Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Human leukocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) is a non-classical class I
molecule expressed in the immune cells, the spleen, and the lungs, and plays a
key role in immunosuppression. HLA-G binds to inhibitory leukocyte
immunoglobulin-like receptor (LILR)B1, LILRB2, and killer cell
immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR)2DL4. LILRA3, a soluble member of the LILR
family and also binds to HLA-G, has a deletion polymorphism. Although the
function of LILRA3 remains elusive, some evidence suggests that LILRA3 might
work as an antagonist of other LILRs including LILRB1 or LILRB2. HLA-G gene
contains a 14bp insertion polymorphism in the 3’UTR, which has been shown to
influence the splicing and affect mRNA stability, thereby leading to low
expression of HLA-G. Previous studies reported association of HLA-G 14bp
ins/ins genotype with systemic lupus erythematosus in the European and Asian
populations. In this study, we examined whether HLA-G 14bp ins/del
polymorphism is associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc), either in itself or
in combination with LILRA3 genotypes.
Methods: 379
Japanese patients with SSc and 765 healthy Japanese controls were examined. All
patients fulfilled the American College of Rheumatology criteria. 127 were
classified as diffuse cutaneous (dc) SSc, while 230 as limited cutaneous (lc)
SSc. 45 patients as having pulmonary hypertension (PH). HLA-G 14bp ins/del
was genotyped by PCR with the product size of 224 or 210bp. LILRA3
ins/del was genotyped by PCR-sequence specific primers method. This study was
reviewed and approved by the ethics committees of each participating institute.
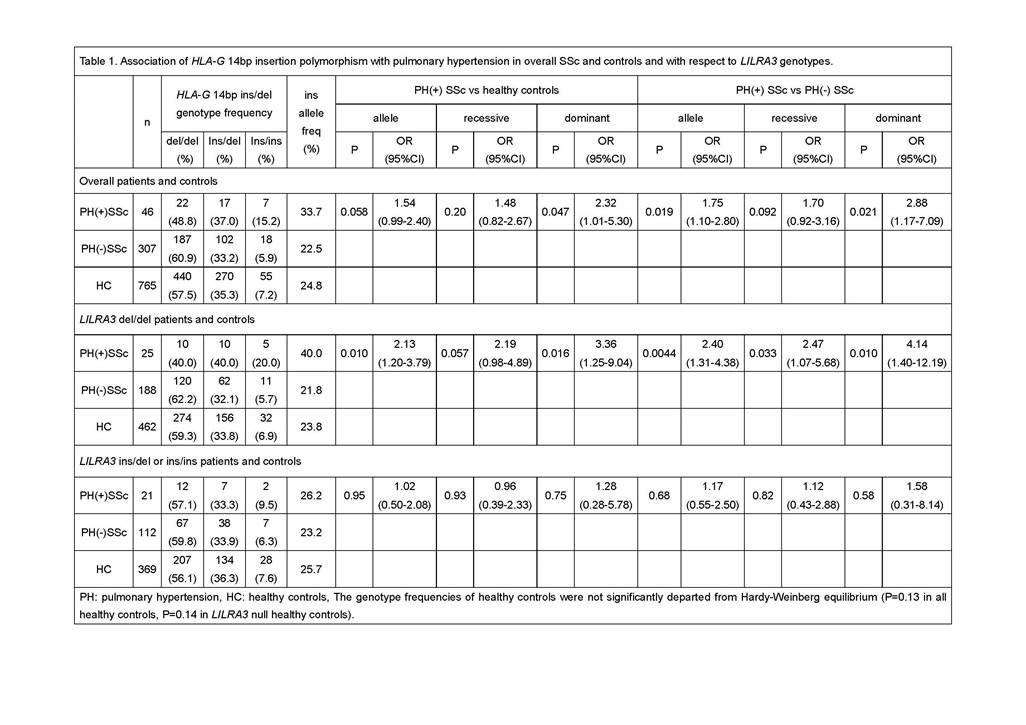
Results: The
results are shown in Table 1. Although significant association of HLA-G ins/del
polymorphism was not observed with overall SSc nor with dc/lc subsets,
significant increase of HLA-G ins allele was observed in SSc patients
with PH when compared with healthy controls (P=0.047, OR 2.32, dominant model) or
with PH(-) SSc (P=0.019, OR 1.75, allele model; P=0.021, OR 2.88, dominant
model). LILRA3 ins/del was not associated with PH. However, when HLA-G
association was examined with respect to the LILRA3 genotypes, more
striking association of HLA-G 14bp ins with PH was observed in the subjects
with LILRA3 del/del genotype (P=0.010, OR 2.13, allele model, and
P=0.016, OR 3.36, dominant model vs healthy controls; P=0.0044, OR 2.40, allele
model, P=0.033, OR 2.47, recessive model, P=0.010, OR 4.14, dominant model vs
PH(-) SSc). In contrast, significant association of HLA-G was not
detected in the patients and controls having one or two copies of LILRA3
allele.
Conclusion:
Association of HLA-G 14bp ins with SSc patients with PH was detected.
The association was more striking in LILRA3 null individuals, suggesting
a possibility that the predispositional effect of HLA-G low expression allele
becomes manifest when its soluble receptor LILRA3 is deficient.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hachiya Y, Kawasaki A, Matsushita T, Furukawa H, Nagaoka S, Shimada K, Sugii S, Setoguchi K, Okamoto A, Chiba N, Suematsu E, Katayama M, Hirohata S, Kono H, Migita K, Sumida T, Tohma S, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Sato S, Takehara K, Tsuchiya N. Association of HLA-G and Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-like Receptor A3 Polymorphisms with the Susceptibility to Pulmonary Hyterpention in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-g-and-leukocyte-immunoglobulin-like-receptor-a3-polymorphisms-with-the-susceptibility-to-pulmonary-hyterpention-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-g-and-leukocyte-immunoglobulin-like-receptor-a3-polymorphisms-with-the-susceptibility-to-pulmonary-hyterpention-in-systemic-sclerosis/