Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In associated ANCA vasculitis (AAV), rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (GN) is one of the most serious complications. In 40% of cases they progress to chronic kidney disease (CKD), others to hemodialysis (HD) or death. According to the classification of the European AAV group (EUVAS), the histopathological findings of the biopsy can predict the outcome renal with better results in the focal class, followed by the mixed and sclerotic class. Our objective is to evaluate the association between outcome renal and histopathological findings of patients with AAV
Methods: Cohort study, retrospective patients with AAV (ACR 1990 / Chapell Hill 2012) and rapidly progressive GN of three centers of high complexity in the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires between January 2012 – December 2018. Demographic, clinical, analytical variables were recorded and follow-up for one year, at diagnosis. The immunoserology patterns (ANCA and PR3 / MPO), Five Factor Score (FFS), BVASv3 (0-63) and VDI (0-64) per year are evaluated. Renal biopsies (optical microscopy and immunofluorescence) were reviewed. The glomerular lesions were classified according to EUVAS and its association with CKD, HD and death was evaluated
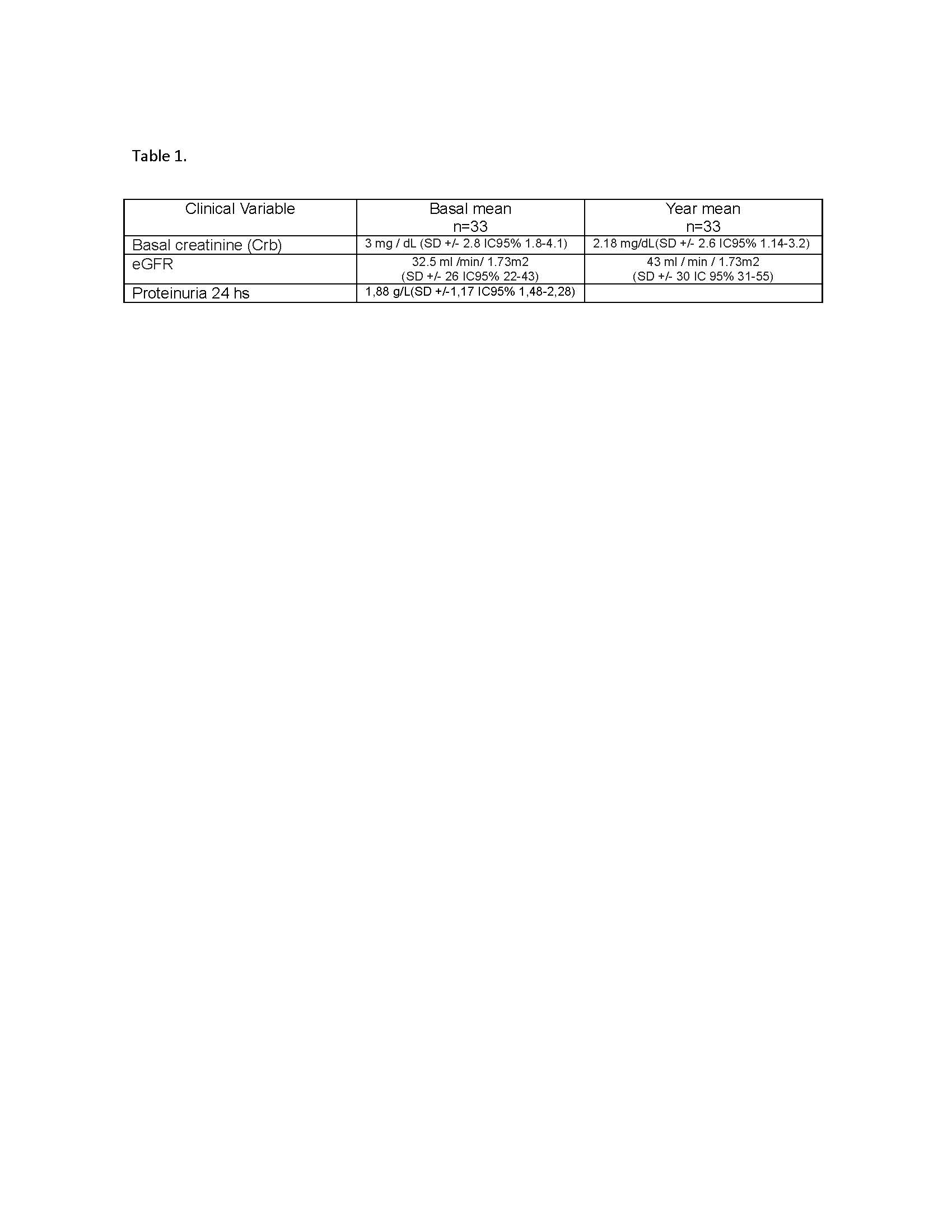
Results: 33 patients were included, 57.6% males. Mean age 51 (SD +/- 16 IC 95% 45-58). GPA 65%, and MPA 33%. ANCAc n: 20, PR3 52%. ANCAp n: 13, MPO 30%. Histopathology: Glomerular lesions: Focal 18%, Crescentic 27% Sclerotic 12% and Mixed 43%. Grade 1: 24%, grade 2: 27% and grade 3: 49%. Fibrinoid necrosis in 61%. Global Interstitial Commitment (tubilitis, tubular atrophy, fibrosis and inflammatory infiltrate) 97%; grade 0: 12%, grade 1: 58%, grade 2: 30%. cell infiltrate in 85% monomorphonuclear 73%, polymorphonuclear 6%. Vascular damage (subintimal sclerosis) 79%: mild 46%, moderate in 36% and severe 11%. The patients presented severe clinical compromise with a median BVASv3 15 (RIC 7-48). FFS: I: 24%; II: 42%; III: 18%; IV: 6%. PCR 23 (RIC 1-321) and VDI at year 3 (RIC 2-5), the baseline clinical variables and at one year are summarized in Table 1.
HD requirement at the start of 36%, achieving independence of HD (HDI) per year by 30%, the variables associated with HDI were Crb and eGFR p = 0.014 and p = 0.012 respectively and focal class with p = 0.032. The CKD was 33%, with the mixed class being the most associated p = 0.017. Relapse in 30% associated with the type of glomerular lesion with p = 0.006. Death 4 (activity and infection). The association between tubulointerstitial involvement and CKD and HDI was not significant.
Conclusion: Crb and the glomerular filtration rate were the best predictors of CKD and HDI. The mixed class was associated with CKD. We found an association between the focal class and the HDI. Relapses are associated with the type of glomerular pattern. The percentage of progression to CKD was low and high rate of HDI. There was no association between tubulointerstitial involvement and progression to CKD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vergel Orduz L, Brigante A, Marino D, Perrotta N, Hassan R, Verna G, Hamaui A, Kerzberg E, Dubinsky D. Association Between Outcome Renal, Clinical Variables and Findings of Renal Biopsy in Patients with ANCA Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-outcome-renal-clinical-variables-and-findings-of-renal-biopsy-in-patients-with-anca-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-outcome-renal-clinical-variables-and-findings-of-renal-biopsy-in-patients-with-anca-vasculitis/