Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15), is a stress induced inflammatory cytokine, member of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily, tissue injury. It is predominantly expressed in cardiomyocytes, adipocytes, macrophages, endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells [Wischhusen J, et al. Front Immunol 2020; 11:951]. The association of this molecule with cardiovascular risk in patients with APS has been documented by measuring carotid intima-media thickness [Tektonidou MG, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2021;61(1):394-399]. It has been reported that high levels of GDF-15 are associated with cognitive performance in older adults in the general population [Jiang J, et al. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2016;29(2):181-6]. The association of mild cognitive impairment in APS patients with plasma GDF-15 levels has not been studied.
The aim of this study is to determine the correlation between cognitive impairment and plasma GDF15 levels in patients with APS.
Methods: We studied patients with APS and healthy controls matched for age, sex, and body mass index. Patients with APS met the 2023 ACR or 2016 Sydney criteria. The participants were invited during the waiting time of a rheumatology outpatient clinic of the Ignacio Chávez National Institute of Cardiology from January 5 to May 21, 2024. All of them underwent the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and the following questionnaires: Damage Index in Antiphospholipid Syndrome (DIAPS), Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ9), General Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD7), Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ-DI), EuroQol, International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ), and Morinsky-Green for assessment of adherence to treatment. Plasma levels of GDF-15 were measured using Human GDF-15 Immunoassay Quantikine ELISA from biotechne R&D SYSTEMS. This protocol was approved by the institute’s ethics committee; all patients gave their informed consent. Kolmogorov-Smirnov’s test, Student’s T test, Mann Whitney U test, chi square test or Fisher’s exact test were used, as appropriate. Correlations were performed with the Spearman method. A value of p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
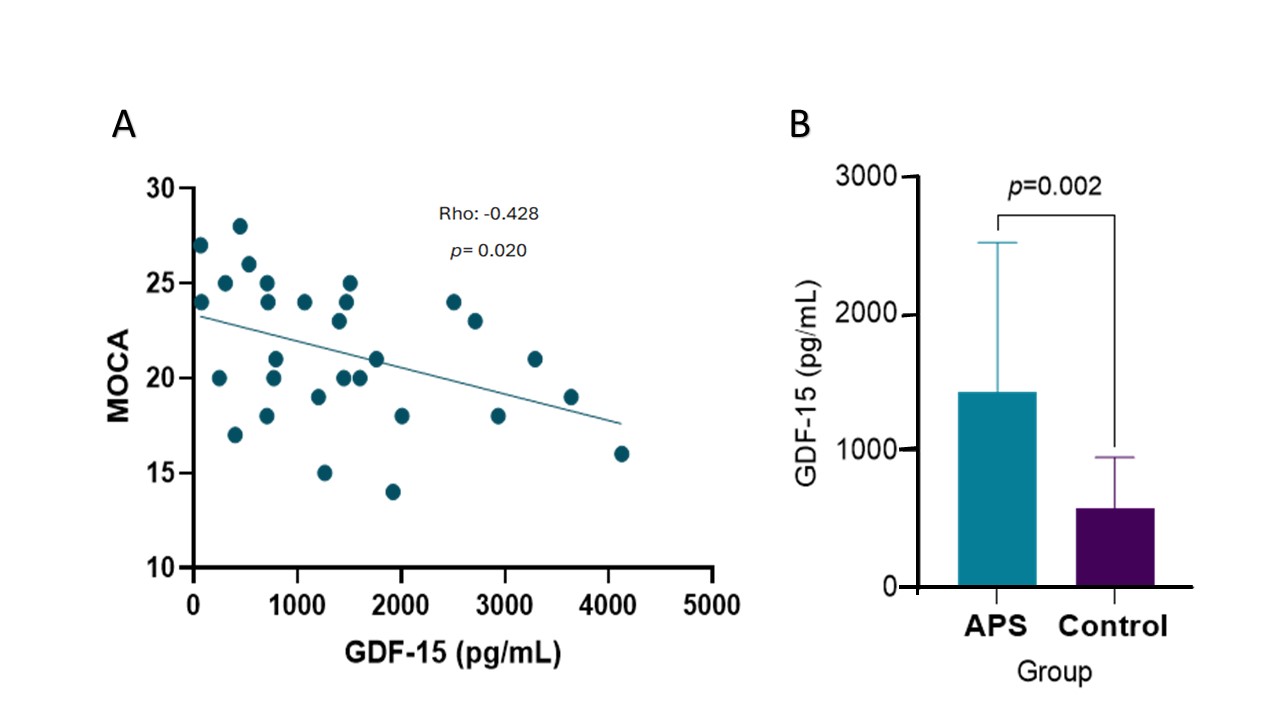
Results: Twenty nine patients with APS and 23 controls were included. 22 of the APS patients were female, median age was 35 (26-46) years; 17 patients had the primary form of the syndrome, and the DIAPS score was 3 (2-4). A negative correlation was found between the MoCA test score and plasma levels of GDF15 (Rho= -0.428, p= 0.020) in patients with APS (n=29) (panel A of figure 1). Panel B of figure 1 shows that the difference in plasma levels of GDF15 between patients and controls was statistically significant, 1262 pg/mL (705-1919) vs 456 pg/mL (308-810); p= 0.002.The PHQ9, GAD7, HAQ-DI, and EuroQol scales were different between patients and controls (p< 0.05), while the physical activity and adherence to treatment scales were not significant.
Conclusion: Mild cognitive impairment in patients with APS was associated with plasma levels of GDF-15; in fact, patients with APS had higher levels. GDF-15 could have a potential role as a marker of mild cognitive impairment. Further studies are necessary to establish this finding.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aranda Cano E, Roldan Ortega J, Juárez-Vicuña Y, Sánchez Muñoz F, Palafox Sosa I, Viruel-Mejia L, Vera Bustamante D, Silveira Torre L, Vargas Guerrero A, Quintanar-Cuevas M, Bautista Jímenez E, Martinez-Martinez L. Association of Cognitive Impairment Measured by Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Plasma Levels of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Patients with Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-cognitive-impairment-measured-by-montreal-cognitive-assessment-and-plasma-levels-of-growth-differentiation-factor-15-in-patients-with-antiphospholipid-antibody-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-cognitive-impairment-measured-by-montreal-cognitive-assessment-and-plasma-levels-of-growth-differentiation-factor-15-in-patients-with-antiphospholipid-antibody-syndrome/