Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: DificuLtAR and ModAL, two spanish-language questionnaires that assess work difficulties and workplace adaptations, were originally developed and validated for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Their performance in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) remains unknown. Objective: (1) to validate DificuLtAR and ModAL in axSpA (2) Identify factors associated with work difficulties and the use of workplace modifications and adaptations reported by employed patients with axSpA.
Methods: An adaptation of the DificuLtAR for EspAax (DificuLtAx) questionnaire was made, Both questionnaires were applied to patients ≥18 years old, both genders, with a diagnosis of axSpA (ASAS-2009) and actively working. Cronbach’s alpha (DifficuLtAx=0.92 and ModAL=0.83) and construct validity were explored through factor analysis. The Eigenvalue values for a single factor (DificuLtAx=0.89 and ModAL=0.81) and correlation coefficients greater than 0.40 for all questions of both questionnaires after varimax rotation were aceptable. Spearman correlation coefficients, Mann-Whitney or Kruskal-Wallis tests, were calculated. (p < 0.05).
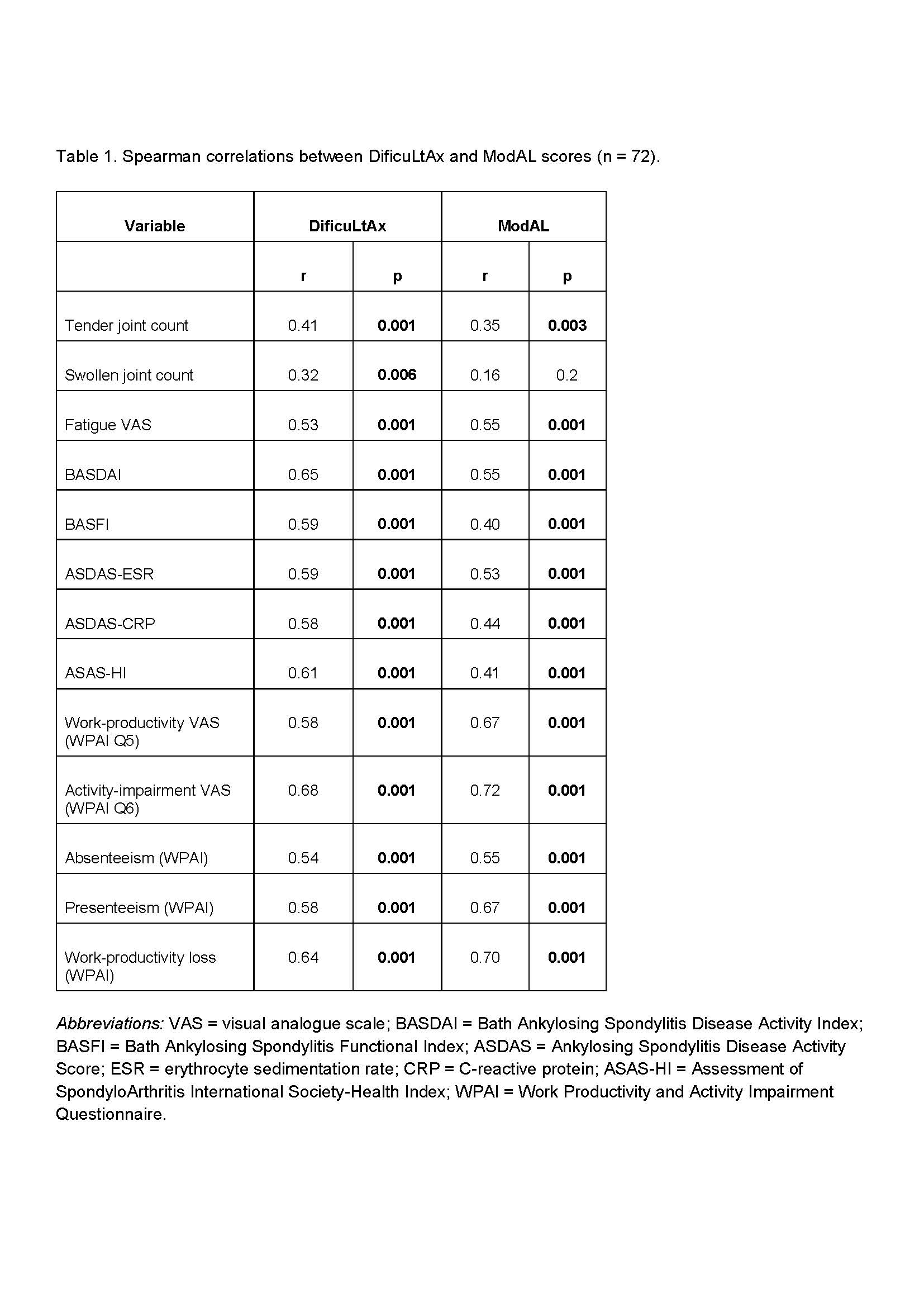
Results: 72 patients were included, 72% men, median age 42 years (IQR 37-53), disease duration 97 months (IQR 40-156), 54% B27positive, and 67% radiographic. The median ASDAS-PCR 2 (IQR 1-3) and BASFI 3.5 (IQR 2-5). 58% were in formal salaried employment and the median WPAI (labor productivity) was 0 (IQR 0-44). The greatest difficulties were sitting or standing for prolonged periods of time (75%) and working crouched (84%) and the most frequent modifications were taking breaks (78%) and furniture changes (45%). The median DificuLtAx 5 (IQR 2-9) and ModAL 3.5 (IQR 2-6), with a correlation between both of rho: 0.67 (p 0.001). See correlations Table 1. Female gender 5.5 vs 3.5 (p 0.001) and boss’s knowledge of the disease 4 vs 3 (p 0.05), were associated with greater modifications.
Conclusion: DificuLtAx and ModAL showed good reliability and construct validity. The main work difficulties were to remain seated or standing and to work crouching/kneeling, and the most frequent modifications were to take breaks and modify the furniture; these were more common in women and in those in whom the boss was aware of the disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
benegas m, Martire M, ferreryra L, Maldonado H, Airoldi C, Casalla L, Dapeña J, Saturansky E, Serrano E, Morbiducci J, Merce A, Zamora N, Flores Trejo J, Sommerfleck F, Buschiazzo E, Molina H, Castro C, Nieto R. Assessment of difficulties, modifications and use of work adaptations in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: validation of the DificuLtAx and ModAL questionnaires [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-difficulties-modifications-and-use-of-work-adaptations-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-validation-of-the-dificultax-and-modal-questionnaires/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-difficulties-modifications-and-use-of-work-adaptations-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-validation-of-the-dificultax-and-modal-questionnaires/