Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is recommended and widely prescribed as the first-line, evidence-based therapy for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Previous studies have demonstrated a significant effect of MTX on biologic therapy; however, these were mainly conducted on bio-naïve patients. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the association of the concomitant use of MTX with efficacy of biologics in RA patients who switched to second-line biologics in a real-world clinical practice setting.
Methods: This study included patients enrolled in the Tsurumai Biologic Communication Registry. RA first-time switchers were eligible for inclusion. To assess the working hypothesis that combination therapy is superior to biologic monotherapy, the primary outcome measure was defined as a change in DAS28-ESR at 24 weeks. Multiple linear regression analysis adjusted for covariates was employed. Additionally, multiple imputation analysis was performed to provide missing data. Excluding individuals with missing data, known as glistwise deletionh, may yield biased estimates. All analyses were conducted in EZR version 1.35 and the package mice for the multiple imputation.
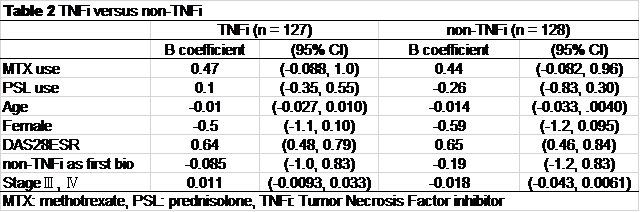
Results: Using linear multivariate regression models, we identified a significant association of the use of MTX with the treatment efficacy of second-line biologics (Table 1). This association did not differ between patients using TNF inhibitors and those using non-TNF inhibitors (Table 2). In the present study, the results from the multiple imputation analysis were consistent with those from the complete case analysis (Table 3).
Conclusion: In our multicenter study using a multiple imputation method, concomitant MTX was found to be associated with an improved second-line biologic therapy in a non-trial, real-world clinical practice setting.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogawa Y, Takahashi N, Ishiguro N, Kojima T. Association between Methotrexate Use and Effects of Treatment with a Second Biologic Agent in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multiple Imputation Approach [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-methotrexate-use-and-effects-of-treatment-with-a-second-biologic-agent-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multiple-imputation-approach/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-methotrexate-use-and-effects-of-treatment-with-a-second-biologic-agent-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multiple-imputation-approach/