Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with SLE may be at increased risk for developing a venous thromboembolism (VTE), particularly in the postpartum period. The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) guideline for postpartum VTE prophylaxis is unique in its inclusion of “active” SLE as an actionable risk factor. In this guideline, a score ≥ 3 drives a formal recommendation for a 6-week prophylactic treatment course with enoxaparin. Although not defined, “active” SLE alone scores 3 points. The inclusion of SLE raises concerns regarding appropriate attribution and subsequent management decisions. The current study applied the RCOG model to a cohort of postpartum SLE patients to determine whether these patients a) qualify as having “active” SLE b) have other risk factors for VTE c) received the recommended prophylaxis and d) had a postpartum VTE.
Methods: The retrospective study comprised 55 pregnancies in 49 patients fulfilling criteria for classification of SLE based on ACR, SLICC or EULAR/ACR definitions consecutively seen over the last 5 years. Disease activity at delivery was assessed by the SLEPDAI using SELENA and Hybrid SELENA definitions for scoring proteinuria. Remission was assigned by applying the DORIS (Definitions of Remission in SLE) criteria. Patients not in remission were considered to have “active” SLE, even if a low level with only one clinical domain scored. RCOG scoring was calculated for each patient prior to and after delivery.
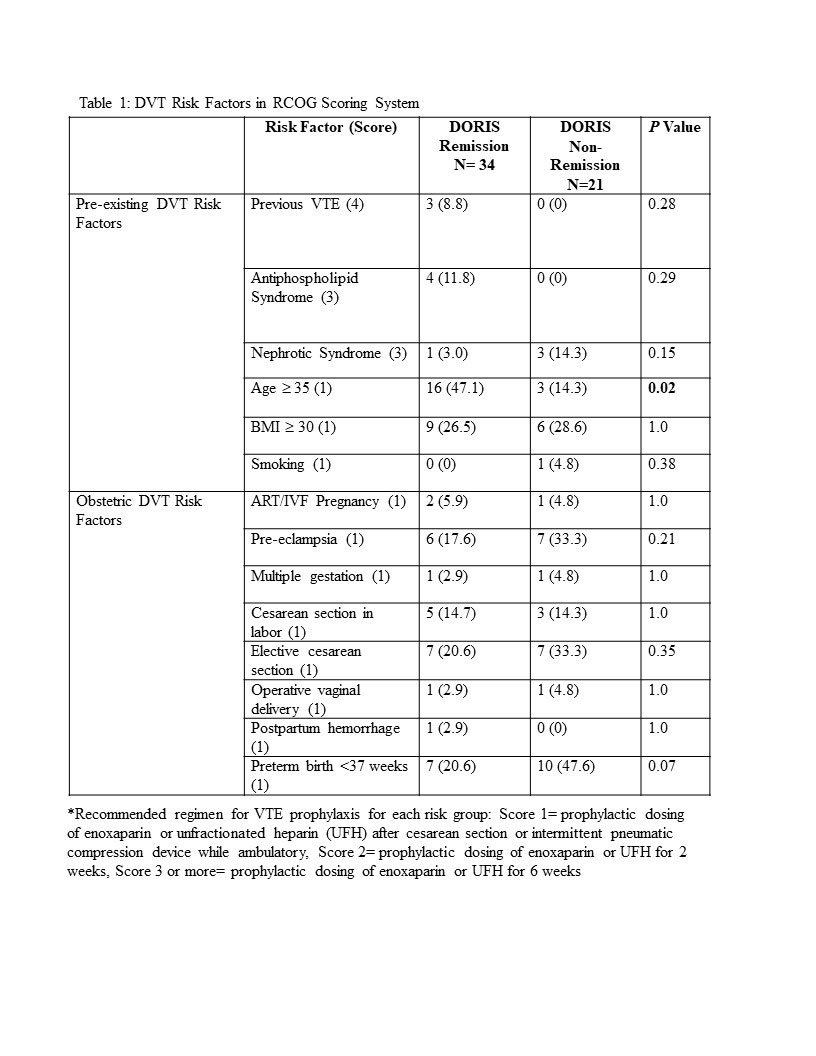
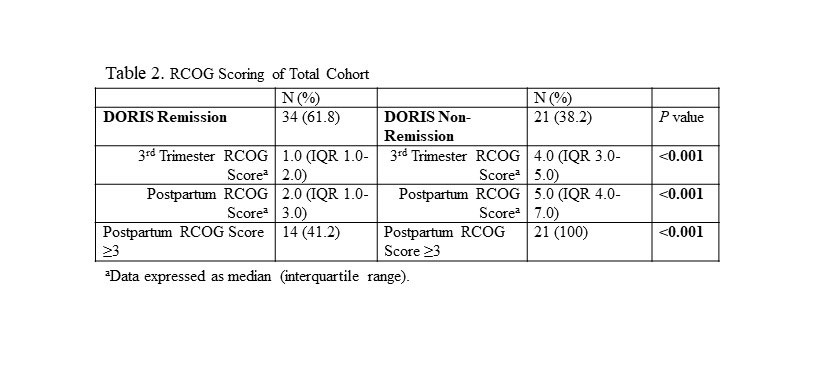
Results: The median age was 32 years (IQR 29-36 years) and the median BMI was 26.6 kg/m2 (IQR 23.0-30.9 kg/m2), with 49.1% African-American, 16.4% Asian, 29.1% White, 5.5% Other and 32.7% of Hispanic ethnicity. The median SELENA and Hybrid SELENA SLEPDAI scores were 2.0 (IQR 0-6) and 2.0 (IQR 0-5) respectively. The components of the RCOG model with each of its elements scored for the cohort (Table 1). 34 pregnancies (61.8%) were in DORIS remission throughout pregnancy. 21 (38.2%) were not in DORIS remission at delivery and received 3 points on the RCOG model, since by not achieving remission their SLE could be considered at least mildly active. Of these pregnancies, only 19% were recommended for VTE prophylaxis despite RCOG score ≥ 3. Only 35.7% of pregnancies in DORIS remission, but with 3 points for non-SLE related VTE risk factors, were recommended for VTE prophylaxis (Table 2). Of the 20 pregnancies in remission with an RCOG score < 3 after assessing all risk factors, 15% were nevertheless recommended for VTE prophylaxis. In contrast, of the 14 inactive pregnancies with RCOG score ≥ 3 for non-SLE activity factors, only 35.7% were recommended for VTE prophylaxis. No patients had a postpartum VTE regardless of therapy.
Conclusion: These data reveal that even for SLE patients in remission at the time of delivery, points for SLE alone should not automatically be assigned on the RCOG model. However, those who are in remission may still warrant VTE prophylaxis if other non-SLE related risk factors are present. Although no patient had a postpartum VTE, prophylactic anticoagulation should be instituted only when clinically appropriate. The healthcare team should carefully consider disease activity before applying 3 points for the diagnosis of SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Engel A, Griffin M, Golpanian M, Nusbaum J, Izmirly P, Belmont M, Mehta-Lee S, Buyon J. Assessment and Application of Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) Risk Scores in the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism Peri- and Postpartum in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-and-application-of-royal-college-of-obstetricians-and-gynaecologists-rcog-risk-scores-in-the-prevention-of-venous-thromboembolism-peri-and-postpartum-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-and-application-of-royal-college-of-obstetricians-and-gynaecologists-rcog-risk-scores-in-the-prevention-of-venous-thromboembolism-peri-and-postpartum-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/