Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Vobarilizumab is a Nanobody consisting of an anti-IL-6R domain and an anti-human serum albumin domain in development for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Main efficacy and safety results of both RA phase 2b studies with vobarilizumab when used in combination with methotrexate (ALX0061-C201) and as monotherapy (ALX0061-C202) were previously reported (ref 1 and 2).
The effect of vobarilizumab on different pharmacodynamic (PD), cartilage degradation and joint inflammation biomarkers was investigated in both studies.
Methods: In study ALX0061-C201, 345 patients were equally randomized to receive during a 24-week treatment period one of the four subcutaneous (s.c.) vobarilizumab dosing regimens (75 mg q4w, 150 mg q2w, 150 mg q4w, 225 mg q2w) or placebo q2w. In study ALX0061-C202, 251 patients were equally randomized to receive during a 12-week treatment period one of the three dosing regimens of s.c. vobarilizumab (150 mg q2w, 150 mg q4w, or 225 mg q2w). An open-label tocilizumab (TCZ) arm was included to obtain parallel descriptive information.
The effect of vobarilizumab and TCZ on the PD biomarkers soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), C-reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was evaluated descriptively. In addition, matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) was evaluated as a cartilage degradation biomarker and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 (CXCL13) as a joint inflammation biomarker. Using validated assays, all biomarkers were measured at baseline and over time in serum, except for sIL-6R which was measured in plasma.
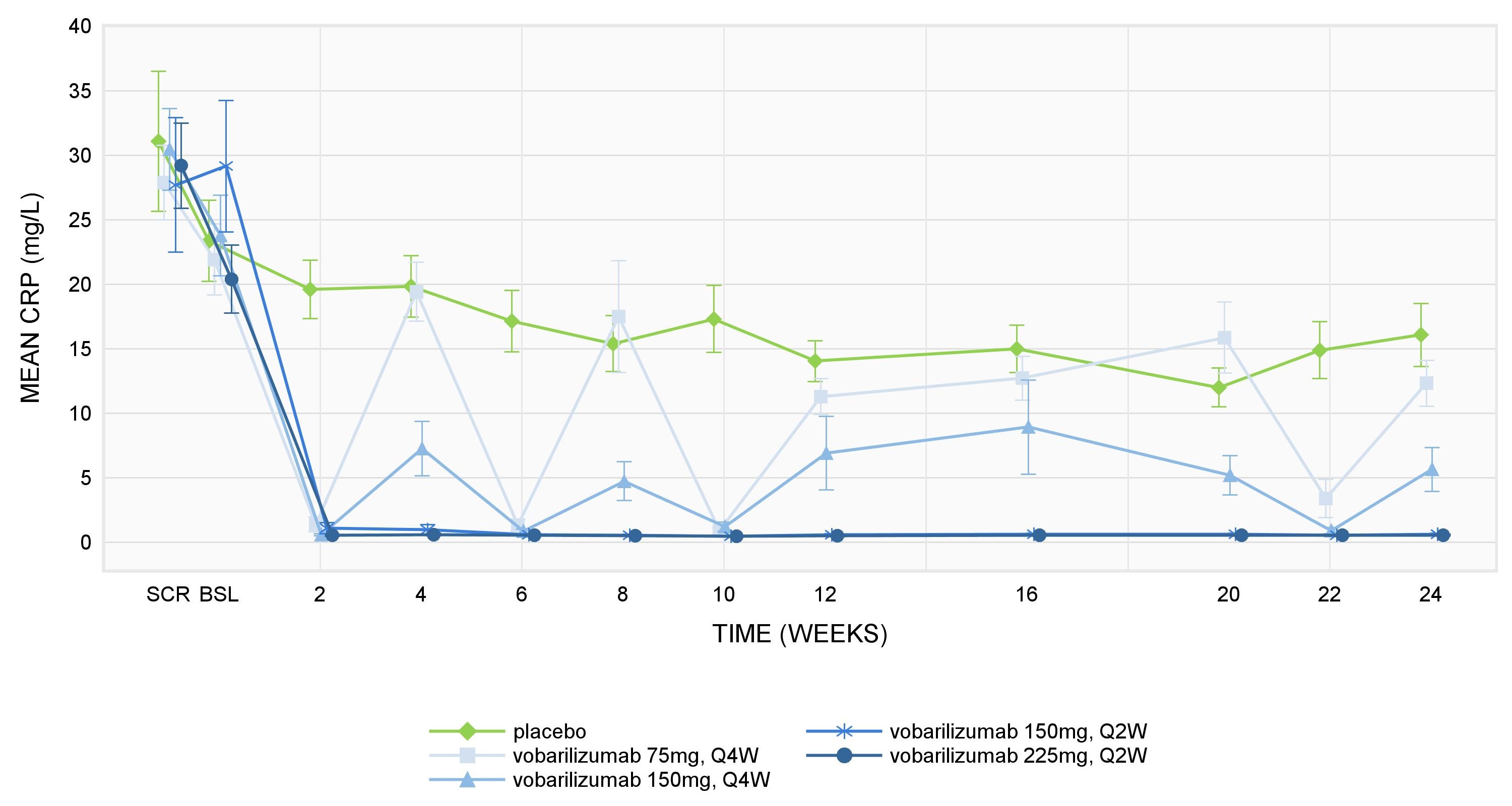
Results: As expected, based on vobarilizumab’s mechanism of action, mean plasma total sIL-6R concentrations increased following vobarilizumab administration and remained increased during the treatment period. A rapid decrease of the PD biomarkers CRP, fibrinogen and ESR was observed after the first administration of vobarilizumab. Over time, mean values of CRP and fibrinogen remained low for subjects in the 2 highest dosing regimens (i.e. 150 mg q2w and 225 mg q2w) (see Figure 1 for CRP results). ESR values remained low for all dosing regimens except for the 75 mg q4w dose used in ALX0061-C201 combination therapy study. Following administration of TCZ, comparable profiles were observed for the different PD biomarkers. Both vobarilizumab and TCZ also lead to a gradual decrease of MMP-3 and CXCL13. After vobarilizumab/TCZ treatment discontinuation, an increase of all biomarkers (except for sIL-6R) was observed.
Conclusion: The observed dose dependent PD biomarker responses and effects on cartilage degradation and joint inflammation biomarkers further support the strong potential for disease modifying activity of vobarilizumab in RA.
1. Weinblatt M. et al. Annual Scientific meeting of the Canadian Rheumatology Association, 2017
2. Dörner T. et al, EULAR 2017
Figure 1: Mean CRP ± SEM levels in ALX0061-C201 trial.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rinaldi M, Van Bogaert T, Van Roy M, Bontinck L, Hohlbaum A, Snoeck V, Dombrecht E, Van Beneden K, Schoen P, Ulrichts H. Assessment of Dose Dependent Effects of Vobarilizumab, an Anti-IL6 Receptor (IL-6R) Nanobody®, on Systemic Biomarkers in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Results of Two Phase 2b Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-dose-dependent-effects-of-vobarilizumab-an-anti-il6-receptor-il-6r-nanobody-on-systemic-biomarkers-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-results-of-two/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-dose-dependent-effects-of-vobarilizumab-an-anti-il6-receptor-il-6r-nanobody-on-systemic-biomarkers-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-results-of-two/