Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis is a major source of pain, functional impairment, and reduced health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in spondyloarthritis (SpA) patients; however, limited information is available in the literature regarding the burden associated with enthesitis in this population. This retrospective cohort study assessed the burden associated with enthesitis among patients with peripheral SpA (known as psoriatic arthritis [PsA]) and axial SpA (axSpA) in the real world.
Methods: Data were taken from the Adelphi Spondyloarthritis Disease Specific Programme, which collected information from rheumatologists/dermatologists and their consulting axSpA and PsA patients across Europe, Asia-Pacific, United States, Latin America, and Middle East between 2015 and 2016. Bivariate descriptive analyses were conducted to describe differences between patients with and without enthesitis, in terms of demographics, clinical characteristics, and humanistic and economic burden as measured by patient-reported pain, HRQoL (EuroQol five-dimensions three-level [EQ-5D-3L] and short-form [SF]-36), healthcare resource utilization (HCRU), and activity impairment (work productivity and activity impairment – general health [WPAI-GH]). Inclusion in the enthesitis group was based on physician reporting clinical enthesitis as one of the symptoms currently present in the patient. Propensity score matching analyses were conducted to compare differences in outcomes between enthesitis and without enthesitis groups, matching patients by demographic and clinical characteristics.
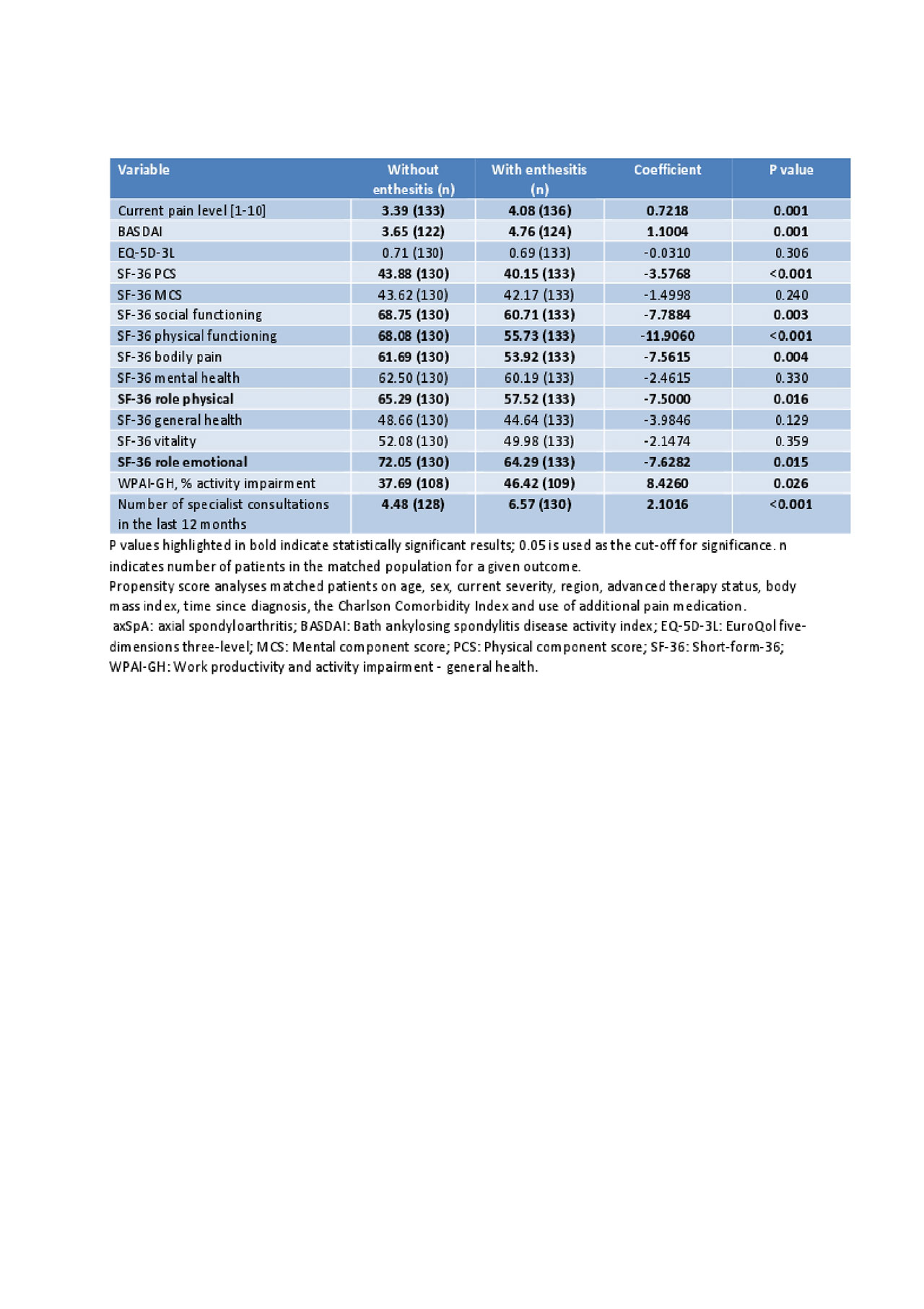
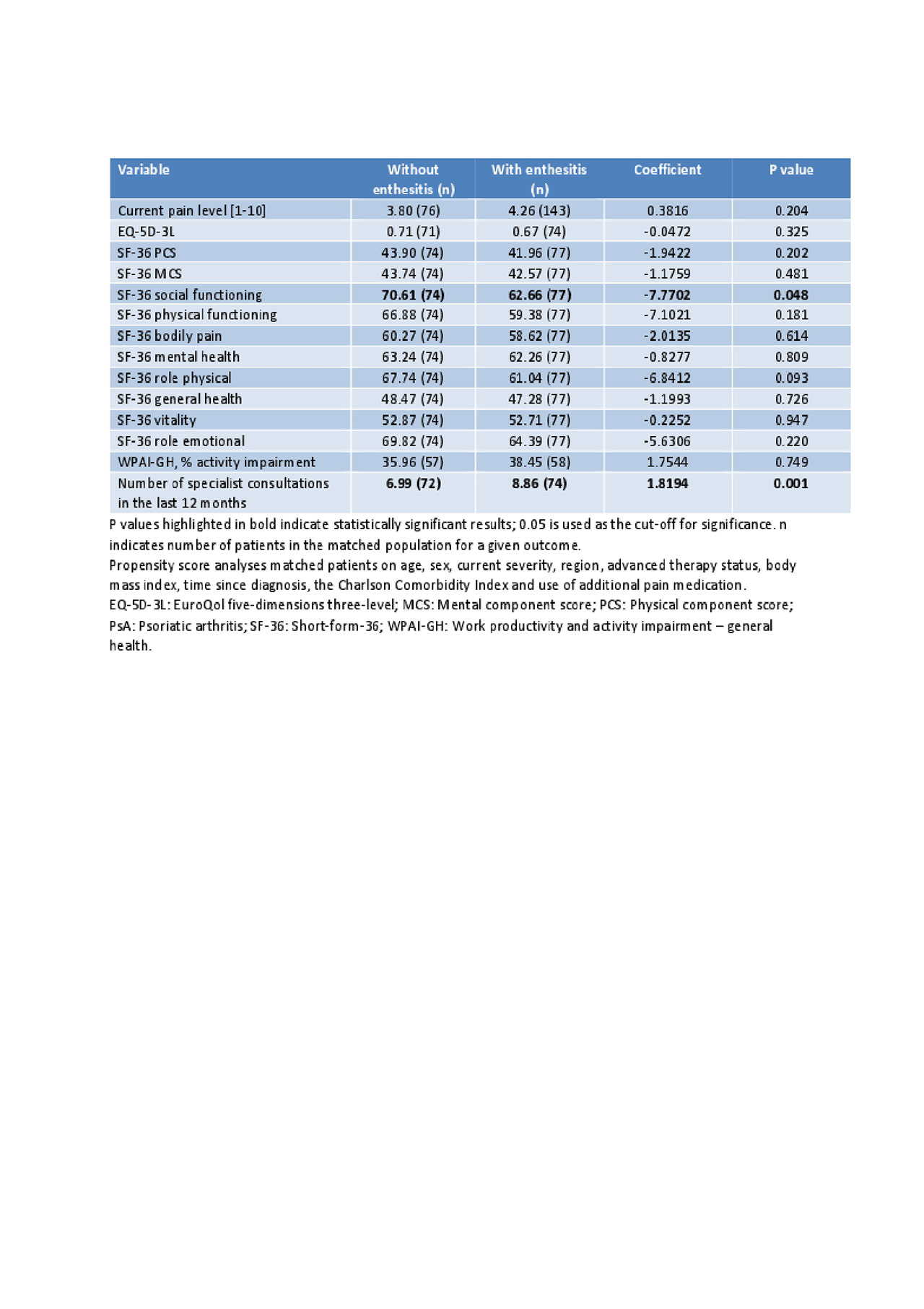
