Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease. The serum uric acid/serum creatinine ratio (SUA/SCr), which represents uric acid levels in the blood with normalized renal function, is associated with an increased cardiovascular risk. Strong associations have been demonstrated between hyperuricemia and the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with RA. The association between SUA/SCr and the presence of carotid plaque (CP) in patients with RA has not been established. Our objective was to compare the relationship between SUA/SCr and the presence of CP in patients with RA.
Methods: A cross-sectional, observational, and descriptive study was conducted where patients aged 40 to 75 years who met the ACR/EULAR 2010 classification criteria for RA were recruited. Patients with a history of cardiovascular disease, overlap syndrome, or pregnancy were excluded. Biochemical profiles were performed. SUA/SCr was calculated using the formula SUA/SCr= Serum Uric Acid / Serum Creatinine. Carotid ultrasound was performed by a board-certified radiologist, blinded to clinical information. The presence of carotid plaque (CP), defined as a diffuse thickness of the carotid intima-media (CIMT) ≥1.2 mm or a focal thickness ≥ 0.5 mm, was assessed to calculate serum SUA and SCr levels. The distribution was evaluated using the Kolgomorov-Smirnov test. Comparisons were made with Chi-square, Fisher’s exact, Student’s T, or Mann Whitney U tests, as appropriate. A p< 0.05 was taken as statistically significant.
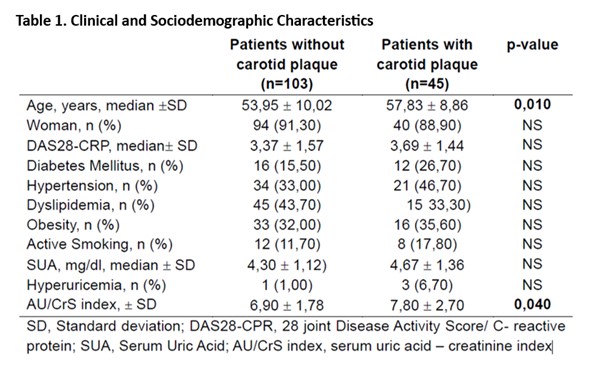
Results: Our study included 148 patients, mainly women (n=134, 90.5%), the mean age was 55 +/- 9.81 years. The presence of CP was reported in 30.4% of patients. The overall average for AU was 4.43 +/- 1.21 and 7.19 +/- 2.13 for SUA/SCr. Demographic characteristics can be seen in Table 1. Patients with CP had higher SUA/SCr than those without CP (7.80 +/- 2.70 vs. 6.90 +/- 1.78; p=0.040). There were no significant differences in UA levels (4.67 +/- 1.36 vs.4.30 +/- 1.12; p=0.1079).
Conclusion: In our cohort, SUA/SCr was higher in patients with CP, despite showing no significant difference in uric acid levels. However, the performance of carotid ultrasounds must be part of an integral cardiovascular evaluation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guajardo Aldaco A, Galarza-Delgado D, Colunga Pedraza I, Azpiri-Lopez j, Cardenas-de la Garza J, Arvizu-Rivera R, Elizondo-Benitez M, Gonzalez-Gonzalez V, Salcedo-Almanza D. Association Between Serum Uric Acid/Serum Creatinine Index and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-serum-uric-acid-serum-creatinine-index-and-carotid-plaque-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-serum-uric-acid-serum-creatinine-index-and-carotid-plaque-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/