Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Life satisfaction (LS) has become an important outcome measure in healthcare, is a relevant indicator of job satisfaction, and might be influenced by depression. The objectives of the study were to investigate life and job satisfaction and the influence of self-reported depressive symptomatology (DS) in patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) to consider these aspects in future treatment concepts.
Methods:
Self-administered questionnaires (Qs) were applied to RA pts and controls (c) not suffering from rheumatic diseases. General life satisfaction Q (FLZ) captured ten domains of satisfaction (see Table 1). Scores are expressed as age&sex standardized stanines (a method of scaling test scores on a normalized nine-point standard scale with a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 2). DS was measured by the German long version of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (ADSL). A separate Q assessed self-reported clinical data. Ethics approval was obtained.
Results:
267 pts (85.0% female (f)) and 177 c (90.3% f) contributed data. Pts’ mean age was 47.7±10.0 (c 42.8±9.8) years, mean disease duration 9.0+8.0 years, mean HAQ 1.1±0.5 (c 0.4±0.1). 85.5% self-reported at least one comorbidity (range 0-8, c 45.2%, range 0-4). In pts 81.7% received at least one immunosuppressive medication (range 0-6), 43.8% steroids < 7.5mg, 9.0% steroids >7.5mg and 61.4% NSAIDS.
Pts’ mean general LS was 236.7±39.6 (c 263.9±31.7, p<1e-15), mean satisfaction with health was significantly lower in pts (26.3±8.6; c 38.6±7.2, p<1e-15). In the FLZ subscales job&profession, finances, self, sexuality and friends pts scored significantly lower than c. Pts' ADS-L score was 18.2±10.7 (c 9.8±6.8, p<1e-15). 27.1% pts and 4.6% c (p<1e-9) scored >23 on the ADS-L which is indicative of depression.
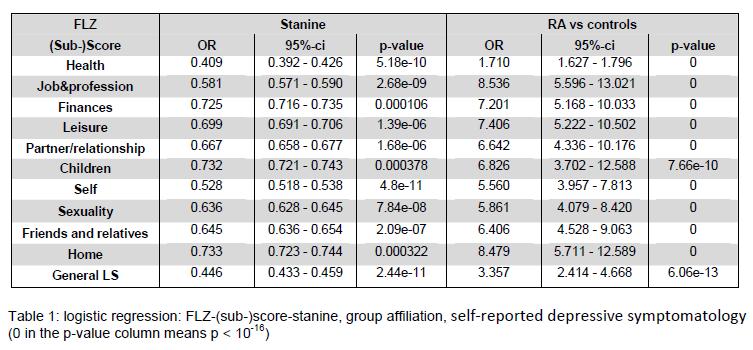
A logistic regression calculated the association between LS (sub-)scale-stanines and DS. Table 1 depicts odds ratios (OR). If the health stanine increases by one unit, a person’s risk with respect to an outcome of DS decreases by a factor of 0.409. For RA pts it increases by an additional factor of 1.710. In all FLZ-scales RA pts had a higher risk of DS. Highest OR was detected in the job&profession subscale.
Conclusion:
RA pts showed low satisfaction in 10 areas of LS and significantly more pts were indicative of depression. Significant ORs were detected in all FLZ scales, domains that are potentially modifiable. The high OR in the job and profession subscale indicates that beside DS social and job related satisfaction issues should predominantly targeted. Apart from already established (QoL) assessments (e.g. HAQ, SF36) routine care and further clinical studies might gain from additional assessments of LS and ADSL as outcome parameters.
Unrestricted grants Ministry of Innovation, Science, Research and Technology of the German State North Rhine-Westphalia, Deutsche Rheuma-Liga e.V., German LE Self-Help Community, Hiller Foundation
Disclosure:
J. G. Richter,
None;
D. R. Brinks,
None;
T. Muth,
None;
M. Vidakovic,
None;
T. Koch,
None;
P. Angerer,
None;
M. Schneider,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-depressive-symptomatology-and-life-and-job-satisfaction-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/