Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To investigate the laboratory indicators of disease activity during follow-up of Takayasu’s arteritis(TAK).
Methods: Electronic data of 588 patients with TAK enrolled in the Chinese Registry for Systemic Vasculitis (CRSV) from 2013 to April 30 of 2019 were exported for analysis. Disease activity was judged with clinical manifestations, BVAS and VDI scoring, laboratory results and vascular imaging including Doppler and/or CTA by a senior rheumatologist in each visit. Records of visit with repeated vascular imaging examinations were collected,and erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR), the serum levels of high sensitive C-reactive protein(hsCRP), interleukin-6(IL6), and tumor necrosis factor-a(TNFa) of these patients in each visit were analyzed for the association with disease activity by logistic regression.
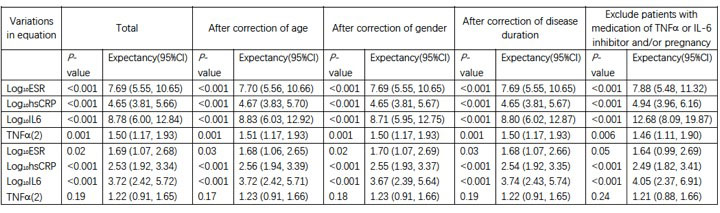
Results: 1483 records of visit were collected. After transformation, log10ESR, log10hsCRP and log10IL6 were found to be distributed normally. Due to the non-normal distribution pattern, TNFa was stratified into 2 groups by the upper normal range in healthy people(< 8.1pg/ml).In univariate logistic regression analysis, log10ESR, log10hsCRP, log10IL6 and TNFa were strongly associated with the disease activity respectively. But in multivariate logistic regression analysis, the association between TNFa and disease activity disappeared. After correction of age, gender or disease duration, the result of logistic regression analysis were similar.After exclusion of records from the patients with medication of TNFa and/or IL6 inhibitors, and the patients with pregnancy during follow-up, the results of univariate logistic regression analysis were similar, but in multivariate analysis association between log10ESR and disease activity disappeared.(Table 1)
Conclusion: Repeated vascular imaging examination in each follow-up visit combined with other clinical evaluation methods had proved the reliability for using ESR, hsCRP, IL6 and TNFa as indicator in evaluation of disease activity in patients with TAK. The effect of hsCRP and IL6 may be stronger than ESR and TNFa.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
LI J, Yang Y, WANG Y, Zhao J, Li M, Tian X, Zeng X. Association Between Acute-phase Reactants, interleukin-6(IL6), Tumor Necrosis Factor-a(TNFa) and Disease Activity in Takayasu’s Arteritis During Follow-up with Repeated Evaluation of Vascular Imaging Manifestations [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-acute-phase-reactants-interleukin-6il6-tumor-necrosis-factor-atnfa-and-disease-activity-in-takayasus-arteritis-during-follow-up-with-repeated-evaluation-of-vascular/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-acute-phase-reactants-interleukin-6il6-tumor-necrosis-factor-atnfa-and-disease-activity-in-takayasus-arteritis-during-follow-up-with-repeated-evaluation-of-vascular/