Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In general, the concomitant use of methotrexate (MTX) and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDS) plays an important role in treating bio-naïve patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA); however, whether concomitant use of MTX is associated with the effects of second bDMARDS treatment in RA patients for whom first bDMARDS treatment has failed remains unclear.
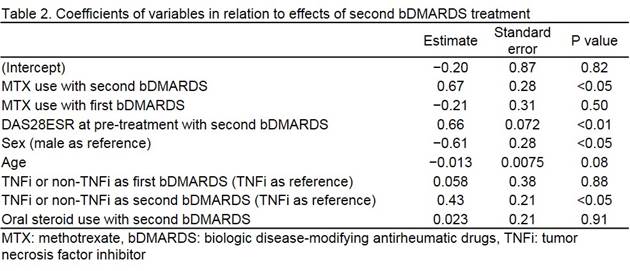
Methods: We used demographic and clinical data obtained from the Tsurumai Biologics Communication Registry, which comprises the Nagoya University and 20 affiliated hospitals in Japan. Patients aged 20–80 years who fulfilled the ACR 1987 revised or the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA were selected, and only those switching to second bDMARDS treatment were included. Linear multiple regression analysis was used to assess the association between MTX use and effects of second bDMARDS treatment, as defined by DAS28-ESR improvement at week 24. Unstandardized coefficients were calculated. Adjustment variables included sex, age, DAS28 at pre-treatment with second bDMARDS, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) or non-TNFi in RA treatments with first and second bDMARDS, MTX use with first bDMARDS, and glucocorticoid use with second bDMARDS.
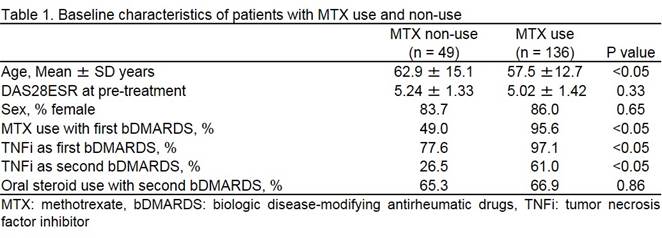
Results: Table 1 summarizes the baseline demographic and disease characteristics of the patients. Some characteristics differed between patients with MTX use and non-use; however, they were adjusted using linear multiple regression analysis. Table 2 presents the unstandardized coefficients. The value of interest was 0.67 (P < 0.05), suggesting that DAS28 improvement in second bDMARDS treatment with MTX is superior to that without MTX. Other variables affecting the treatment effects were sex and TNFi or non-TNFi with second bDMARDS, which are well-known influential factors for biologic therapy.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that the concomitant use of MTX was independently associated with increased effects of second bDMARDS treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogawa Y, Takahashi N, Kojima T, Ishiguro N. Association Between Methotrexate Use and Effects of Treatment with a Second Biologic Agent in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-methotrexate-use-and-effects-of-treatment-with-a-second-biologic-agent-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-methotrexate-use-and-effects-of-treatment-with-a-second-biologic-agent-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/