Results: The analysis included data for 5,660 axSpA (with enthesitis: 506 [9%]; without: 5154 [91%]) and 3,570 PsA (with enthesitis: 260 [7%]; without: 3310 [93%]) patients. Bivariate analysis showed a significantly higher proportion of axSpA and PsA patients with enthesitis currently had severe disease and were more likely to require additional pain medications compared to those without enthesitis (Table 1). Patients with enthesitis experienced significantly higher levels of pain, worse HRQoL, greater activity impairment, with a higher number of specialist consultations in the last 12 months compared to those without enthesitis, in both axSpA and PsA subgroups (Table 1). After adjusting for confounding factors in propensity score analysis, burden in terms of pain, HRQoL, activity impairment, and HCRU was mostly significantly higher in patients with enthesitis vs those without in axSpA (Table 2). PsA patients with enthesitis experienced higher burden compared to those without enthesitis, although most differences were not statistically significant, in part due to low sample size (Table 3).
Conclusion: Results from this multinational real world analysis demonstrate that axSpA and PsA patients with enthesitis experience more disease burden than patients without enthesitis. Treatment regimens with demonstrated efficacy on enthesitis should be considered to improve patient outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Deodhar A, Conaghan P, Gilloteau I, Massey O, Tian H, Yocolly A, Booth N, Alten R. Assessing the Humanistic and Economic Burden of Enthesitis Among Patients with Peripheral and Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results from a Multi-National Real World Survey Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-humanistic-and-economic-burden-of-enthesitis-among-patients-with-peripheral-and-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-a-multi-national-real-world-survey-database/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-humanistic-and-economic-burden-of-enthesitis-among-patients-with-peripheral-and-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-a-multi-national-real-world-survey-database/