin D, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Folate and EULAR Response in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-dietary-intake-of-vitamin-d-omega-3-fatty-acids-folate-and-eular-response-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-dietary-intake-of-vitamin-d-omega-3-fatty-acids-folate-and-eular-response-in-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/
