Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriasis is a common feature of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) occuring in approximately 10% of patients with axSpA. It has been presumed that such an association may be associated with a particular phenotype of the disease, which has not been extensively investigated so far. The purpose of the study was to analyze the association between clinical phenotype and radiographic progression and skin psoriasis in patients with axSpA.
Methods: Altogether 210 patients with axSpA (115 with radiographic and 95 with non-radiographic axSpA) were included in the analysis. Radiographs of the spine and sacroiliac joints (SIJ) were scored by two readers in a randomly selected order according to the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score (mSASSS) and the grading system of the modified New York criteria. A sacroiliitis sum score was calculated as a sum of the grades for the left and right SIJ. Mann-Whitney analysis was performed for group comparisons. A multivariable regression analysis was performed to analyze the influence of of the psoriasis on radiographic progression.
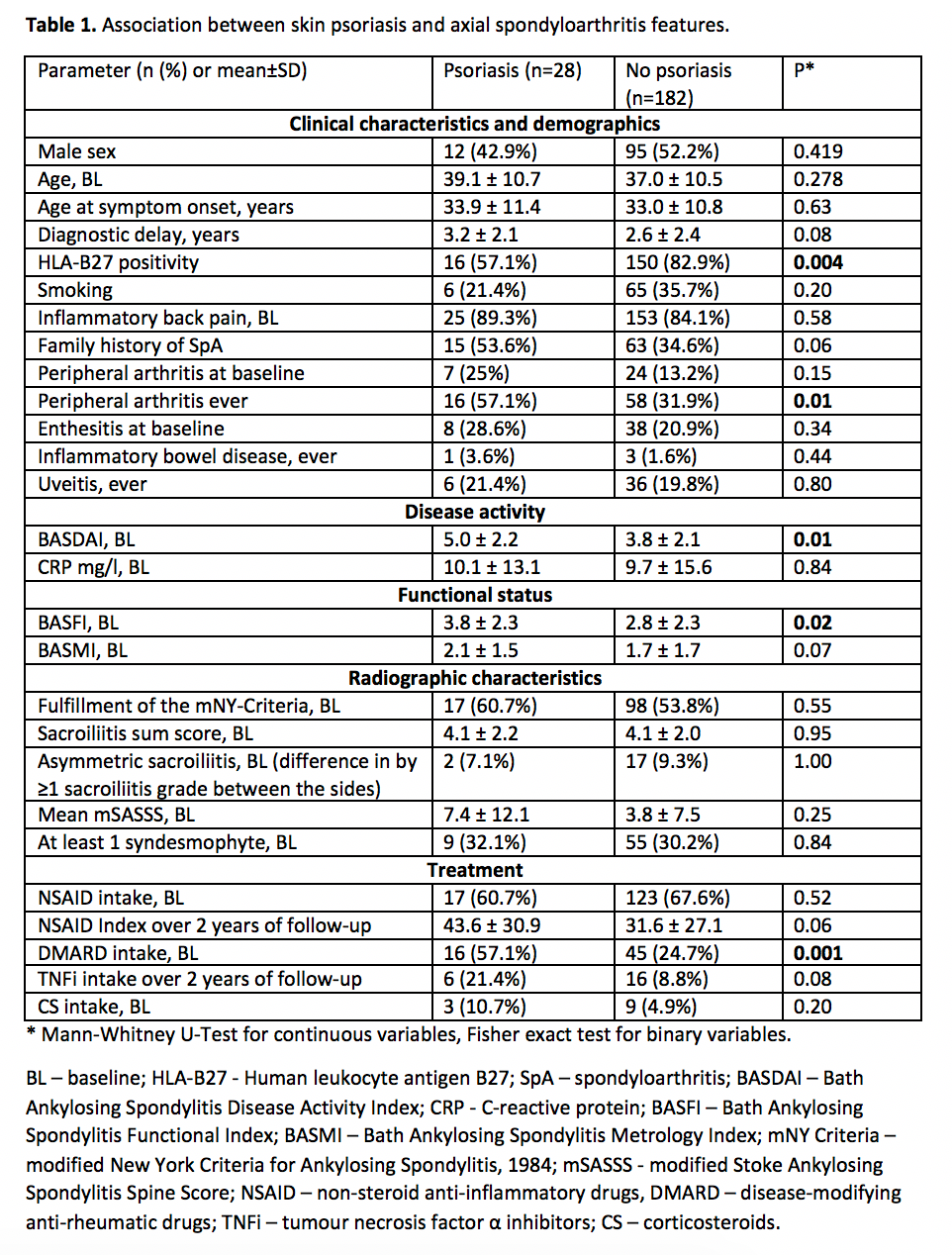
Results: Overall, 28 patients (13.3%) with axSpA had skin psoriasis. Patients with psoriasis were less frequently HLA-B27 positive, had higher anamnestic prevalence of peripheral arthritis (16 (57.1%) vs. 58 (31.9%), p=0.01), higher disease activity (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) 5.0 ± 2.2 and 3.8 ± 2.1, respectively, p=0.01) and worse physical function (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) 3.8 ± 2.3 and 2.8 ± 2.3, respectively, p=0.02) They were also more frequently treated with DMARDs. Baseline radiographic characteristics were comparable between the groups (Table 1). Radiographic progression was generally comparable between the groups. (Table 2). In a multivariable regression analysis (adjusted for the smoking status, sex, NSAID intake, presence of syndesmophytes at the baseline and time-averaged ASDAS), there was no significant association of psoriasis with radiographic progression in the spine (OR 2.93, 95% CI 0.81 to 10.58) or sacroiliac joints (OR 1.98, 95% CI 0.72 to 5.43).
Conclusion: Presence of skin psoriasis in patients with axSpA was associated with HLA-B27 negativity, peripheral arthritis, higher disease activity and worse functional status and did not impact the radiographic progression in axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Protopopov M, Proft F, Sieper J, Haibel H, Rudwaleit M, Poddubnyy D. Association of Clinical and Radiographic Phenotype of Axial Spondyloarthritis and Skin Psoriasis: Results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-clinical-and-radiographic-phenotype-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-skin-psoriasis-results-from-the-german-spondyloarthritis-inception-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-clinical-and-radiographic-phenotype-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-skin-psoriasis-results-from-the-german-spondyloarthritis-inception-cohort/