Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The existing literature on the genetics of polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is limited to candidate gene studies with small sample sizes. There is a need for larger genetic studies in PMR to investigate genetic associations throughout the whole genome. In this study, we aimed to perform a genome wide association study (GWAS) of PMR in the UK Biobank and compare our results with the FinnGen cohort.
Methods: UK Biobank is a cohort study of around 500,000 individuals from United Kingdom. The study collected genomic information on all participants which include 850,000 measured variants with over 90 million imputed variants using reference databases. The genetic data is linked with patient’s clinical record through International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-10 in addition to procedure and treatment codes. Patients with ICD-10 codes M31.5 Giant cell arteritis with polymyalgia rheumatica and M35.3 Polymyalgia rheumatica were included as cases. Controls were drawn from the same cohort in 1:20 case-control fashion and matched with regards to age, sex, and ancestry. The genome wide association analysis was performed using PLINK 2.0 software through firth logistic regression using age, sex and first 5 principal components (PC) as covariates. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) were filtered to include those with mean allele frequency greater than 5% and imputation quality score greater than 0.95. Summary statistics for GWAS in the FinnGen cohort was downloaded from the most recent publicly available data release. The FinnGen GWAS was performed by defining individuals with ICD-10 code M35.3 as cases and using REGENIE software with a two-step associated test utilizing firth logistic regression and having sex, age, first 10 PCs and genotyping batch as covariates.
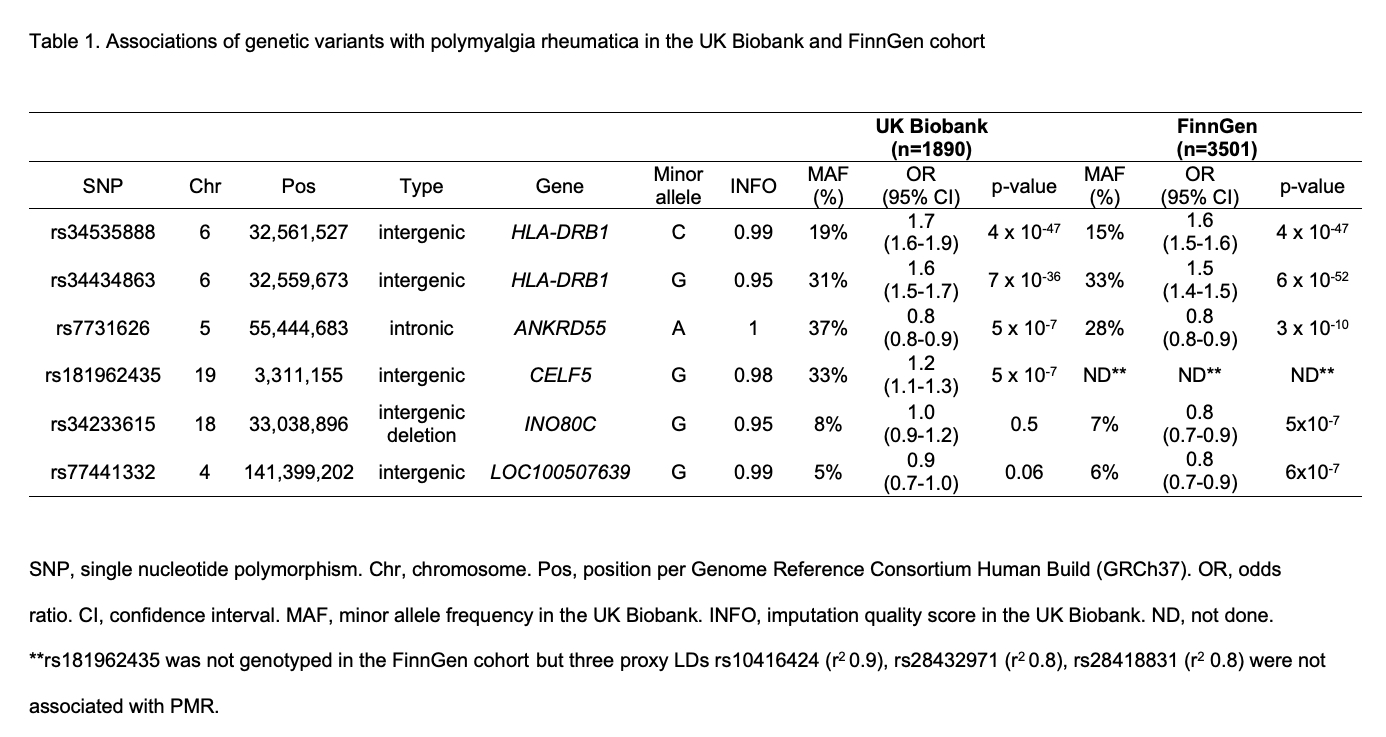
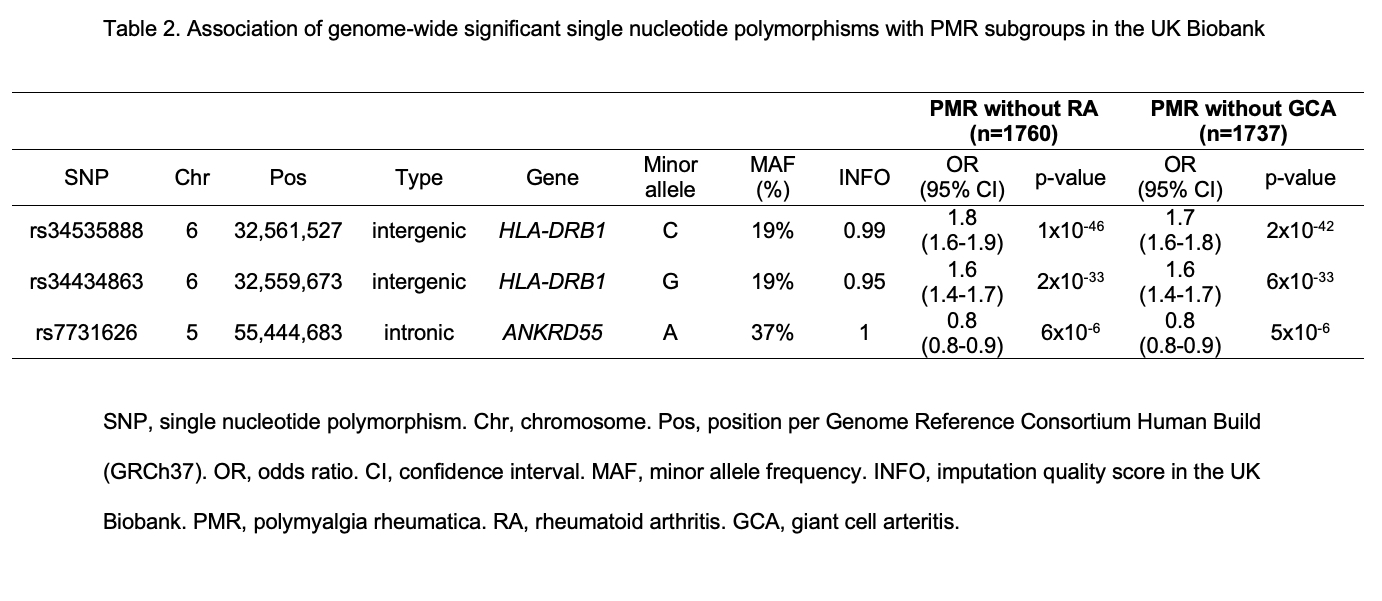
