Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Critically ill patients with COVID-19 infection have a profound hypercoagulable state and can often develop thromboses in many different vascular beds. Given the presence of anti-phospholipid antibodies among COVID-19 patients reported previously, we hypothesized that poor outcomes and thrombosis could also be promoted by autoimmunity. In this retrospective case control analysis, we aimed to evaluate associations between aPL titers, clinical outcomes and mortality in hospitalized patients admitted with COVID-19 infection.
Methods: We analyzed 138 electronic medical records of patients who were admitted to NYU Langone Hospital – Long Island between the months of March-April 2020 with findings of COVID-19 positivity via PCR and who had aPL titers determined. Patients with elevated titers of beta-2-Glycoprotein IgG, IgM, IgA and/or cardiolipin IgG, IgM, IgA were compared to those who were not elevated. Patients with positive lupus anticoagulant titers only were excluded due to prevalent use of anti-coagulation during this time.
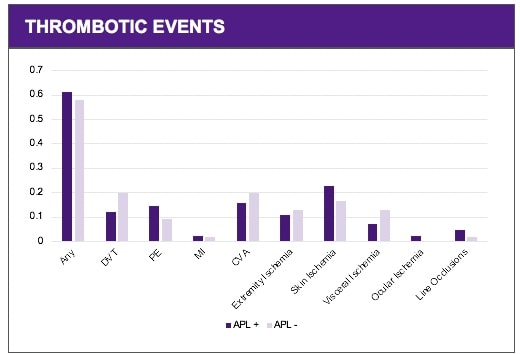
COVID-19 positive patients with aPL titers were assessed for clinical events (including DVT, PE, MI, CVA, extremity ischemia, skin ulcerations, visceral thrombosis and ocular and line occlusions) and mortality. The control group included patients that were negative for aPL antibody titers. Associations between Anti-Phospholipid (aPL) titer positivity and clinical events was assessed by Chi-square analysis using Fisher’s exact test.
Results: The predominant aPL species that was noted in COVID-19 patients was anti-cardiolipin IgM. Of those patients with elevated antibody titers, cardiolipin IgM, IgG, IgA, and β2GPI antibodies were prevalent at rates of 98.9%, 26.7%, 19.2%, and 16.5%, respectively. Multiple aPL isotypes were detected in several patients.
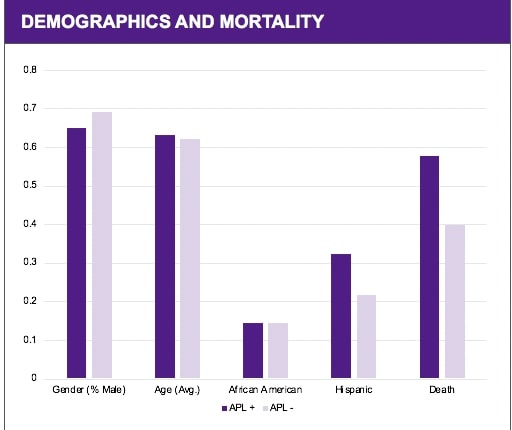
There was a positive association between aPL positivity and elevations in IL-6, CRP, D-dimer, and LDH (P< 0.05). There was an increased incidence of clinical events in patients with COVID-19 and positive aPL titers (52/83 or 62%) compared to those who were aPL negative (32/55 or 58% ), however this association was not statistically significant. No significant association was detected between positive aPL titers and gender, age, or self-identified ethnicity. An increased incidence of ARDS and a rising serum creatinine was noted in the aPL positive group (P = 0.03 and P= 0.05 respectively). A significant increase in mortality was identified for the aPL positive group (P=0.01).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that aPL titers may provide insight into disease prognosis and outcome in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Despite lack of significant association with discrete thrombotic events, association of aPL positivity with rising serum creatinine and ARDS suggest that aPL may contribute to end organ dysfunction through enhanced microthrombosis, resulting in increased mortality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yaich D, Ptak B, Roellke E, Miller E, Kim J, Gaztanaga J, Drewes W, Ciancarelli J, Divers J, Winner M, Rapkiewicz A, Carsons S. Association of Anti-phospholipid Antibodies (aPL) with Poor Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-anti-phospholipid-antibodies-apl-with-poor-clinical-outcomes-in-hospitalized-patients-with-covid-19/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-anti-phospholipid-antibodies-apl-with-poor-clinical-outcomes-in-hospitalized-patients-with-covid-19/