Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. The long-term safety and clinical efficacy of tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily (BID) has been reported in patients (pts) with active RA up to 105 months.1-3 We evaluated the long-term effects of tofacitinib on progression of radiographic structural damage in pts with RA from a long-term extension (LTE) study.
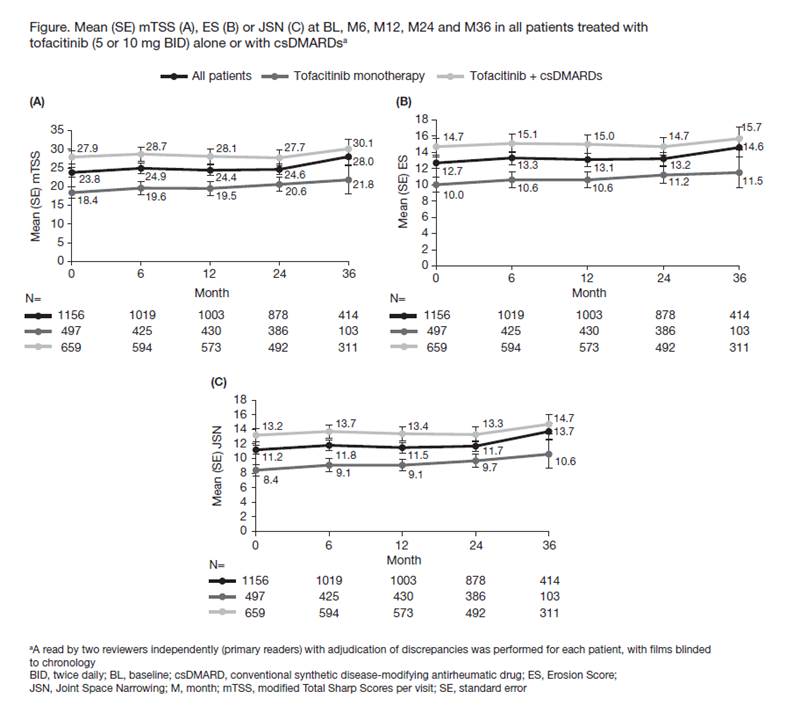
Methods: Data were analyzed from an open-label LTE (NCT00413699 [ongoing; database not locked at Mar 2017 data-cut]) of pts with RA who participated in Phase 2 (NCT01164579, methotrexate [MTX] naïve, early RA) or Phase 3 (NCT00847613, MTX-IR; NCT01039688, MTX naïve) tofacitinib index studies. Baseline (BL) was defined as last visit in the index study prior to LTE entry. In the index studies pts received tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID as monotherapy (mono) or with conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs); at the physicians’ discretion pts could switch tofacitinib dose in the LTE, and were assigned to 5 mg BID if average total daily dose was <15 mg/day or to 10 mg BID if ≥15 mg/day. Outcomes to evaluate structural damage from BL to Month (M)36 included: mean and mean change (Δ) from BL in van der Heijde modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS), Erosion Score (ES), and Joint Space Narrowing Score (JSN); % of pts with no radiographic progression (ΔmTSS ≤0.5); and % of pts with no new erosions (ΔES≤0.5). Observed data were analyzed descriptively.
Results: A total of 1156 pts from the index studies were pooled in the LTE radiographic analysis; x-rays available in 88% (n=1019) of pts at M6; 497 pts received tofacitinib mono (5 mg BID, n=42; 10 mg BID, n=455) and 659 pts received tofacitinib with csDMARDs (5 mg BID, n=53; 10 mg BID, n=606). N at M12 was 86.8%, at M24 76.0%, and at M36 35.8% of the BL value. From LTE entry, mean duration of tofacitinib treatment in the total population was 1113 days (range 21–2396), and mean mTSS, ES, and JSN only slightly increased from BL to M36 (Figure). Mean (standard error [SE]) ΔmTSS was 0.25 (0.05) at M12 and 1.17 (0.28) at M36. Mean (SE) ΔES and ΔJSN were 0.21 (0.03) and 0.24 (0.02) at M12 and 0.68 (0.17) and 0.78 (0.13) at M36. The % (SE) of all tofacitinib-treated pts with radiographic non-progression decreased from 91.2% (0.9) at M6 to 84.5% (1.1) at M12 and 72.2% (2.2) at M36, and the % of pts with no new erosions decreased from 96.0% (0.6) at M6 to 92.3% (0.8) at M12 and 85.3% (1.7) at M36. Similar trends were observed for all endpoints from BL to M36 in the tofacitinib mono and csDMARD groups (Figure); change from BL in mTSS, ES, and JSN score was similar at most time points in the csDMARD and mono populations (data not shown).
Conclusion: Structural damage progression was limited during treatment with tofacitinib alone or with csDMARDs for up to 3 years in pts with RA.
References
1. Wollenhaupt J et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015; 67 Suppl 10; A1645
2. Wollenhaupt J et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68 Suppl 10; A1647
3. Wollenhaupt J et al. J Rheumatol 2014; 41: 837–852
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van der Heijde D, Wollenhaupt J, Cohen SB, Strengholt S, Terry K, DeMasi R, Kwok K, Lazariciu I, Wang L. Assessment of Radiographic Progression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Tofacitinib: Data from an Open-Label Long-Term Extension Study over 3 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-radiographic-progression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib-data-from-an-open-label-long-term-extension-study-over-3-years/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-radiographic-progression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib-data-from-an-open-label-long-term-extension-study-over-3-years/