Results: There were 1890 and 3501 patients of PMR in the UK Biobank and FinnGen respectively. In the GWAS analysis in the UK Biobank, 2460 variants in the MHC locus at chromosome 6 passed the genome wide significance level at 5×10-8 and our quality filters. Our top hit was rs34535888, a SNP close to HLA-DRB1 gene. In the FinnGen, the top hit was rs34434863, a variant close to HLA-DRB1 gene. Outside of the MHC locus, only rs7731626, an intronic variant at the ANKRD55 gene passed genome-wide significance. Prior literature shows that the ANKRD55 variants affect the expression of the neighboring gene IL6ST in various immune cells. There were three further loci with genome wide suggestive association (< 1x10-6) in either UK Biobank or FinnGen, but none of these variants were replicated in both cohorts (Table 1). When we restricted the analysis to patients without concomitant RA or GCA diagnosis in the UK Biobank, the effect sizes were similar albeit with larger p-values (Table 2).
Conclusion: In this study, we report the first genome-wide association analysis of patients diagnosed as PMR in the population from the UK Biobank and FinnGen cohorts. We show that HLA-DRB1 and ANKRD55/IL6ST regions are associated with PMR diagnosis. Both regions have strong biological plausibility due to previous research implicating HLA-DRB1 variants in genetic susceptibility to PMR and the evidence for the role of IL-6 in the disease pathogenesis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hocaoglu M, Mikdashi J, Perry J, Hong C. Association of HLA-DRB1 and ANKRD55/IL6ST Regions with Polymyalgia Rheumatica Diagnosis: A Genome Wide Association Study from UK Biobank and FinnGen [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-drb1-and-ankrd55-il6st-regions-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica-diagnosis-a-genome-wide-association-study-from-uk-biobank-and-finngen/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-drb1-and-ankrd55-il6st-regions-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica-diagnosis-a-genome-wide-association-study-from-uk-biobank-and-finngen/