Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster III: Biosimilars and New Compounds
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
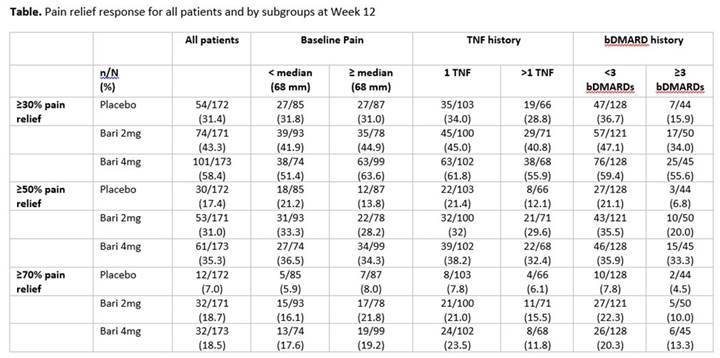
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI) 2 mg and 4 mg once daily demonstrated significant clinical improvements compared to placebo in the phase 3 study of RA patients on 1 or 2 cDMARDs with an inadequate response or intolerance to ≥1 tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (bDMARD-IR) (RA-BEACON).1 In this RA population, patients often experience pain, a key factor influencing quality of life. The objective of this post hoc analysis was to characterize the effects of BARI on pain relief by baseline pain and RA treatment history.
Methods: 527 patients were randomized to placebo (n=176), BARI 2 mg (n=174), or 4 mg (n=177) once daily for 24 weeks. The time of the primary endpoint was Week 12. Pain was assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS, 0-100 mm) at each study visit. The proportion of patients achieving ≥30%, ≥50%, and ≥70% pain relief at Week 12 was compared between BARI 2 mg or 4 mg vs placebo using logistic models. The treatment comparisons within each subgroup category (pain < median [68] vs ≥median, number of prior TNF inhibitors [1 vs >1] and prior bDMARDs [<3 vs ≥3]) on pain relief were performed. Missing pain values were imputed using modified last observation-carried-forward (mLOCF).
Results: Mean baseline pain scores were 65, 62, and 66 mm for placebo, BARI 2 mg, and BARI 4 mg, respectively. Approximately 40% of patients had received >1 TNF inhibitor and a quarter of patients had received ≥3 bDMARDs, representing patients with highly refractory disease. At Week 12, significantly more patients achieved ≥30%, ≥50%, and ≥70% pain relief with BARI 2 mg or 4 mg vs placebo (P<0.05, for all comparisons).2 Consistent results were observed regardless of baseline pain (Table). Prior TNF inhibitor history appeared to influence the achievement of ≥70% pain relief, but had limited effect on the ≥30% and ≥50% pain thresholds. Variability in response for the 3 treatment groups was observed at the different pain relief thresholds for patients with <3 vs ≥3 bDMARDs. Regardless of treatment history, patients receiving BARI 2 mg or 4 mg were more likely to reach all pain relief thresholds than placebo.
Conclusion: BARI 2 mg or 4 mg provided greater pain relief in bDMARD-IR patients with RA compared with placebo in all patients and in patients with different baseline pain severity and prior treatment history.
References: 1Genovese MC, et al., N Engl J Med 2016;374:1243-52; 2Taylor PC, et al., Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:788
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pope JE, Quebe A, Zhu B, Sun L, Gaich CL, de Leonardis F, Cardoso A, Genovese MC. Assessment of Pain Relief with Baricitinib By Treatment History in Patients with Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-pain-relief-with-baricitinib-by-treatment-history-in-patients-with-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-pain-relief-with-baricitinib-by-treatment-history-in-patients-with-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/