Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Although guidelines support integrative health practices as complementary treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), little is known about the prevalence of integrative health behaviors and their association with health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in real world practice. We describe the association of physical activity (PA), diet, and integrative health behaviors with HRQoL in women with RA.
Methods: Women aged 18-65 years evaluated by a Hospital for Special Surgery rheumatologist ≥2 times from 2020-2022 were enrolled in the Rheumatology Women’s Reproductive Health and Wellness Cohort. Women with RA (identified by ≥2ICD-10 codes ≥7 days apart) who self-reported type and frequency of PA, dietary quality, and integrative health practices and answered questions on HRQoL across 4 individual domains (life satisfaction, life worthwhile, happiness, anxiety, each scored on a 0-10 scale, with 0 “not at all” and 10 “completely”) developed by the United Kingdom Office for National Statistics were included in this cross sectional analysis. We used descriptive analyses to summarize self-reported demographic, medical characteristics, diet, physical exercise, and integrative health practices among participants. We also stratified by life satisfaction, life worthwhile, happiness, and anxiety levels (medium/low versus high/very high according to previously defined thresholds).
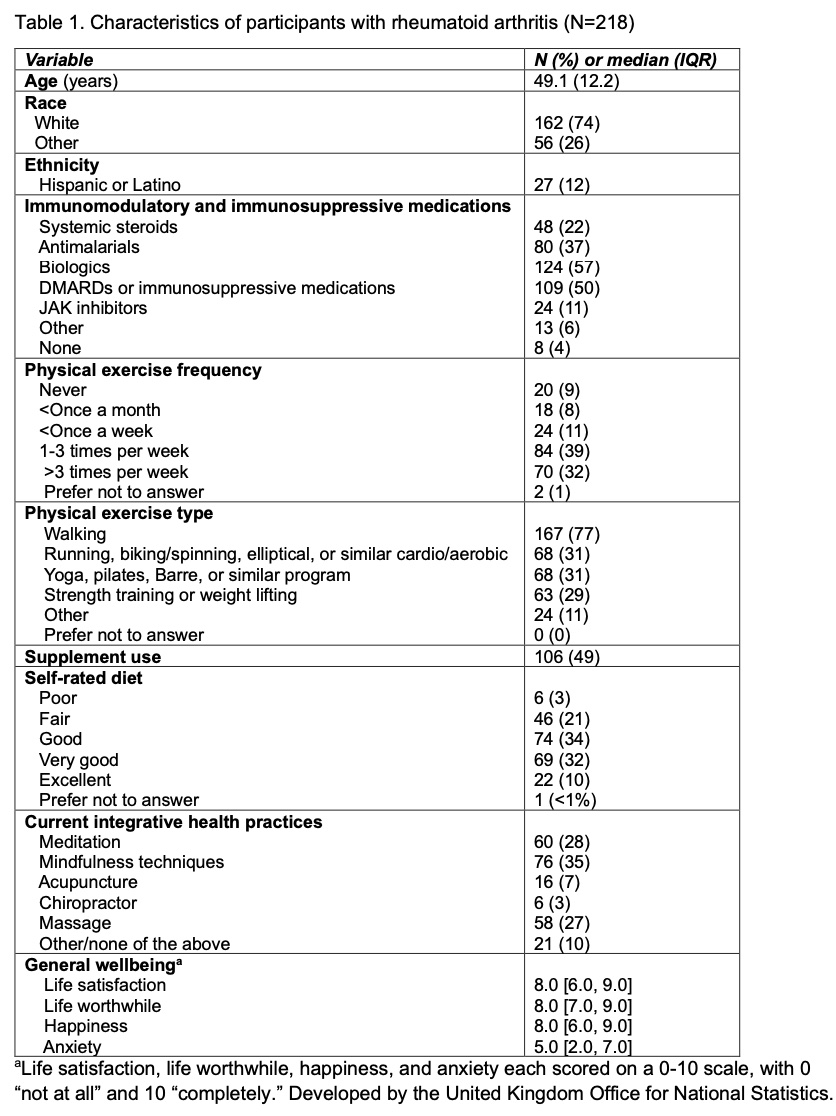
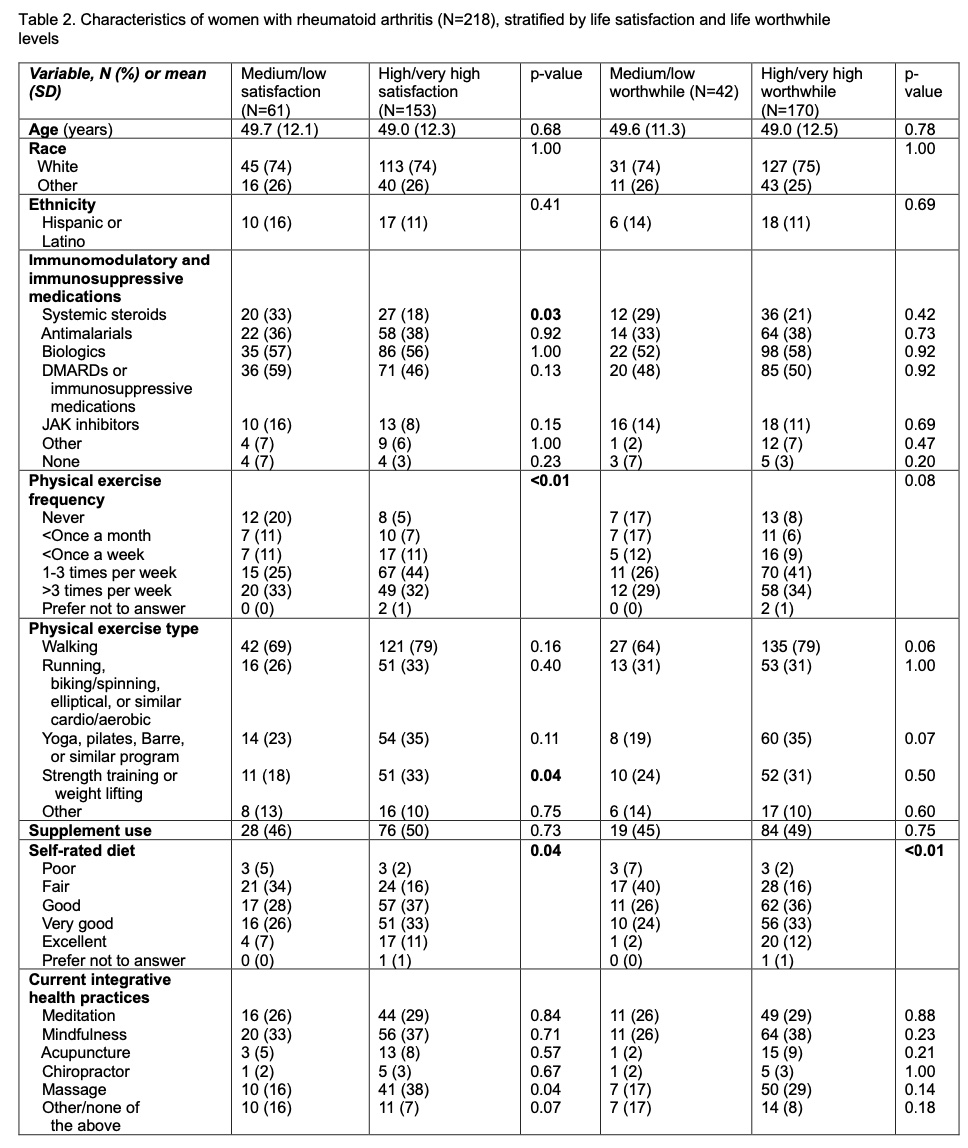
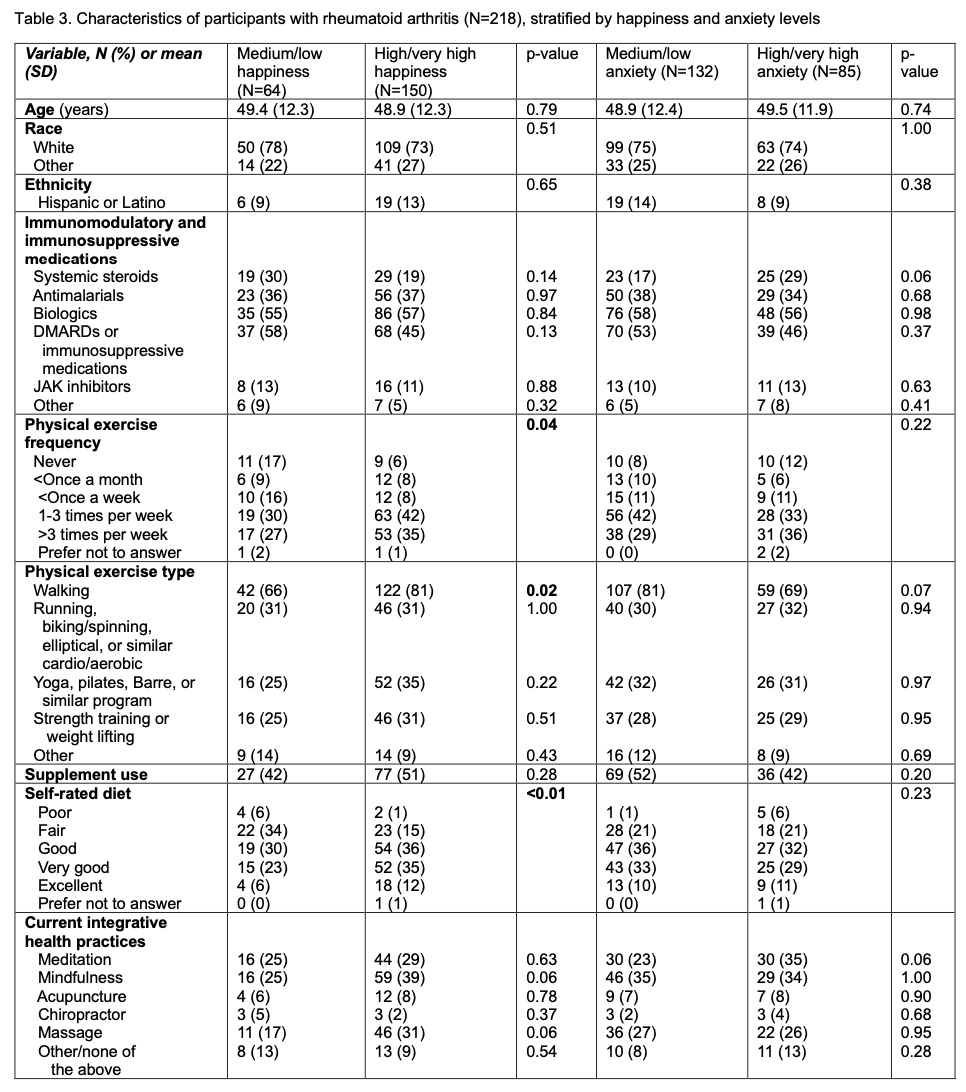
Results: Of 218 participants (mean age 49.1 ±12.2 years), 154 (71%) self-reported exercising at least 1-3 times per week and 91 (42%) self-rated diet as very good to excellent. Any type of integrative health practice was used by 130 (60%) individuals, with mindfulness techniques, massage and yoga being the most common (Table 1). Among those with high/very high (versus medium/low) life satisfaction (N=153, 71%) and happiness (N=150, 70%), a higher proportion described greater physical exercise levels (p≤0.04, Tables 2 and 3). Among those with high/very high (versus medium/low) life satisfaction, sense of worthwhile (N=170, 80%), and happiness, a higher proportion described better self-rated dietary quality and increased physical exercise, particularly strength training (p≤0.04). A higher proportion of those with high/very high (versus medium/low) life satisfaction self-reported walking for physical exercise.
Conclusion: About 60% of those with RA engaged in integrative health behaviors in this real world practice. Physical exercise and healthy diet may be associated with greater HRQoL. Further evaluation of these factors is needed to develop patient-centered strategies to enhance the health and wellbeing of those with RA in conjunction with physician-directed therapies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lieber S, Masto L, Smole A, Lan R, Parides M, Levine J, Stamm B, Siegel C, Mandl L, Lockshin M, Barbhaiya M, Sammaritano L. Association of Integrative Health Practices with Health-Related Quality of Life in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-integrative-health-practices-with-health-related-quality-of-life-in-women-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-integrative-health-practices-with-health-related-quality-of-life-in-women-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/