Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
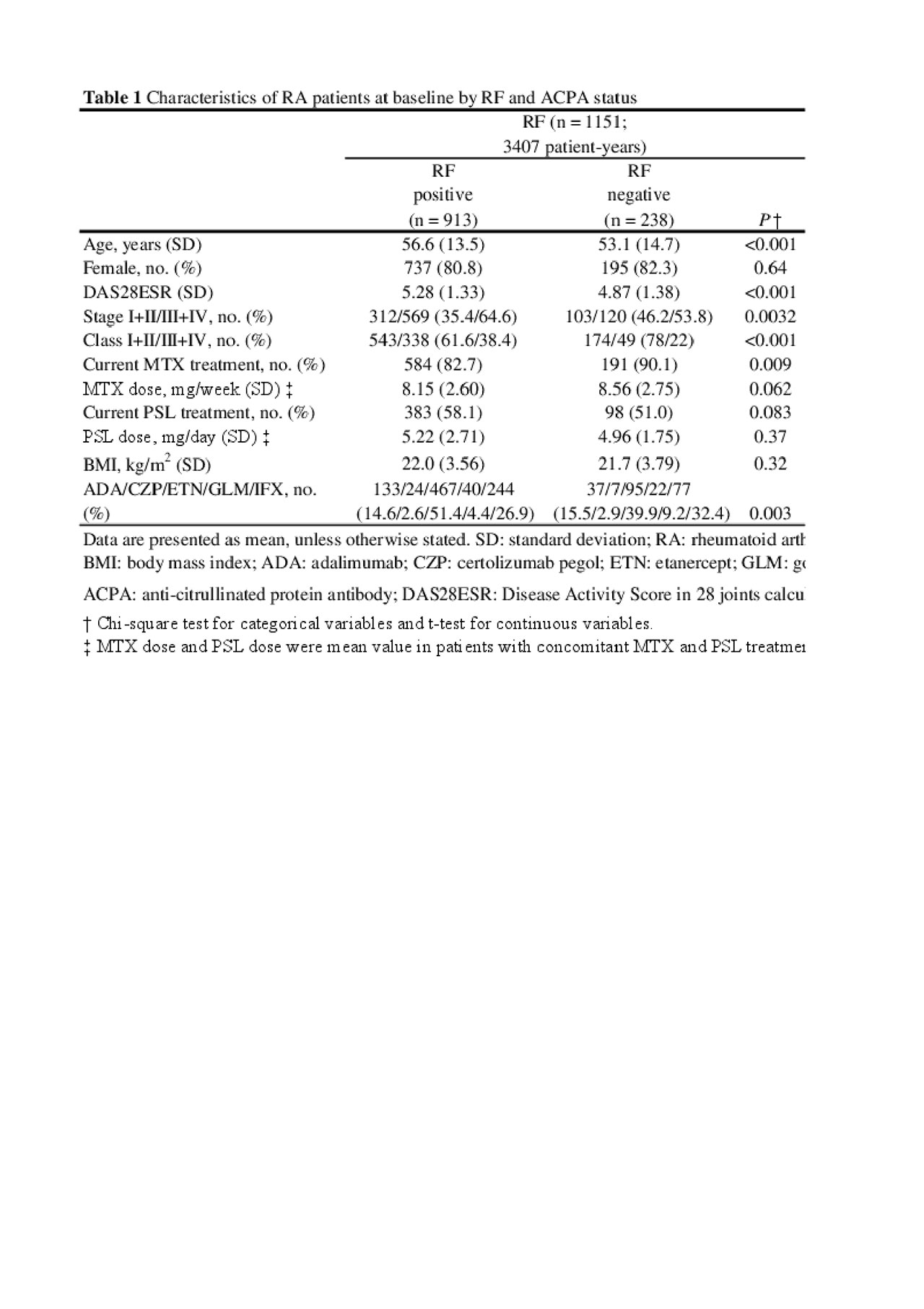
Background/Purpose: Discontinuation of biologic therapy in rheumatoid arthritis is attributable to various reasons, with the most important cause being insufficient response. In this study, we investigated the association between rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti–citrullinated protein autoantibody (ACPA) status and the discontinuation of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) therapy due to ineffectiveness in bio-naïve rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
Methods: This study included patients enrolled in the Tsurumai Biologic Communication Registry in Japan. The crude comparison of TNFi discontinuation due to insufficient response between seropositive and seronegative patients was analyzed using the cumulative incidence function of competing events and Gray test. We assessed the associations between baseline characteristics and discontinuation of TNFi treatment due to insufficient response using Fine-Gray proportional hazard regression. Fine-Gray proportional hazard analysis considered competing events of interest, including insufficient response, adverse event, palliation, and personal reasons.
Results: Of 1237 patients evaluated, 79.3% were positive for RF and 85.4% for ACPA; 72.6% were double positive and 11.1% were double negative. TNFi therapy had been discontinued because of insufficient response at 200 weeks in 19.8% RF-positive, 16.7% RF-negative, 23.0% ACPA-positive, and 13.8% ACPA-negative patients. There was a significantly higher discontinuation rate due to insufficient response in ACPA positive patients than in ACPA negative patients using Gray test, with a similar trend as that for RF status. RF positivity was significantly predictive of the discontinuation of TNFi treatment due to insufficient response using Fine-Gray proportional hazard regression analysis after adjusting for baseline characteristics, including age, sex, stage, class, disease activity at baseline, methotrexate use, and prednisolone use (hazard ratio 1.73 [95% confidence interval 1.07–2.80]).
Conclusion: Using Fine-Gray proportional hazard regression, we demonstrated that RF positivity was related to a higher discontinuation rate of TNFi treatment due to insufficient response in bio-naïve RA patients.
A. Discontinuation of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors therapy due to ineffectiveness, stratified by rheumatoid factor -RF- status -P = 0.14 by Gray test-.
B. Discontinuation of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors therapy due to ineffectiveness, stratified by anti-citrullinated protein antibody -ACPA- status -P < 0.05 by Gray test-.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogawa Y, Takahashi N, Kojima T, Ishiguro N. Association Between Seropositivity and Discontinuation of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors Due to Insufficient Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-seropositivity-and-discontinuation-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-due-to-insufficient-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-seropositivity-and-discontinuation-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-due-to-insufficient-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/